Biologically Active Peptides Section of Peptides International ...
AQUA peptides, QCAT concatemers, and full-length isotope...
Transcript of AQUA peptides, QCAT concatemers, and full-length isotope...

AQUA peptides, QCAT concatemers, and
full-length isotope-labeled proteins:
Which choice for protein absolute
quantification ?
Virginie Brun
CEA/INSERM U880 Etude de la Dynamique des Protéomes, Grenoble

Protein absolute quantification
Definition: Exact determination of a protein concentration in a sample
Targeted approach
Applications:
Qualification of biomarkers
Medical diagnosis
Quality control
Analytical performances required:
Accuracy
Precision reproducibility, repeatability
Linearity in a (large) dynamic range
Sensitivity false negatives
Specificity false positives

Principle of protein absolute quantification
using isotopic dilution and MS
1. Selection of marker peptides (LC-MS/MS and LC-MS)
Selection parameters:
Sequence uniqueness specificity
No M, C, W residues
Retention time
Ionization capacity
No miscleavages
2. Standardization
= Addition into the samples of a defined quantity of
quantification standards. These standards correspond to (or
generate)the same marker peptides as the target proteins.
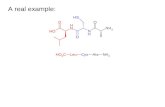
However, one/several AA is/are isotopically labeled.
Same chemicophysical properties but mass increasem/z
im/z
Peptide
marqueur
natif
Peptide
marqueur
alourdi
m/z
im/z
m/z
im/z
Peptide
marqueur
natif
Peptide
marqueur
alourdi
Marker peptide (light)
Standard peptide (heavy)

Absolute quantification tools
AQUA peptides Stemmann et al., Cell, 2001; Gerber et al., PNAS, 2003
QCAT/polySIS concatemers Beynon et al., Nat. Methods, 2005
Full-length isotope-labeled proteins (PSAQ) EDyP Patent

AQUA peptides
Isotope-labeled peptides chemically synthetized
2 suppliers: Sigma + Thermo
500 $ for 5 nanomoles
Recommendations:
Advantage: possible phosphorylation(s)
Use: Add before digestion (in solution) or before LC-MS analysis
Supplier:
• Defined labeling: R, I, L, K, F, P and V
• Length 15 AA
• No chemically M, C, W, N-ter.Q
(chemical reactivity)
Our team:
• High MS detectability at low
concentrations
• Avoid peptides generating multiple ion
forms
• Avoid C-ter labeling

AQUA peptides
Selected application
Absolute quantification of cyclin-dependent kinases multisite phosphorylation
From Mayya et al., MCP 2006
Jurkat cells, IP of Cdk1 and Cdk2
IGEGTYGVVYK detected by SRM
4 phosphorylated/unphosphorylated versions
Phosphorylation inhibitory effect
M PhaseG1, S, G2 Phase

AQUA peptides
Pitfalls
Absolute quantification of C-reactive protein in the serum of patients
with rheumatoid arthritis
From Kuhn et al., Proteomics, 2004
Processed healthy serum sample containing exogenous CRP (121 µg/mL)
CRP concentration by MRM
(µg/mL)
Recovery
(%)
Marker peptide 1 83.3 66
Marker peptide 2 35.4 28
Marker peptide 3 0.23 0.2
Marker peptide 4 30.4 24
• Serum depletion
• Size exclusion chromatography
• DTT/iodoacetamide
• Size fractionation
• SDS-PAGE
• trypsin digestion
• MRM
• NO ASSESSMENT of analyte losses during the prefractionation steps
• NO ASSESSMENT of tryptic digestion yield
• Solubility/conservation of AQUA peptides

QCAT/polySIS concatemers
QCAT = concatemer of isotope-labeled marker peptides
Design of QCAT protein:
Synthesis of QCAT gene:
Retro-translation
Synthesis of 5’ phosphorylated overlapping oligonucleotides
Ligase Chain Reaction + PCR artificial gene
QCAT gene cloning into an expression plasmid
Expression and labeling:
In vivo or in vitro
ARG and LYS labeling preferred
Purification / quantification
Use: Add before tryptic digestion or eventually before SDS-PAGE
From Beynon et al., Nat. Methods, 2005

QCAT/polySIS concatemers
Selected application
Absolute multiplexed quantitative analysis of protein expression
during muscle development using QconCAT
From Rivers et al., MCP, 2007
Pro
tein
(nm
ol/g tis
sue)
• Quantification of chicken muscle proteins during growth
• Soluble fraction of pectoralis muscle
• Preliminary optimization of proteolysis conditions
• Addition of QCAT= concatemer of 20 tryptic peptides from 20 chicken muscle proteins
• Trypsin digestion
• LC-MS analysis

QCAT/polySIS concatemers
Pitfalls
Efficiency of labeling
labeling + metabolic scramble in vivo
Use: predigested or codigested ?
Differential sensitivity of to proteolysis
y = 0.5429x
R2 = 0.999
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
Injected SEA (pg)
Esti
mate
d S
EA
(p
g)
QCAT Analytes
• NO ASSESSMENT of analyte losses during the
prefractionation steps
• RISK : Analyte underevaluation in the case of
incomplete proteolysis
From Rivers et al., MCP, 2007
From Brun et al., MCP, submitted

Full-length isotope-labeled proteins (PSAQ)
PSAQ = Protein Standard Absolute Quantification
Cloning of genes into expression plasmids (with
cleavable tags)
Expression and labeling:
In vivo or in vitro
ARG and LYS labeling preferred
Purification, tag cleavage and quantification
Use: Add directly in the sample to be analyzed

PSAQ
Selected application
y = 0.2117x
R2 = 0.9805
y = 0.5795x
R2 = 0.9952
y = 1.0458x
R2 = 0.9924
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
0 20 40 60 80 100
Added SEA (ng/ml urine)
Es
tim
ate
d S
EA
(n
g/m
l u
rin
e)
y = 0.0347x
R2 = 0.758
y = 0.1885x
R2 = 0.9826
y = 1.0834x
R2 = 0.99
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
0 50 100 150 200 250
Added TSST-1 (ng/ml urine)
Es
tim
ate
d T
SS
T-1
(n
g/m
l u
rin
e)
Urine
sample
Protein capture
on Strataclean
resin
SDS-PAGE Trypsin
digestion
nanoLC-MS
analysis
A
B C
PSAQ standard
QCAT standard
AQUA standard
PSAQ standard
QCAT standard
AQUA standard
PSAQ
standards
QCAT
standard
AQUA
peptides
y = 0.2117x
R2 = 0.9805
y = 0.5795x
R2 = 0.9952
y = 1.0458x
R2 = 0.9924
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
0 20 40 60 80 100
Added SEA (ng/ml urine)
Es
tim
ate
d S
EA
(n
g/m
l u
rin
e)
y = 0.0347x
R2 = 0.758
y = 0.1885x
R2 = 0.9826
y = 1.0834x
R2 = 0.99
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
0 50 100 150 200 250
Added TSST-1 (ng/ml urine)
Es
tim
ate
d T
SS
T-1
(n
g/m
l u
rin
e)
Urine
sample
Protein capture
on Strataclean
resin
SDS-PAGE Trypsin
digestion
nanoLC-MS
analysis
Protein capture
on Strataclean
resin
Protein capture
on Strataclean
resin
SDS-PAGE Trypsin
digestion
nanoLC-MS
analysis
nanoLC-MS
analysis
A
B C
PSAQ standard
QCAT standard
AQUA standard
PSAQ standard
QCAT standard
AQUA standard
PSAQ
standards
QCAT
standard
AQUA
peptides
Staphylococcal toxins
SEA and TSST-1
From Brun et al., MCP, submitted
Absolute quantification of Staphylococcus aureus toxins in urine

PSAQ
Pitfalls
Labeling efficiency
(labeling + metabolic scramble in vivo)
Post-translational modifications
Differential oxydation state/ folding between analyte and standard

Conclusion
AQUA peptides QCAT/polySIS concatemers
Full-length isotope-labeled proteins (PSAQ)
Accuracy - to +++ - to +++ +++
Precision +++ +++ +++
Execution Easy and short Difficult and long
or Entelechon GmbH
Easy and short/long
Compatibility with prefractionation
NO NO YES
Discrimination of variants/isoforms
+/- +/- ++
Study of protein complexes (stoichiometry)
+/- +++ ++
Post-translational modifications
+++ (phosphorylation)
NO NO
Cost Very high High Moderate to High

ALWAYS ASSESS
the completeness of proteolysis
PREFERRED APPLICATIONS:
AQUA peptides peptidomics and phosphorylation studies
QCAT concatemers protein complexes (stoichiometry)
PSAQ standards accurate quantification in prefractionated samples
Summary







![Fitzgerald v The Medical Board of Queensland [2010] QCAT 565](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/61b485bdae16c609d55a09dc/fitzgerald-v-the-medical-board-of-queensland-2010-qcat-565.jpg)



![Leggett v BHP Coal Pty Ltd & Anor [2017] QCAT 77](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/61f6766480a7cd45d405f5e9/leggett-v-bhp-coal-pty-ltd-amp-anor-2017-qcat-77.jpg)





