Annealing Effects on the Structural, Optical and … No. 2 2018...Keywords: Cds Thin Film, Chemical...
Transcript of Annealing Effects on the Structural, Optical and … No. 2 2018...Keywords: Cds Thin Film, Chemical...

InternationalJournalofNanoelectronicsandMaterialsVolume11,No.2,Apr2018[221‐232]
AnnealingEffectsontheStructural,OpticalandElectricalPropertiesofChemicallyDepositedCdSThinFilmsusingNH4ClComplexing
Agent
1RummanaMatin,1M.S.Bashar*,1MuniraSultana,2AnindaNafisAhmedand2A.Gafur.
1InstituteofFuelResearchandDevelopment(IFRD),BangladeshCouncilofScientificandIndustrialResearch(BCSIR),Dhaka,Bangladesh.
2PilotPlantandProcessDevelopmentCenter(PP&PDC),BangladeshCouncilofScientificandIndustrialResearch(BCSIR),Dhaka,Bangladesh.
Received14September2017;Revised26October2017;Accepted1January2018
ABSTRACTThis study aims to deposit different thicknesses of CdS thin films with a variation ofdeposition time by using chemical bath deposition technique. The aqueous solution ofcadmium chloride, ammonium chloride, ammonium hydroxide and thioureawere usedDuringthedepositionprocess.Theanalysiswasdonetoobservetheeffectofannealingonstructural,opticalandelectricalpropertiesoftheCdSthinfilms.Fromthex‐raydiffraction,thishelps to confirm the cubicCdSphase formation,withapreferredorientationalong(111).Thefinding indicatesthatthecrystallitesize is larger in filmswhen it isdepositedwith low deposition rate. The crystallite size increased with increasing thickness anddecreasedafterannealing.Afterannealing,themobilityandcarrierconcentrationoftheCdS thin films of different thicknesses is increasing and the resistivity decreasing. Thisstudyshowedthatthecrystalstructure,bandgap,UrbachenergyandelectricalpropertiesofCdSthinfilmscanbechangedwhenCdsthinfilmsexperiencedannealing.Keywords:CdsThinFilm,ChemicalBathDeposition,AnnealingEffect,XRD,BandGap.
1. INTRODUCTION
Asabufferlayerinasolarcell,heterostructurecadmiumsulfide(CdS)playsasignificantrolebecauseofitspropertiesasdirectn‐typesemiconductorwithabandgapofabout2.4eVandlargeabsorptioncoefficientof4×104cm−1[1].Amongvariousotherpromisingcadmium‐freebuffer layer; indium(III) sulfide (In2S3),Zinc sulfide (ZnS), tin sulfide (SnS), tinoxide (SnO),etc,CdSshowedhighestefficiencytobeused insolarcells [2].Amongnonvacuumorsol‐geltechniques;spraypyrolysis,spincoating,anddipcoating,thechemicalbathdeposition(CBD)is known as most simple and low‐cost method and produces uniform, adherent andreproduciblefilms.Inaddition,theCBDtechniqueisalowtemperaturetechniqueandcanbeusedforCdSdepositionintoawiderangeofsubstrates.Generally, the formation of CdS thin films by CBD is governed by two mechanisms,heterogeneousgrowth, i.e. ionby ioncondensationofCd+2andS−2 ionsonthesubstrateandhomogeneousgrowthi.e.adsorptionofcolloidalparticlesonthesubstrate.Attheearlierstageofdeposition,theCd+2 ionsinthesolutionwill formcomplexeswithacomplexingagentandNH3.Atthisstage,morefreeCd+2ionsareavailableinthesolutionandtheseionsreactwithS−2ionsandproduceaclustertypeofCdSparticles.ThereafterwhentheconcentrationofCd+2*CorrespondingAuthor:[email protected]

RummanaMatin,etal./AnnealingeffectsontheStructural,OpticalandElectrical…
222
ionsgraduallydecreasesathigherNH3concentration,Cd+2ionsarestronglycomplexedbyNH3ions.Duetothis,thereisnofreeCd+2ionsareformedinthesolutionsothatfurtherformationofCdSparticlesisnotpossible.AtthisstageheterogeneousmechanismgovernsthedepositionofauniformthinlayerofCdS[3,4].PreviousstudiesfocusonobtaininghighqualityCdSthinfilmsbymanipulatingtheparametersof CBD method, such as deposition time, temperature, pH value and by varying theconcentrationsofvariousreagentsaswellastheircomplexingagents[4–9].ThehomogeneityandgrowthrateofCdSthinfilmsdependsontheuseofcomplexingagentduringchemicalbathdeposition.ItisreportedthatgoodqualityCdSthinfilmscanbegrownbyusingammoniaandammonium chloride as the complexing agent [5]. The anions from the cadmium andammoniumsaltsareclaimedtoplayasignificantrolewhengrowingtheCdSfilms.Thisroleissuspectedtobethatofacomplementarycomplexingagent[10,11].
There are several post deposition treatments such as annealing inN2/Air/H2 atmosphere atdifferent temperatures have been carried out to see their effect on structural and opticalpropertiesofCdSthinfilm.Maticiucetal.[12]foundthatdifferentpropertiesofCdSfilmaredependingon theneutral, reducingor oxidizing annealing gas.Oxygen in phases CdSO3 andCdOareobservedfromXRDpatternsforair‐andN2‐annealedCdSfilmsat400ºC.LongestN2annealing generated pure CdS layers, similarlywith the H2‐ annealed ones. Lichimura etal.[13]annealedCdSthinfilmsattemperaturesupto500°C.Thecubicphaseoftheas‐depositedfilm remains dominant until the annealing temperature reach higher than 400°C.When theannealingachieves450°C,theXRDpatternturnstothatofhexagonalphase.Thebandgapisdecreased by annealing done below 400°C and then abruptly increased by the annealing at450°C. Islam etal. [5] annealed the CBD processed CdS thin films for 30min at 400ºC and500ºC, respectively in a vacuum furnace with pressure 500mTorr. The cryatallinity of thefilmsincreasedwithincreasingannealingtemperature.Inthisstudy,thelow‐costCBDtechniqueisusedforthedepositionofCdSthinfilms.Ammoniaand ammoniumchlorideareused as the complexingagent. TheCdS thin filmsare grownatdifferentdepositiontimetoanalyzethefilmgrowth.Theas‐depositedfilmswereannealedinN2environmentat430ºCtoseetheannealingeffect.Theresultsfoundfromtheaboveanalysisare compared for as‐prepared and annealed CdS thin films of different thicknesses withrespecttothepreparationprocesses.2. EXPERIMENTALDETAILS
The CBD processed CdS thin films were grown onto sodalime glass substrates from thedecomposition of thiourea in an alkaline solution containing a cadmium salt and suitablecomplexingagentammonia(NH3)andammoniumchloride(NH4Cl).WhenCdCl2isusedasCdsource, NH4Cl is implemented as a buffer that controls the emission of ions during thedepositionprocess.Thecombinationhelpstoobtainastablecomplex.The substrateswere cleaned successively using ultrasonic bath and degreased inmethanol‐acetone‐methanol‐deionized (DI) water for 10 minutes. Following to this, the degreasedsubstrates is dried on a hotplate. CdS precursors were prepared with 0.0199 M of CdCl2,0.019835MofNH4Cland0.1423MofThioureainDIwaterforalltypesofCdSthinfilms.First,abeakercontainingDIwaterwasimmersedintheChemicalbath.TheprocedurecontinuesbyaddingCdCl2withDIwaterandwhilecontinuouslystirring,theNH4Clwasaddeddropbydropintothemixture.Thecleanedsubstrateswereimmersedinthebeakersvertically;thebeakerswerethencoveredandheated.At50ºCammoniawasmixedwiththesolution.TheThioureawasmixedwiththesolutionatthetemperatureof80ºC.Thebathtemperaturewasfixedat80ºCduringdepositionbecause,ithasbeendeducedthat,atlowsolutiontemperatureconditions

InternationalJournalofNanoelectronicsandMaterialsVolume11,No.2,Apr2018[223‐234]
223
(Ts < 60 ºC), the deposition mechanism can be achieved only with a lower activationtemperatureprocessi.e.theionbyionone.Whereasathighertemperatures(Ts>60ºC),thedeposition rate encompasses of larger activation energy, which lead the cluster by clusterprocessasthedominantgrowthmechanism.AnincreaseinthesolutiontemperatureinduceshigherhydroxideclusterCd(OH)2andsulfide ionconcentrations [6]. Inorder toensure thatthe pH is remained at 10, ammonia solution (28% of NH3 solution)was then added to thesolution.Afterthedepositionprocess,sampleswerewashedandultrasonicatedwithDIwaterfor1mintoremovethesurfaceimpurities,andthendriedonahotplate.Thedepositiontimewas varied from 20, 30 and 40minutes to obtain different thicknesses. The deposited thinfilms were annealed in an annealing chamber (MTI corporation, GSL– 1100X) in N2environmentunderadynamicvacuumofaround2Torrandat430ºCtemperaturefor1hour.The Surface Profilometer (DAKTAK‐150) is used to measure the thickness of the cadmiumsulfide(CdS)thinfilms.Later,theX‐raydiffractionanalysis(XRD)wasperformed,byaBrukerD8XRDwithcopperkαradiationtoinvestigatethecrystallinestructureofthematerials.Theabsorbance and transmittancewere recorded using a duel beam UV‐vis spectrophotometer(Shimadzu,UV‐1601V).Thisspectrometerwasusedtomeasuretherelativetransmittanceandabsorbance of CdS thin films. The sheet resistance was measured by a four‐point probemeasurementset‐upandthemobilityandcarrierconcentrationwasmeasuredbyaHalleffectmeasurementsetup(ECOPIA,HMS‐3000,SK).3. RESULTSANDDISCUSSIONS
3.1 DepositionRate
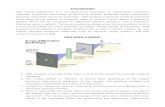
Figure1showsthechangeinthicknessofCdSthinfilmswithincreasingdepositiontime.Itisobserved that the thickness increases faster following slower increase with increasingdeposition time. It has been reported that heterogeneous process is highly desirable ratherthanhomogeneousdepositionforuniformthinfilms.Addingtothat,thehomogeneousprocessformsprecipitationofCdSinthesolutionresultingnon‐adherentpowderyfilms.Thereactionsforbothprocessesaregivenasfollows:Cd2++S2‐→CdS(heterogeneousnucleation)Cd(NH3)n2+↔Cd2++nNH3(homogeneousnucleation)nCd2++2n(OH)‐→[Cd(OH)2]n[Cd(OH)2]n+nS2‐→nCdS+2nOH‐[7]Inourcase,theprecipitationofCdSisobservedafter30minutesofdeposition.Thisisbecauseattheearlierstageofdeposition,theCdSfilmsaredominantlygovernedbytheheterogeneousmechanismandshowsauniformthinlayer.However,thisthinlayerisgraduallygrowingwiththe homogeneousmechanism. Ouachtari etal. reported that increasing the concentration ofthe cadmium ions in the CBD process produces a higher final film thickness; also, longerdeposition time is needed to attain the final film thickness. In addition, after a certaindeposition time, the absorption and/or dissolution process predominates over theheterogeneousandhomogeneousprecipitation[11].

RummanaMatin,etal./AnnealingeffectsontheStructural,OpticalandElectrical…
224
50
100
150
200
250
300
15 25 35 45
Th
ickn
ess
, d
(nm
)
Deposition Time, t (Sec)
Figure1.Variationofthicknessatdifferentdepositiontime.3.2.CrystalStructureIt is reported that cadmium sulfide can exist in both sphalerite cubic and hexagonal forms.CubicCdSgrows in thezincblendestructurebyconsideringmetastablephase [14].TheXRDpatternsofCdSthinfilmsareshowninFigure2.ThreediffractionpeaksmatchedwithJCPDS01‐074‐9663 correspond to (111), (220) and (311) reflections at 2Θ of 26.5°, 44°, and 52°,respectivelyindicatingthattheobtainedCdSfilmshaveacubicstructurewiththepreferentialorientation normal to the (111) direction. A similar film structure has been reportedpreviouslybyotherresearchers[15,16].AlltheXRDpatternsexhibitabroadhumpnearthe(002)peakat2θ=26.7˚,whichisduetotheglasssubstrate.Acomparisonbetweenthespectraofthefilmsshowsthatthepeakintensityincreaseswhenthedepositiontimeisincreasingi.e.with increasing thickness the thicker filmhasmore crystallinity than the thinner films. Thedegree of preferred orientation along (111) increasedwhen the thickness is increases. Thepeak intensity of each of the three films increased after annealing indicating an increase incrystallinity [16]. Annealing helps the atoms to rearrange themselves and eliminate defectdensityinthefilmresultingingoodcrystallinity.Tomasetal.[17]reportedthattheN2orArannealing brings reorientation of as‐deposited CdS films with a significant improvedcrystallinequalitybyincreasingthegrainsizeanddecreasingthenumberofgrainboundariesin CdS films.Also, such some annealing leads to phase transition from themetastable cubicphase to a stablehexagonalphaseofCdS [18],which isundesirablewhen stackingCdS filmwithacubicCdTeabsorber[12]. InourcaseCdS, thin filmsarenotgonethroughanyphasetransition but improved in structural orientation due to annealing at 430°C in the N2environment.ThecrystallinesizeoftheCdSthinfilmsfilmiscalculatedusingFWHMdataandDebye‐Schererformula[13].
B
d
cos
(1)
wheredisthecalculatedgrainsizeofthefilm,λisthewavelengthofx‐rayradiation(1.54059Åof CuKα radiation). is full width at half‐maximum (FWHM), B is a peak position of thediffractedX‐raybeam.Theparticlesizescalculatedare5.62,2.38and1.53nmforas‐depositedand 4.7, 1.53 and 1.38nm for annealed CdS thin films deposited for 20, 30 and 40 mins

InternationalJournalofNanoelectronicsandMaterialsVolume11,No.2,Apr2018[223‐234]
225
respectively.Thus, it canbeconcluded that theparticlesize increasedwhenthe thickness isincreasedanddecreasedafterannealing.Moulkia etal. (2009) [6] explained the reduction of the grain size by the variation of thegrowthrate.Athighdepositionrates(thickerfilms),thenucleationstepisfast,thereforethenucleationsitesconcentrationislarge.Duetothis,thenucleisizeenlargementislimitedandblockedbythesurroundingnuclei.However,at lowdepositionrates(thinner films), the lowconcentration of the nuclei sites enables the nuclei to grow and attain a larger size.Consequently,thegrainsizeislargerinfilmsdepositedwithlowdepositionrate.
Figure2.SuperimposedXRDpatternofas‐depositedandannealedCdSthinfilmsdepositedfor20,
30and40minutes.3.3.OpticalPropertiesUV‐Visspectrometryisusedtoobservetheopticalpropertiessuchastransmission,absorptionandoptical band gapof the thin films.Ablank sodalimeglass slidewasplaced in thebeamdirection during the scanning process. Figure 3(a) and 3(b) shows the variation oftransmittanceT(%)withwavelengthλ(nm)inthewavelengthrangefrom300to800nmforas‐depositedCdSthinfilmsofvariousdepositiontimeand20mindepositedannealedCdSthinfilm.Themaximumtransmittanceobservedare82%,58%,and84%respectivelyinthevisibleregion (400 to700nm). Figure3(b) shows that the transmittanceT (%) isdecreasingafterannealingduetothedenserCdSformationduringtheprocess[5].ItisfoundthattheannealedCdSthinfilmsexhibitthemaximumtransmittance(between40%to75%)inthevisiblerangeandhavesharp fall at thebandedgewhich isgood foroptoelectronicdevices,especially forsolarcellwindowlayers,confirmingthepresenceofcrystallinityofCdSthinfilms[5,21].
10 20 30 40 50 60
2 (Degree)
Inte
nsi
ty (
a. u
.)
20 min (As-deposited)
20 min (Annealed)
40 min (As-deposited)
30 min (As-deposited)
40 min (Annealed)
30 min (Annealed)

RummanaMatin,etal./AnnealingeffectsontheStructural,OpticalandElectrical…
226
Figure3.Transmittancevs.wavelengthplotsfor(a)Differentdepositiontime(b)As‐depositedandannealedCdSthinfilms.
Figure4(a)showsthevariationofabsorbancemeasuredinthewavelengthrangingfrom300to800nmwiththevariationofdepositiontimei.e.20,30and40min.Duetothevariationofdepositiontimethethicknesseswerefoundabout100,200and250nmfor20,30and40minrespectively.Figure4(a)showsanincreaseintheabsorbancewhentheCdSfilmthicknessisincreasing.Figure4(b)representanincreaseofabsorbanceafterannealingwhichindicatestheformationofdenserCdSthin filmsduetoannealing.Thefinding issimilartothestudy fromIslametal. [5].Fromtheabsorbancespectra, it isalsoobservedthatforalltypesofCdSthinfilmsthemaximumabsorbanceofCdSthinfilmsisobservedataround300nm.Inthevisibleregiontheabsorbancerisesveryrapidlybefore300nm,attainsitsmaximumvalueandthendecreasesrapidlyupto600nmi.e.theabsorbancedecreasesrapidlyfromultraviolettovisibleregion.
Figure4.Absorbancevs.wavelengthplotsfor(a)Differentdepositiontime(b)As‐depositedandannealedCdSthinfilms.
0
20
40
60
80
100
300 400 500 600 700 800
20 min
30 min
40 min
b
a
c
Wavelength, (nm)
a
b
c
Tra
nsm
itta
nce
%
0
20
40
60
80
100
300 400 500 600 700 800
As-deposited
Annealed
a
b
Tra
nsm
itta
nce
%
Wavelength, (nm)
a
b
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
200 400 600 800
Wavelength, (nm)
Ab
sorb
ance
20 min
30 min
40 min
a
ca
c
b
b
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
200 400 600 800
Wavelength, (nm)
Ab
so
rba
nc
e
As-deposited
Annealed
b
a
a
b

InternationalJournalofNanoelectronicsandMaterialsVolume11,No.2,Apr2018[223‐234]
227
The absorption coefficient, α, [22] is calculated from the measured absorbance data fordifferentwavelengthscorrespondingtodifferentphotonenergiesatroomtemperatureusingequation(2).
d
A303.2
(2)
where )(log 010 I
IA is the absorbance and d is the thickness of the film. An idea of the band
structureandelectronictransitioninvolvedinabsorptionprocesscanbeobtainedbystudyingthedependenceofopticalabsorptioncoefficientonthephotonenergy.The spectral dependenceofα, on thephoton energy, h, for as‐deposited and annealedCdSthinfilmsisshowninFigure5.TheabsorptioncoefficientofallCdSthinfilmsincreaseswithincrease inphotonenergy.Theabsorptionco‐efficient increaseddue to annealing indicatingdenserfilms.
Figure5.Absorptioncoefficientvs.photonenergyplotsforas‐depositedandannealedCdSthinfilms.
Incrystallineandamorphousmaterials, thephotonabsorption isobserved toobey theTaucrelation[23],
αh=B(h‐Eopt)n(3)where, h is the incident photon energy, h Planck constant, the frequency of incidentradiation, B an energy independent constant, Eopt the optical band gap and n is an indexdependingonthetypeofopticaltransitioncausedbyphotonabsorption.Theindexnequals½and2foraccepteddirectandindirecttransitionsrespectively.Therefore,thedirecttransitionenergygap(Eqd)canbeobtainedbyplotting(αh)2versushcurveandthenextrapolatingthelinearportionoftheplotstotheinterceptinthehνaxis.Figure6showsthechangeinbandgapduetoannealing.AnincreaseinthebandgapofCdSthinfilmsisobservedafterannealing.Thebandgapsobtainedforas‐depositedandannealedCdSthinfilmsofdifferentthicknessesarelisted inTable1.FromTable1 itcanbedepictedthatthebandgapenergy ischanging from2.66to2.82eVforas‐depositedCdSthinfilmsofdifferentthicknessesandforannealedthatare ranged from 3.60 to 3.87 eV for CdS thin films of different thicknesses. The increase ofbandgapafterannealingcanbeattributedduetotheformationofCdOduringannealing.Itisobservedthatthebandgapchangesslightlywiththevariationofdepositiontimei.e.thereisalittleincreaseofbandgapwithincreasingthicknessmaybeduetosomestructuralchangesas
0
10
20
30
40
50
1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5
Photon energy, h (eV)
cm
x 10
-4
As-deposited
Annealed
(b)
(a)
(a)
(b)

RummanaMatin,etal./AnnealingeffectsontheStructural,OpticalandElectrical…
228
alsodepictedfromXRD.Butafterannealingthebandgapdecreasedwithincreasingthickness.Thismaybeduetothefactthat,asthethicknessisincreasing,therelativeamountofformationofCdOdecreases.ThishappensbecausetheCdOformsontothesurfaceoftheCdS.Butwhenthethicknessincreases,theO2cannotpenetratethethickerfilms.Ontheotherhand,itisfoundthat the band gap energy of the CdS thin films increased significantly after annealing. ThisoccurrencecanbeexplainedbasedontheO2 incorporation.SimilarexplanationonannealedCdS thin film has previously reported by Islam (2013) [5].Wu etal. (2004) studied on RF‐sputteredCdSdepositionusinganO2/AratmosphereandshowedthattheCdS:OfilmsbecometransparentinthewavelengthrangeabovethebandgapofCdSandsuggestedthatCdSfilmsgrownwithinclusionofoxygenduringdepositioncanbeabetterchoiceforthinfilmsolarcellsas oxygenation will further increase their band gap [21]. The changes of band gap withincreasingannealing temperaturearecausedbychanges in thedefects, thecompositionandthecrystallinepropertiesof theCdS thin films.Thespectraldependenceofαwasstudiedatphotonenergieslessthanthebandgapofthefilms.
Figure6.(αhν)2vs.hνplotsforas‐depositedandannealedCdSthinfilms.
TheUrbachenergyiscalculatedfromtheslopeoftheplotsof lnαvshν.Thisslopegivesthewidth of the localized states associated with amorphous states in the band gap at photonenergies less thanthebandgap.Theabsorptioncoefficientnear the fundamentalabsorptionedgeisexponentiallydependentontheincidentphotonenergy[24].
α=α0exp(hν/Eu) (4)whereα0 is a constant and Eu is the Urbach energy. Thus, the plots of lnα should be linearwhose slope gives Urbach energy. The lnα vs hν plots for as‐deposited CdS thin films ofdifferentthicknessesareshowninFigure7(a)andthatofannealedCdSthinfilmsareshowninFigure7(b).TheUrbachenergiesarecalculated fromtheslopesof theUrbachplotsandarelisted inTable1. TheUrbach energies are ranging from2.61 to 5.1 eV for as‐deposited and2.34 to3.4eV for annealedCdS thin filmsofdifferent thicknesses.FromTable1 thatas thethicknessincreasedthebandgapandtailwidthofCdSfilmsincreasedduetotheincreaseindisorder/impurityandfilmstoichiometrywiththicknessordepositiontime.Dingyuetal.[20]reportedthatthechangeofbandgapandtailwidtharerelatedtofilmstoichiometryinwhichitchangeswithdepositionoftheparameter.ItcanbenoticedthattheUrbachenergydecreasesafterannealingforallthethicknesses.Thisbehaviormaybeduetoadecreaseinthedegreeofdisorderanddecrease indensityofdefectstates(whichresults in thereductionof tailingofbands). Due to this, it showed an increase in crystallinity. It is also found that the Urbach
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
Photon energy, h(eV)
( h
)2
Annealed
As-deposited
(b)
(a)
(a)
(b)

InternationalJournalofNanoelectronicsandMaterialsVolume11,No.2,Apr2018[223‐234]
229
energy increaseswith increasingthickness indicatingan increase indisorderordefectswiththicknessordepositiontime.
Figure7.Urbachplots(lnαvshνcurves)for(a)as‐depositedCdSthinfilmswithdifferentthicknessesand(b)annealedCdSthinfilmswithdifferentthickness.
Table1Variationofbandgapwiththedepositiontimeofas‐depositedandannealedCdSthinfilms
CdS thin
film Deposition Time (min)
Film Thickness (nm)
Band Gap (eV)
Urbach energy (eV)
As-deposited 20 30 40
100 200 250
2.66 2.75 2.82
2.61 3.60 5.10
Annealed 20 30 40
100 200 250
3.87 3.70 3.60
2.34 3.12 3.40
7.6
7.8
8.0
8.2
8.4
8.6
8.8
2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6
Photon energy, h (eV)
ln [
(cm
-1)]
20 nm
30 nm
40 nmc
b
a
a
c
b
6.6
6.7
6.8
6.9
7.0
7.1
7.2
7.3
2.3 2.4 2.5
Photon energy, h (eV)
ln [
(cm
-1)]
20 min
30 min
40 min
c
b
a
c
b
a

RummanaMatin,etal./AnnealingeffectsontheStructural,OpticalandElectrical…
230
3.4.ElectricalPropertiesTo characterize the electrical properties of the thin films, Four Point probe and Hall effectmeasurements are performed in air at room temperature. The as‐deposited films exhibitsemiconductingbehaviorswithresistivity in therangeof10‐2Ω.cm foras‐depositedCdS thinfilms and 10‐3Ω.cm for annealed CdS thin films. The resistivity decreased one order ofmagnitudeafterannealing.Thisdecreaseisattributedtotheimprovedcrystallinity,growthingrainsizeandtheimprovementinfilmstoichiometry,asisindicatedbytheXRDpatterns.n‐typeconductivity isobservedbytheHallmeasurements forbothtypesof theCdSthin films.Themobilityandcarrierconcentrationofas‐depositedandannealedCdSthinfilmsaregiveninTable2. It isobserved thatbothof themobilityandcarrierconcentrationof theCdS thinfilmsofdifferent thicknesses are increasing (and accordingly the resistivitydecreases) afterannealing. Generally, the carrier concentration and mobility have increased due to theinterstitialCd+2 ionsor sulfurvacancieswhichexist in the film.Thesecarriersactasdonorsandresultsinanincreaseinthecarrierconcentrationaswellasaconsequentdecreaseintheresistivity [10].Anysignificant change in carrier concentrationandmobility isnotobservedduetothicknessvariation.
Table2Electricalparametersforas‐depositedandannealedCdSthinfilms
4. CONCLUSION
In this study, the investigation is carried out to explore the structural, optical and electricalpropertiesofCBDdeposited films. It is found thatat theearlier stageofdeposition, theCdSfilmsaredominantlygovernedbytheheterogeneousmechanismbecauseitshowsauniformthin layer.However,gradually theCdS films finishedwithhomogeneousgrowth.Apart fromthis,fromtheXRDpattern,thegraphindicatedshowedthatthepeakintensityincreasedwhenthedepositiontimeisincreasing.Also,thepeakintensityofeachofthethreefilmsincreasedafterannealingindicatinganincreaseincrystallinity.Theopticalbandgapliesintherangeof2.66 to 2.82 eV for as‐deposited and 3.6 to 3.87 eV for annealed CdS thin films of differentthicknesses.TheUrbachenergiesarerangingfrom2.34to5.1eVforas‐depositedand2.61to3.4 eV for annealed CdS thin films of different thicknesses. Both of themobility and carrierconcentration of the CdS thin films of different thicknesses increase (and accordingly theresistivity decrease) after annealing. The structural, optical and electrical properties of CdSthinfilmsareimprovedafterannealing.TheseCdSthinfilmsdepositedbyCBDtechnique,withtheaddedadvantagesofcost‐effective,largeareadepositionandeasythicknesscontrol,canbeveryimportantforsolarcellapplication.
CdSthinfilm FilmThickness(nm)
Resistivity(Ohm.cm)
Mobility(cm2/Vs)
Carrierconcentration(cm‐3)
As‐deposited 100200250
4.08x10‐25.00x10‐26.43x10‐2
9.62x1011.46x1005.40x101
5.45x10112.80x10119.62x1011
Annealed 100200250
3.32x10‐32.21x10‐31.81x10‐3
2.96x1011.41x1021.68x102
1.60x10123.05x10126.12x1012

InternationalJournalofNanoelectronicsandMaterialsVolume11,No.2,Apr2018[223‐234]
231
REFERENCES[1] L.B.Freund,S.Suresh,Thinfilmmaterialsstress,defectformationandsurfaceevolution,
CambridgeUniversityPress,UK(2003).[2] Y.Sánchez,M.Espíndola‐Rodríguez,H.Xie,S.López‐Marino,M.Neuschitzer,S.Giraldo,M.
Dimitrievska, M. Placidi, V. Izquierdo‐Roca, F. A. Pulgarín‐Agudelo, O. Vigil‐Galán, E.Saucedo,SolarEnergyMaterials&SolarCells158(2016)138.
[3] J.M.Doña,J.Herrero,J.Electrochem.Soc.144(1997)4081.[4] C.K.Kumar,N.T.Q.Hoa,S.G.Yoon,E.T.Kim,JournaloftheKoreanPhysicalSociety55
(2009)284.[5] M.A.Islam,M.S.Hossain,M.M.Aliyu,P.Chelvanathan,Q.Huda,M.KarimR.K.Sopian,N.
Amin,EnergyProcedia33(2013)203.[6] H.Moualkia,S.Hariech,M.S.Aida,N.Attaf,E.L.Laifa, J.Phys.D:Appl.Phys.42(2009)
135404.[7] R.K.Choubey,D.Desai,S.N.Kale,S.Kumar,JMaterSci:Mater.Electron.27(2016)7890.[8] R.Y.Mohammed,S.Abduol,A.M.Mousa,InternationalLettersofChemistry,Physicsand
Astronomy11(2014)146.[9] K. Lingeswaran, S. S. P. Karamcheti, M. Gopikrishnan, G. Ramu,Middle‐East Journal of
ScientificResearch20(2014)812.[10] H.Khallaf,I.O.Oladeji,G.Chai,L.Chow,ThinSolidFilms516(2008)7306.[11] F. Ouachtari, A. Rmili, S. E. B. Elidrissi, A. Bouaoud, H. Erguig, P. Elies, J.Mod. Phys.2
(2011)1073.[12] NataliaMaticiuc,MartKukk,NicolaeSpalatu,TamaraPotlog,MalleKrunks,VelloValdna,
JaanHiie, Comparative study of CdS films annealed in neutral, oxidizing and reducingatmospheres,EnergyProcedia44(2014)77.
[13] MasayaIchimura,FumitakaGoto,EisukeArai,StructuralandopticalcharacterizationofCdSfilmsgrownbyphotochemicaldeposition.
[14] J. N. Ximello‐Quiebras, G. Contreras‐Puente, G. Rueda‐Morales, O. Vigil, G. Santana‐Rodrı´guez,A.Morales‐Acevedo,SolarEnergyMaterials&SolarCells90(2006)727.
[15] F.Lisco,P.M.Kaminski,A.Abbas,K.Bass,J.W.Bowers,G.Claudio,M.Losurdo,J.M.Walls,ThinSolidFilms582(2015)323.
[16] HMetin, R Esen, Annealing effects on optical and crystallographic properties of CBDgrownCdSfilms,Semicond.Sci.Technol.18(2003)647.
[17] TomasSA,VigilO,Alvarado‐GilJJ,Lozada‐MoralesR,Zelaya‐AngelO,VargasH,Ferreirada Silva A, Influence of thermal annealings in different atmospheres on the band‐gapshiftandresistivityofCdSthinfilms.JApplPhys78(4)(1995)2204.
[18] MishraS,IngaleA,RoyUN,GuptaA.Studyofannealing‐inducedchangesinCdSthinfilmsusingX‐raydiffractionandRamanspectroscopy.ThinSolidFilms516(2007)91.
[19] Ed. F. A. Devillanova, W. W. D. Mont, Hand Book of Chalcogen Chemistry, The royalsocietyofchemistry,UK(2013).
[20] YangDingyu,ZhuXinghua,WeiZhaorong,YangWeiqing,LiLezhong,YangJun,andGaoXiuying,StructuralandopticalpropertiesofpolycrystallineCdSthinfilmsdepositedbyelectronbeamevaporation,JournalofSemiconductors32(2011).
[21] X.Wu,Y.Yan,R.G.Dhere,PhysicsStatusSolidiC4(2004)1062.[22] M. Birkholz, Thin Film Analysis by X‐ray Scattering Wiley‐VCH, Frankfurt, Germany
(2006).[23] J.Tauc,A.Menth,D.Wood,Phys.Rev.Lett.25(1970)749.[24] F.UrbachPhys.Rev.92(1953)1324.