Animal Nutrition. nutrition Food taken in, taken apart and taken up Herbivores – plants/algae...
-
Upload
elizabeth-eaton -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
5
Transcript of Animal Nutrition. nutrition Food taken in, taken apart and taken up Herbivores – plants/algae...

Animal Nutrition

nutritionFood taken in, taken apart and taken up
Herbivores – plants/algae
Carnivores – eat other animals
Omnivores – consume animals and plants/algae
Most animals are opportunistic – they will eat anything outside their diets when normal foods are not available.

Adequate dietMust satisfy 3 nutritional needs
Chemical energy for chemical processesOrganic building blocks for macromoleculesEssential nutrients – preassembled organic
molecules and mineralsEssential fatty acidsEssential amino acidsVitaminsminerals
Malnutrition – lacking 1 or more of the essential nutrients

Food processing – 3 steps1. ingestion – act of eating or feeding
2. digestion – food broken down into molecules small enough for the body to absorb.
3. absorption – take up of small molecules such as amino acids and simple sugars
Elimination – undigested material passes out of the digestive system

DigestionDigestive enzymes (amylase) begin digestion in
mouth.
Intracellular digestion – food vacuoles, paramecium
Extracellular digestion – Gastrovascular cavity – hydraComplete digestive tract – alimentary canal,
mouth and anus

Figure 33.8
Tongue
Salivaryglands
Liver
Gall-bladder
Pancreas
SmallintestineLargeintestine
Rectum
Anus
Oral cavity
Pharynx
Esophagus
Sphincter
Sphincter
Stomach
Liver
Pancreas
Gallbladder
Duodenum ofsmall intestine
Stomach
Smallintestine
Largeintestine
RectumAnus
SalivaryglandsEsophagus
Mouth

Accessory glands of digestive system
Mouth – salivary glands (accessory)
Pancreas – endocrine gland
Liver – filters blood, produces bile
Gall bladder – stores bile, releases to S. Intestine
Peristalsis – waves of contraction/relaxation to move food throughout alimentary canal.
Sphincters – muscular rings that regulate passage to organs.

Oral cavity, pharynx and esophagus
Oral cavity – mouth, digestion beginsTongue – helps shapes digested food into a ball –
bolus
Pharynx – splits into 2 passagesTrachea – respiratoryEsophagus – leads to stomach

stomachStores food, begins digestion
Secretes components of a digestive fluid – gastric acidHCL – makes pH around 2, denatures proteinsPepsin – protein-digesting enzymeGastric acid does not affect cells lining stomach
because of mucus released by cells
Gastric ulcers – damaged areas of stomach lining

stomachDigestion occurs by churning of food (peristalsis)
about every 20 seconds.
Chyme – acidic nutrient rich broth made from food
Stomach sphincters closed during digestion
Acid reflex – chyme backflows into esophagus “heartburn”

Digestion in Small Intestine
Most digestion of macromolecules from food, higher pH than stomach, trypsin enzymes
Longest part of alimentary canal, 20 feet, 6 meters
Duodenum, first 25 cm of small intestine, chyme mixes with digestive juices from pancreas, liver and gall bladder.
Bile – product of liver, contains bile salts

Absorption in the small intestines
Most absorption occurs across folded surfaceVilli, microvilliSurface area is roughly the size of a tennis court!
Increase rate of absorption

Absorption of large intestines
Includes the: Colon – ascending, transverse, descending, recovers
water Cecum – pouch that ferments ingested material
Appendix – finger like extension of the human cecum, contains bacteria to break down material, accessory
Rectum – terminal portion, store feces until eliminated. Has two sphincters to regulate defecation
Irritation of lining of colon – diarrhea

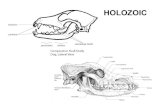
Dental/mutualistic adaptations
Assortment of teach reflect the diet of the animal.
Mutualistic bacteria and protists live in some digestive organs of certain animals to help with digestion.Koala – to break down eukalyptusRuminant digestion – 4 chambered stomachRabbits/rodents – bacteria in L.ITermites – protists to help break down cellulose

Regulation of digestion Nervous system involved by triggering of
substances to be released (saliva, gastric juices)
Endocrine system – controls digestion with release of hormones released by stomach and duodenum.
Energy storage -