Ancient Egypt
description
Transcript of Ancient Egypt

ANCIENT EGYPT6th Grade World History

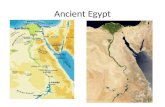
The Nile Valley Essential Question:
How did the geography of the Nile River valley lead to the growth of a civilization there?

A Mighty River Nile River
Drank from itBathed in itCooking and cleaningFish

A Sheltered Land Before it reaches the Mediterranean
Sea, the Nile forms a delta Desert located on either side – keeps
armies away from Egypt’s territory Traded in the Mediterranean Sea and
the Red Sea

The River People Nile floods were predictable and
consistentLeave behind a layer of dark, fertile mud
Irrigation TechniquesDug canals to carry water to fields
beyond the river’s reach Papyrus – reed plant
Baskets, sandals, river rafts and paper!



Hieroglyphics Created symbols that stood for
objects, ideas and sounds Few people could read and write
Scribes: Few Egyptian men ○ Kept records for rulers, priests and traders○ Carved hieroglyphics into stone monuments

The Rise of Government in Ancient Egypt Irrigation systems had to be built and
maintained Surplus grain had to be stored and
passed out in the case of need Disputes over land ownership had to be
settled Earliest rulers were village chiefs who
would gradually take over neighboring villages

Upper and Lower Egypt 4000 B.C.E. – Egypt was made up of 2 large
kingdomsLower EgyptUpper Egypt
3100 B.C.E. – Upper Egypt conquered Lower Egypt
Egypt was ruled by 31 dynasties grouped into 3 categoriesOld KingdomMiddle Kingdom New Kingdom


Egypt’s Social Classes Pharaoh Priests and Nobles Traders, Artisans, Shopkeepers and
Scribes Farmers and Herders Unskilled Workers


Family Life Men were often considered the head
of the household However, Egyptian women enjoyed
more rights than females in almost every other early civilization
Few Egyptian children attended schoolMothers taught daughtersFathers taught sons

Making Connections 1. What is papyrus and how did the
Egyptian’s use it?
2. Cause and Effect: Name three things that led to the growth of government in Ancient Egypt.
3. Answer the Essential Question: How did the geography of the Nile River valley lead to the growth of a civilization there?

Egypt’s Old Kingdom Essential Question:
What characterized the religious beliefs of the Ancient Egyptians?

Old Kingdom Rulers – 2600-2300 B.C.E. Pharaoh
All powerful ruler who guided all activityLived in grand palacesAppointed officials to carry out their
wishesConsidered to be the son of Re – The
Sun God

Egypt’s Religion Worshipped many deities who were
believed to control nature and human activitiesRe – The Sun GodIsis – Worshipped as the ideal wife and
motherOsiris – God of the DeadHapi – Ruled the Nile River

Life After Death Hopeful view that life after death would be
better than the life before it Book of the Dead
Collection of spells and prayers to obtain life after death
For centuries, Egyptians believed only the pharaohs and elite few could enjoy the afterlife and their spirit would travel to the afterlife after deathBody could not be decayed for this journey

Enbalming and Mummification
Remove organs from body
Mummy is placed inside wooden coffin inside tomb
Body is tightly wrapped in linen
Body cleaned with special oils
Apply natron, a special salt to the body
Body is stored for several days to dry
Body is filled with spices and perfumes
Body is sewed shut
Protection for the Pharaoh’s Body
Egyptians learned much about the human body through embalming

The Pyramids Protected bodies of dead pharaohs from floods,
animals and grave robbers Held supplies pharaohs would need in the afterlife
ClothingFurnitureJewelryFood
Skilled artisans used copper tools to cut stone into huge blocks
Pulled stone on sleds to pyramid site Dragged and pushed them up ramps to be set in
place Great Pyramid at Giza




Making Connections 1. What might Egyptians have learned
from embalming bodies?
2. Answer the Essential Question: What characterized the religious beliefs of the Ancient Egyptians?


The Egyptian Empire Essential Question:
How did Akenaton upset the traditional order of the New Kingdom?

The Middle Kingdom 2050-1670 B.C.E.
New dynasty came to power Moved Egyptian capital to Thebes Golden Age of stability, prosperity and
achievement Forced conquered people to send tribute
to the pharaoh

The Arts Blossom Painters covered walls of tombs and
temples with colorful scenes of the deities and daily life
Sculptors created large statues of pharaohs
Tombs were cut into the side of cliffs – Valley of the Kings


The New Kingdom Queen Hatshepsut
More interested in trade than conquestTraded beads, gold, ivory, ebony and
incense for woodTrade under her rule brought great
wealth to Egypt

Expanding the Empire Thutmose III’s armies expanded
Egypt North of Mesopotamia and into Africa
Enslaved prisoners of warCould own land, marry and eventually be
granted freedom

The Legacies of Two Pharaohs Amenhotep/Akhenaton
Introduced one god worship of AtonRemoved priests who resisted the
changesPeople saw this as an attack on Egypt
itselfDevotion to a new religion caused him to
ignore the attack of the Hittites who took over much of the empire

The Legacies of Two Pharaohs Tutankhamen – The Boy King
Restored the old religionDied unexpectedly – murder?Most famous of all pharaohs because of
his brilliant gold funeral mask

End of the New Kingdom Ramses II – rebuilt the empire and
constructed new temples KarnakThebesTemples were the homes of gods and
goddesses

Egypt’s Decline and Fall Later pharaohs have difficulty
controlling a large empire Egypt was attacked by people from
the MediterraneanIron weapons
Egypt changed hands several times 670B.C.E. – Egypt is taken over by
the Assyrians

Making Connections 1. What improvements did the Middle
Kingdom rulers make?
2. Answer the Essential Question: How did Akenaton upset the traditional order of the New Kingdom?