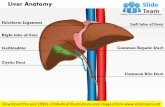
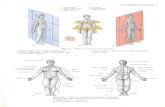
Anatomy 2-images*
-
Upload
rachel-perry -
Category
Education
-
view
316 -
download
0
Transcript of Anatomy 2-images*
• The term muscle refers to multiple bundles of muscle fibres held together by connective tissue
• Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by bundles of collagen fibres known as tendons
!
• Muscle belly - fascicle (bundles of muscle fibres) - myofibrils - actin and myosin - sacomere (contractile unit)
• Myofibrils are composed of long proteins such as actin, myosin
• as myofibrils shorten, the entire muscle cell contracts
• sarcomere is the functional unit that all the components needed for contraction are contained
Structure
Actin + Myosin
• Muscles are composed of two major protein filaments: a thick filament composed of the protein myosin and a thin filament composed of the protein actin.
• Muscle contraction occurs when these filaments slide over one another in a series of repetitive events.
• Stabilisation and grounding
• Movement and transitions
• Stabilisation takes constant effort.
• Sthira sukham asanam
• Stabilisation linked to uddiyana and mula bandha
• Muscles rarely work alone, muscles often work in pairs….
Opposing muscles
• muscles usually work in pairs
• Extensors and flexors work in synchronicity
• Bicep and the tricep
Skeletal muscles create movement at a joint. Where the attach it is often referred to as;
• Origin
• Insertion
This is useful but the body doesn't always move from anatomical position. Perhaps, Instead think of the muscle attaching to the distal and proximal end of the bone
Muscle contractionsiso metric = same length = held position Iso tonic = same tone = with movement
eccentric = contracting while lengthening concentric = contracting while shortening
Proprioception
"sense of self". !!!
The proprioceptors are sensors that provide information about joint angle, muscle length, and muscle tension, which is integrated to give information about the position of the limb in space
Muscle spindles are sensory receptors within the belly of a muscle !The muscle spindle is one type of proprioceptor that provides information about changes in muscle length !They convey length information to the central nervous system via sensory neurons !This information can be processed by the brain to determine the position of body parts.
Muscle spindles
Golgi Tendon
The Golgi tendon organ is another type of proprioceptor that provides information about changes in muscle tension !Located in the tendons that attach muscle to bone !if the body is carrying a heavier load than necessary, the Golgi tendon reflex jumps in to protect it. For example, if a weight lifter tries to bicep curl a heavy weight he or she cannot lift, rather than continuing to fight physics and risk muscular damage, the reflex causes this hypothetical person to drop the weight.!!
Reciprocal inhibition!
!• Joints are controlled by two opposing sets of
muscles, extensors and flexors, which must work in synchrony for smooth movement. !
• When a muscle is stretched and the stretch reflex is activated, the opposing muscle group must be inhibited to prevent it from working against the resulting contraction.
Hyper mobility• four factors that may contribute to
joint hypermobility.
• the structure of your collagen (a type of protein found in some types of tissue)
• the shape of the ends of your bones
• your muscle tone
• your sense of your joint movements (proprioception)
• Genetics
Take aways!
• Muscles create movement and stabilisation
• Reciprocal Inhibition
• Six factors that affect the way we move:
• Karmic
• Genetic
• Modelling
• Prior Activity
• Prior Injury
• Yoga
• Start to reflect on our own bias about others and about ourselves. Work towards a more neutral teacher role (and student!)