Amyloidosis
-
Upload
pathologybasics -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
2.317 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Amyloidosis

1
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
AMYLOIDOSIS

2
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
OVERVIEW
1. Definition 2. Properties
a. Physical b. Chemical
3. Appearance 4. Pathogenesis 5. Classification
a. Localized b. Systemic c. Hereditary
6. Types in detail 7. Organ wise morphology 8. Summary chart

3
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
* DEFINITION Deposition of a 1. pathologic 2. acellular proteinaceous substance 3. in extracellular space
in various tissues and organs, in many different clinical settings.
* PROPERTIES Physical properties
1. 7.5 to 10 nm in diameter 2. continuous, non branching fibrils 3. randomly arranged

4
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
Chemical properties
Protein Glycoprotein (P protein) (95%) 5%
Types of protein component
AL Made up of complete immunoglobulin light chains (λ chains) secreted by plasma cells. Found in plasma cell tumors
AA Made from proteolysis of SAA (serum amyloid associated protein) synthesized in liver Circulates in association with HDL Deposited in inflammatory states as a part of acute phase response Hence also known as acute phase protein
β amyloid protein Derived from larger protein known as Amyloid Precussor protein Constitutes core of cerebral plaques found in Alzheimer’s Also deposited in walls of cerebral blood vessels
Transthyretin (TTR) Protein that is bound to thyroxin and retinol and helps in transporting them Normal TTR is deposited in heart tissue with age (k/a Senile systemic amyloidosis) Mutant TTR is deposited in Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy
β 2 microglobulin (A β 2 m)
It’s a component of MHC class I A β 2 m is deposited in patients on
Prions Misfolded proteins accumulate in CNS in prion disease

5
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
* APPEARANCE LIGHT MICROSCOPY Stains Appearance H&E STAIN: Amorphous Eosinophilic Hyaline Homogenous Extracellular Acellular substance Produces atrophy of adjacent cells
Deposition of amyloid in splenic blood vessel wall CONGO RED STAIN: On H&E – pink red On polarizing microscopy – apple green birefringence
Deposition of amyloid in lymph node – congo red – LM

6
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
Amylod depositon in glomerulus – congo red – polarizing microscopy THIOFLAVIN:
Amyloid deposited in wall of cerebral blood vessel in alzheimer’s –
Thioflavin S stain

7
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
TOLUIDINE BLUE:
Perimyocytic amyloid deposition in semi-thin plastic-embedded
myocardium. This micrograph illustrates perimyocytic amyloid deposits (pale purple-blue) surrounding and distorting individual myocytes (dark purple-blue). The toluidine blue sections are used to map the areas to be examined in ultrathin sections in electron microscopy.
ALCIAN BLUE:
Microscopy of cardiac tissue from autopsy demonstrates amyloid
deposition between cardiac myocytes as homogeneous light pink material (left). Sulfated Alcian blue staining shows extensive amyloid deposition as green amorphous material (right)

8
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
METHYL VIOLET/ CRYSTAL VIOLET:
Metachromatic rose-pink staining amyloid in glomerulus SIRIUS RED STAIN
Amyloid deposition in nerve fibre

9
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
X RAY CRYSTALLOGRAPHY Cross beta pleated sheet configuration
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY
Infrared spectra of amyloids from isotope-labeled amyloid-β proteins

10
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
ELECTRON MICROSOCOPY

11
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
* PATHOGENESIS
Abnormally folded proteins
1. Normal proteins prone that misfold due to systemic conditions 2. mutant proteins that are prone to misfolding and aggregation
escape degradation in proteosomes / by macrophages 1. either due to abnormal enzymes in proteosomes 2. due to structure of proteins that resist degradation
deposition in extracellular sites
Example: Deposition of amyloid in chronic inflammatory conditions Liver cells IL-1 & IL-6 produced by inflammatory cells SAA (Serum Amyloid associated protein) Degraded in Proteosomes/ If there is a defect in Macrophages End products enzymes of proteosomes/ defective structure Macrophages of SAA Deposition of abnormal/ Non degraded SAA in Extracellular sites Amyloidosis

12
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
* CLASSIFICATION
Hereditary Non hereditary Generalised Localised
1 Systemic senile amyloidosis
1 Familial Mediterranean fever 2 Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy
1 Primary amyloidosis (immunocyte dyscrasias) 2 Secondary amyloidosis (reactive systemic amyloidosis) 3 Hemodialysis associated amyloidosis
1 Senile cerebral amyloidosis 2 Endocrine system related a. Medullary Ca thyroid b. Islets of langerhans c. pheochromocytoma d. undifferentiated Ca stomach 3 Isolated atrial amyloidosis

13
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
* EACH TYPE IN DETAIL (i) PRIMARY AMYLOIDOSIS (AL TYPE) (IMMUNOCYTE DYSCRASIAS)
Most common form
Associated with plasma cell dyscrasias
Monoclonal plasma cells synthesize either λ or κ chains, that gives a M spike on electrophoresis
Due to small molecular size – bence jone’s protein is found in urine
Amyloid deposits are seen in the kidney of this patient. The entire filtering apparatus pictured here is inundated with amyloid deposits.

14
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
(ii) SECONDARY AMYLOIDOSIS (AA TYPE)
1. Secondary to infective conditions like TB, bronchiectasis, chronic osteomyelitis 2. Inflammatory conditions like Rheumatoid arthritis, Ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory
bowel disease, Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis 3. skin popping in heroin abusers 4. non immunocyte derived tumors like renal cell carcinomas and Hodgkin’s
AA-amyloidosis of the splenic vessels in rheumatoid arthritis

15
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
(iii) HEMODIALYSIS ASSOCIATED AMYLOIDOSIS (aβ 2 MICROGLOBULIN)
In patients with renal disease, β 2 microglobulin is present in high concentrations
Also this protein is not filtered through the dialysis membranes
It gets deposited in synovium / tendons / joints
May lead to carpal tunnel syndrome
A cell block prepared from the knee synovial fluid of a patient with dialysis-related beta-2 microglobulin amyloidosis showed amorphous material that stained with Congo red. This material also showed
characteristic apple-green birefringence with polarized light microscopy.

16
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
(iv) FAMILIAL MEDITERRANEAN FEVER (AA PROTEIN) FAMILIAL MEDITERRANEAN FEVER is a hereditary genetically restricted disease commonly found among Jews originating from North African countries, Armenians, Turks and Arabs. FMF is recognized by two independent manifestations: 1.) acute, short-lived painful, bouts of stomach pain (peritonitis) or pleuritis with fever 2) nephropathic amyloidosis, which can lead to terminal renal failure even at a young age. The cause is a lack of pyrin, a neutrophil protein which slows down neutrophils when enough have reached an area Lacking pyrin, neutrophils mob body cavities every once in a while. Colchicine, famous for its ability to slow down neutrophils (as in acute gout), controls the attacks and prevents the dread complication of secondary amyloidosis.

17
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
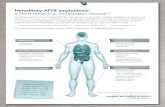
(v) FAMILIAL AMYLOIDOTIC POLYNEUROPATHY (mutant aTTR)
Familial amyloid neuropathies(FAP) are a group of familial systemic amyloidoses with involvement of peripheral nerves. The most common FAP is caused by an autosomal dominant mutation of the transthyretin gene on 18q11. The mutant protein is deposited in the form of amyloid and damages peripheral nerves, the heart, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and other organs. In nerves, amyloid damages first and most severely small fibers, causing loss of pain and temperature sensation and autonomic dysfunction. Transthyretin is produced in the liver. Liver transplantation arrests the progression of the disease.
Familial amyloid neuropathy. Amyloid deposition in nerve. Sirius red stain

18
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
(vi) SENILE SYSTEMIC AMYLOIDOSIS/SENILE CARDIAC AMYLOIDOSIS) (NORMAL aTTR)
Elderly patients
Present with restrictive cardiomyopathy and arrythmias
CARDIAC (HEART) AMYLOIDOSIS]. . Amyloidosis is an insoluble extracellular deposition of abnormal fibrillar
substance composed of specific protein fragments. Cardiac amyloidosis is usually seen in two clinical settings, either as part of systemic amyloidosis or isolated senile cardiac amyloidosis not involving any other organs. The systemic
amyloidosis is generally seen in patients with underlying plasma cell dyscrasia, with abnormal plasma cells producing monoclonal immunoglobulin light chain, usually lambda light chain. The senile cardiac amyloidosis is due to
deposition of a mutant form of transthyretin. Amyloid appears as light-pink hyaline extracellular deposits (left arrow) displacing cardiac myocytes (right arrowhead).

19
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
(vii) DEPOSITION OF AMYLOID IN ENDOCRINE DISORDERS / TUMORS PRODUCING HORMONES a. MEDULLARY CARCINOMA OF THYROID (a CAL) (CALCITONIN)
Amyloid deposition in medullary ca thyroid
MTC can be remembered by the 3 Ms: aMyloid. Median node dissection. MEN 2A & MEN 2B
b. IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES MELLITUS (a IAPP) (islet associated polypeptide)
The amyloid is deposited in the Islets of Langhans, the endocrine pancreas

20
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
(viii) ISOLATED ATRIAL AMYLOIDOSIS (a ANF) (atrial natriuretic factor) Deposition of atrial natriuretic factor (ix) SENILE CEREBRAL AMYLOIDOSIS (a β protein) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) is a fundamental part of the pathology of many disorders causing dementia and/or cerebral haemorrhage. In Alzheimer's disease (AD), CAA is due to the deposition of amyloid alpha protein (Abeta) within the adventitia and media of leptomeningeal and brain parenchymal arteries. Although virtually all cases of AD show CAA to a greater or lesser extent, the brain distribution of CAA is not uniform with the occipital lobe being the most commonly and most severely affected region. In vessels affected by CAA, local muscle and elastic elements are lost and replaced by amyloid fibrils, thereby weakening the overall structure of the vessel. Consequently, CAA predisposes towards cerebral infarction and cerebral haemorrhage,

21
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
* ORGAN WISE MORPHOLOGY Gross:
1. The affected organ is enlarged 2. painting with iodine imparts yellow color which turns blue after application of sulphuric
acid
Section of myocardium stained with iodine

22
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
Microscopy: KIDNEY – Early
1. subtle thickening of mesangial matrix 2. widening of
a. basement membrane b. peritubular interstitium c. walls of arteries
Late 1. depositions cause capillary narrowing and distortion of vascular tuft 2. glomerulus becomes a confluent mass of amyloid
SPLEEN –
Two patterns
Deposition in follicles Deposition in walls of sinuses (SAGO SPLEEN) (tapioca /sabudana ) In red pulp – resembling Pig fat (lard) Known as LARDACEOUS SPLEEN Later fusion of both areas gives the Appearance of map like areas in the spleen

23
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
Sago spleen Lardaceous spleen

24
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
The amyloid material is diffusely spread throughout the splenic parenchyma.
LIVER – Early – deposition in space of Disse Late – deposition in liver parenchyma Sinusoids Vessel walls Kupfer cells
Hepatic amyloidosis

25
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
HEART –
1. Subendocardial deposits 2. in between myocardial fibres
GIT – Initially around blood vessels
Amyloidosis of esophagus
TONGUE – MACROGLOSSIA
Macroglossia amorphous eosinophilic hyaline deposits

26
Notes on Amyloidosis… By Dr. Ashish Jawarkar Contact: [email protected] Website: pathologybasics.wix.com/notes Facebook: facebook.com/pathologybasics
* SUMMARY CHART