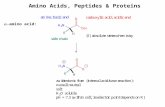
Amino acids
-
Upload
abbot-sanders -
Category
Documents
-
view
39 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Amino acids
Amino acids
R-groups non-polarpolaracidicbasic
proteins condensation between carboxylic acids and amines
+ + H2O
carboxylic acid amine amide
CO
OHNH C
O
N
Amides
amides resonance structure
alanine glycine Ala-Gly +H2O
dipeptide
CO
NC
O
N
CH2N
H
CO
OHCH3
CH2N
H
CO
OHH
CH2N
H
CO
H
CN
H
CO
OHHCH3
Polypeptides“backbone”
N1-C1-C1-N2-C2-C2-N3-C3-C3-
peptide bonds
_
H_H =
OOH
_
H_
H
=O
=
O
_R _R _
R
N-terminal residue
C-terminalresidue
biological activity = structure
protein structure 4 levels
Primary structure
sequence of amino acids
hemoglobin transports O2 and CO2 4 protein chains 300 amino acids
6th amino acid from N-terminus
Glu Val
-CH2CH2-CO2H -CH(CH3)2
R
Sickle cell anemia
water soluble water insoluble
Secondary structure
hydrogen bonding backbone groups
H-bond donors
N1-C1-C1-N2-C2-C2-N3-C3-C3-
_
H_H =
OOH
_
H
_
H
=
O
=
O
_R _R _
R
H-bond acceptors
Two main secondary structures: -helix
-sheet
Alpha helix
Every C=O bonded to N-H 4 residues away
forms a helix core is backbone
R-groups outside
3.6 amino acids per turn
proline
breaks helix
=
O
C
no H-bondingC=
O
N
H
Beta sheet
Every C=O bonded to N-H far apart in 1o structureon different chains
peptide chains extended side-by-side
maximal H-bonding for anti-parallel chains
small R-groups above and below the sheet
if not -helix or -sheet random coil
Proteins
1o structure amino acid sequence
2o structure - helix -sheet
H-bonding betweenC=O and N-H of backbone
- +
some proteins only have 1o and 2o structure:
fibroin (silk) -sheet
keratincollagen
hairskin
- helixinsoluble in H2O
non-polar residues
Fibrous
Gly-Glu- His-Ala-Phe-Ser-Ser-Val- His-Ile-Met-Arg-Asp-Val- Asn-
Tertiary structurePrimary structure sequence of amino acids
Alanine
Non-polar
Phenylalanine
Polar
Serine
Valine
Acidic or Basic
Glutamic acidHistidine
Isoleusine Methionine
Arginine
AsperagineAspartic acid
Glycine
Ala-Phe-Ser-Ser-Val-Glu-His-Ile-Met-Arg-Asp-Val-His-Asn-Gly
Tertiary structureAla-Phe-Ser-Ser-Val-Glu-His-Ile-Met-Arg-Asp-Val-His-Asn-Gly
arrange these in an -helix
Ala 1
Phe2
Ser3
Ser
4
Val 5Glu
6
His7
Ile8
Met9
Arg10
Asp11
Val 12
His13
Asn14
Gly15
non-polarpolarinterior
exterior
Tertiary structure
interaction of the R-groups-
-
+
-+
-
- +
proteins fold aroundnon-polar groups
globular proteins
hydrophobic residues inside
polar and charged residues outside
Tertiary structure
1. Hydrophobic interactions non-polar R-groups
LDF2. Hydrogen bonding
between H-bonddonors and acceptors
polar R-groups
3. Ionic bonds (salt bridges) acidic and basic R-groups
4. Covalent bonds (disulfide) cysteins
ion-ion
interactions of R-groups
Denaturing treatments
1. Heat above 50-60oC frying eggsunburn
2. pH disrupt salt bridgesapproach pHI
3. detergents unfold globular proteins SDS
SO4-
Na+
-
-
+
-+
-
- +