AMINO ACID METABOLISMS. Amino acid structure Essential amimo acids Val, Leu Ile Phe Met, Thr, Lys,...
-
Upload
louise-arnold -
Category
Documents
-
view
235 -
download
1
Transcript of AMINO ACID METABOLISMS. Amino acid structure Essential amimo acids Val, Leu Ile Phe Met, Thr, Lys,...

AMINO ACID METABOLISMS

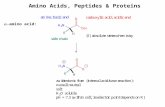
Amino acid structure


Essential amimo acids
Val, Leu Ile Phe Met, Thr, Lys, Arg*, Hys*, Trp
Non essential amino acids
Gly, Ala, Ser, Pro, Hyp1, Cys, Tyr, Asn, Gln, Asp, Glu, Hyl1

AMINO ACID METABOLISM
BODY PROTEINS
Proteosynthesis Degradation
AMINO ACIDSDIETARYPROTEINS
GLYCOLYSISKREBS CYCLE
Digestion
Transam
ination
NONPROTEINDERIVATIVESPorphyrinsPurinesPyrimidinesNeurotransmittersHormonesKomplex lipidsAminosugars
GLUCOSE CO2 KETONBODIES
UREA NH3
Con
vers
ion
(Car
bon
skel
eton
)

Enzymes cleaving the peptide bonds
Endopeptidases – hydrolyse the peptide bond inside a chainPepsin, trypsin, chymotrypsin
Exopeptidases – split the peptide bond at the end of a protein moleculeAminopeptidase, carboxypeptidases
Dipeptidases
Pepsin (pH 1.5 – 2.5) – peptide bond derived fromTyr, Phe,bonds between Leu and Glu
Trypsin (pH 7.5 – 8.5) – bonds between Lys a Arg
Chymotrypsin (pH 7.5 – 8.5) – bonds between Phe a Tyr

NH2 transamination keto acid
+ amino acid
R C H
COOH decarboxylation amine
deamination keto acid
General reactions of amino acids are transamination anddeamination of amino group
Decarboxylation reaction gives biologically active amines
General reactions of amino acids

The glutamate which is produced by these transaminase reactions is oxidatively deaminated by glutamate dehydrogenase to release ammonium:
Transamination reactions

Transamination reactions(enzymes aminotransferases)
(aspartate--ketoglutarate transferase)
(Alanine--ketoglutarate transferase)
Transaminases are enzymes which transfer the amino group from an amino acid to a keto acid, usually alpha-ketoglutarate, essentially swapping an amino group with a keto group:
another similar reaction yields more common products:

These reactions are mediated by pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), a derivative of pyridoxine (vitamin B6):

pyridoxal phosphate pyridoxamine phosphate
pyridoxamine phosphate pyridoxal phosphate

Clinicaly important transaminases
ALTAlanine--ketoglutarate transferase
Clinical marker for irreversibile liver damage
ASTaspartate--ketoglutarate transferase
Clinical marker for irreversibile myocardial damage

Amino acids with three carbons are converted to pyruvate:•Alanine •Serine •Cysteine
Serine is deaminated by serine dehydratase to form pyruvate + NH4+ in a reaction which doesn't involve the transaminase but does use pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) as a reactive group.
Similarly, threonine can be dehydrated and deaminated to yield pyruvate.
Glycine can be converted to serine for degradation, or it can be cleaved to release CO2, NH4+ and an activated one-carbon unit. In addition, three carbons from tryptophan are converted to pyruvate by way of alanine.

Amino acids with three carbons are converted to pyruvate

Amino acids with five carbons are converted to alpha-ketoglutarate:•Arginine •Glutamine •Histidine •Proline
These amino acids are first converted to glutamate which is transaminated to alpha-ketoglutarate.


Some amino acids are converted to succinyl-CoA:•Methionine •Valine •Isoleucine
These amino acids are converted to propionyl-CoA which is carboxylated to methylmalonyl-CoA which is converted to succinyl-CoA. This last step is an isomerization catalyzed by Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, an enzyme which uses cobalamin (vitamin B12).

Degradation of valine, leucine, and isoleucine requires the oxidative decarboxylation of an alpha-keto acid.
If this enzyme is defective, these acids accumulate in the blood and urine, resulting in maple syrup urine disease (branched chain ketoaciduria).
This disease is characterized by physical and mental retardation.
Leucine and Lysine are converted to acetyl-CoA and acetoacetate:

A serious disease results from the inability to oxidize phenylalanine by a defective phenylalanine hydroxylase.
This results in high levels of phenylpyruvate developing (phenylpyruvate is the result of transamination of phenylalanine with an amino acid).
The disease is phenylketonuria (PKU), and results in severe mental retardation and shortens the life span so that half the carriers are dead at 20 and 75% are dead at 30 if it is untreated. It is a genetic disorder and can result from aberrant splicing of the normal phenylalanine hydroxylase transcript.
Therapy for the disease involves restricting the intake of phenylalanine, and must be started immediately after birth. Screening for the disease occurs at birth so that as many effects as possible can be avoided.
Phenylalanine and Tyrosine are converted to fumarate and acetoacetate

Degradation of aminoacids gives intermediates
for saccharides and lipides synthesis
The twenty common amino acids are degrade to a total of seven different compounds, all of which are related to the citric acid
cycle:

Interconversion of amino acids and intermediates of carbohydrate metabolism

Ala Hyp Leu IleArg Met LysAsp Pro PheCys Ser TrpGlu Thr TyrGlu ValGlyHis
Glucogenic ketogenic glucogenic + ketogenic
Amino acids

Enzymes which metabolised amino acides containe vitamines as cofactors
Vater soluble vitamins B
THIAMINE B1 (thiamine diphosphate) oxidative decarboxylation of -ketoacids
RIBOFLAVIN B2 (flavin mononucleotide FMN, flavin adenine dinucleotide FAD)oxidses of -aminoacids
NIACIN B3 – nicotinic acid (nikotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD+
nikotinamide adenine dinukleotide phosphate NADP+)dehydrogenases, reductase
PYRIDOXIN B6 (pyridoxalphosphate)transamination reaction and decarboxylation
FOLIC ACID (tetrahydropholate)Meny enzymes of amino acid metabolism

Nitrogenous derivatives of amino acids
Glycine heme, purine, creatine, conjugation of bile acids
Histidinehistamine
Ornithine a arginincreatine, polyamines (spermidine, spermine)
Tryptophanserotonine (melatonine)
TyrosineEpinephrine, norepinephrine
Glutamic acid-aminobutyric acid (GABA)

Aspartame (NutraSweet) consists of a methly ester of L-aspartate and L-phenylalanine: