Algorithm & flow chart
-
Upload
baabtracom-mentoring-partner-first-programming-school-in-india -
Category
Education
-
view
1.911 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Algorithm & flow chart


Disclaimer: This presentation is prepared by trainees of baabtra as a part of mentoring program. This is not official document of baabtra –Mentoring PartnerBaabtra-Mentoring Partner is the mentoring division of baabte System Technologies Pvt . Ltd

Week Target Achieved
1 21 19
2 24 21
3 25 22
4 25 23
Typing Speed

Jobs Applied# Company Designation Applied Date Current Status
1 cs3Infomat Pvt. Ltd Software trainee 13-9-2013
2
3

Algorithm & flowchart
Waseem [email protected]/
waseemhassantwitter.com/waseemhassan456in.linkedin.com/in/
waseemhassan9567850028

Algorithm
• An algorithm is just a detailed sequence of simple steps that are needed to solve a problem
• Flowchart is the graphical representation of an algorithm
Flowchart

Steps to create an algorithm
• First produce a general algorithm
• Refine the algorithm successively to get step by step detailed algorithm that is very close to a computer language.

Pseudo code
• Pseudo code:Pseudo code is an artificial and informal language that helps programmers to develop algorithms. Pseudo code is very similar to everyday English.
• Input a set of 4 marks• Calculate their average by summing and dividing by 4• if average is below 50
Print “FAIL”else
Print “PASS”

Detailed Algorithm Step 1: Input M1,M2,M3,M4
Step 2: GRADE (M1+M2+M3+M4)/4 Step 3: if (GRADE < 50) then
Print “FAIL” else
Print “PASS”end

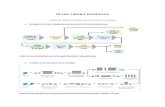
Flowchart Symbols
Oval
Parallelogram
Rectangle
Diamond
Hybrid
Name Symbol Use in Flowchart
Denotes the beginning or end of the program
Denotes an input operation
Denotes an output operation
Denotes a decision (or branch) to be made. The program should continue along one of two routes. (e.g. IF/THEN/ELSE)
Denotes a process to be carried oute.g. addition, subtraction, division etc.
Flow line Denotes the direction of logic flow in the program

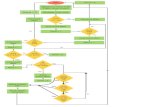
Example• START
• Input• M1,M2,M3,
M4
• GRADE(M1+M2+M3+M4)/4
• If • GRADE<
50
• PRINT• “FAIL”
• STOP
• Y• N
PRINT“pass”
Step 1: Input M1,M2,M3,M4Step 2:GRADE (M1+M2+M3+M4)/4 Step 3: if (GRADE <50) then
Print “FAIL” else
Print “PASS” end

Example
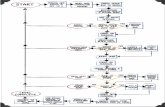
ALGORITHM
Step 1: Input A,BStep 2: if (A> B) then
MAX Aelse
MAX Bend
Step 3: Print “The largest value is”, MAX

• The expression A>B is a logical expression
• it describes a condition we want to test
• if A>B is true (if A is greater than B) we take the action on left
• print the value of A
• if A>B is false (if A is not greater than B) we take the action on right
• print the value of B

Flowchart
• MAX A
• Print• “The largest value is”, MAX
• STOP
• Y • N
• START
• Input• A,B
• MAX B
• if• A>B

If this presentation helped you, please visit our page facebook.com/baabtra and like it.
Thanks in advance.
www.baabtra.com | www.massbaab.com |www.baabte.com

Contact Us
Emarald Mall (Big Bazar Building)Mavoor Road, Kozhikode,Kerala, India.Ph: + 91 – 495 40 25 550
NC Complex, Near Bus StandMukkam, Kozhikode,Kerala, India.Ph: + 91 – 495 40 25 550
Start up VillageEranakulam,Kerala, India.
Email: [email protected]