Air Masses
description
Transcript of Air Masses

Air Masses

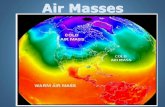
Air Mass - an extremely large body of air whose properties of temperature and moisture content (humidity), at any given altitude, are fairly similar in any horizontal direction.

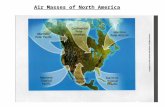
Geographic areas where an air mass originates.
Gives the air mass its characteristics (dry, moist, cool, warm)
Source Regions

Polar latitudes (P) - located near the poles
Tropical latitudes (T) - located near equator
Continental (c) - located over large land masses--dry
Maritime (m) - located over the oceans ---moist
Classifications:

cP continental polar cold, dry, stable cT continental tropical hot, dry, stable air aloft--unstable surface air
mP maritime polar cool, moist, and unstable
mT maritime tropical warm, moist, usually unstable
Combinations of the classifications can be used to describe various types of air masses.:



The boundary between contrasting air masses
Fronts:

1. Warm Front – warm air displaces cooler air◦Shallow leading edge◦Warm air rides up over the cold, dense air
mass◦Warmer temps. and light precipitation over
large area for an extended period of time◦Wind shift from east to southwest
cool air air movement
warm air
4 types of fronts

2. Cold Front – cold, dense air displaces warmer air
◦Steep leading edge◦Moves more quickly than warm fronts◦Forceful lifting of air◦Heavy downpours and gusty winds◦Temps. drop and winds shift
warm air air movement
cool air

3.Stationary Front – No movement of surface position
◦Almost parallel air movement to the line of front
◦Possible light precipitation
cold airair
movementwarm air

4. Occluded Front – Occurs cold front overtakes a warm
front Cold front wedges warm front upward Most precip. formed from rising warm air Newly formed front can produce precip.
air movement

Warm front

Cold Front

Occluded front