Air Masses
description
Transcript of Air Masses

Air Masses

Air Mass
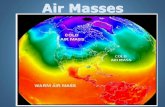
An air mass is a body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given altitude.
can be 1600 km and several km thicktake several days to move
Source region- Characteristics that air takes on from it’s place of origin

Movement of air masses
As it moves the characteristics of an air mass change= weather change in the area where to air mass moves

Classifying air masses
1. Temperature2. Surface of which they form
Continental air masses – form over land= dry Maritime- form over water = humid


4 basic air masses
1. Continental polar(cP)- dry and cool
2. Continental tropical (cT)- dry and warm or hot
3. Maritime polar (mP)- cold and humid
4. Maritime tropical (mT)- warm and humid

Weather in North America
Influenced by cP and mT air masses
cP- cause large amount of snow over the Great Lakes (lake effect snows)
mT- cause high temperatures and oppressive humidity in eastern US

Air mass tracks or paths:• If moving from the south, they move east and
north. • From the north they move east and south.• For the most part they move from the west to
east.

FRONTS
Boundary that separates 2 air masses
-created when two air masses meet

Types of Fronts
1. Cold Fronts2. Warm Fronts3. Stationary Fronts4. Occluded Fronts

WARM FRONTS
• Forms when warm air moves into an area formerly covered by cooler air– Gradual slope– Slow movement– Produces rain or snow

Cold Fronts• Forms when cold, dense air move into a
region occupied by warmer air– Steep slope– Move quickly– Violent weather (heavy downpours and gusty
winds)– cold weather – after the front– passes

Stationary and Occluded FrontsStationary: Forms when movement is almost parallel to line of
front so front does not move
Occluded: forms when an active cold front overtakes a warm front = some precipitation