AhighresoluonreanalysisfortheEastAustralianCurrent...
Transcript of AhighresoluonreanalysisfortheEastAustralianCurrent...

A high resolu,on reanalysis for the East Australian Current: Which observa,ons best capture the dynamics?
A work in progress by Cole?e Kerry1, Moninya Roughan1, Brian Powell2, Peter Oke3 1 Coastal and Regional Oceanography Lab, School of Mathema,cs and Sta,s,cs, UNSW, Sydney, Australia
2 Department of Oceanography, School of Ocean and Earth Sciences, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu, HI, United States 3 CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research, Hobart, Australia
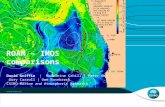
Brisbane
Byron Bay
Coffs Harbour
Newcastle
Sydney
Narooma
150 155 160
SSH
(m)
0
1
153 10!E 153 20!E 153 30!E
30 20!S
30 10!S
CH070 CH100
151 00!E 151 10!E 151 20!E 151 30!E 34 10!S
34 00!S
33 50!S ORS065
SYD100 SYD140
PH100
150 E 151 E 152 E 153 E 154 E 155 E 156 E 37 S
36 S
35 S
34 S
33 S
32 S
31 S
30 S
29 S
28 S
27 S
RRK
NNB
Brisbane
Coffs Harbour
Sydney
Narooma
Tasman Sea
NEMO12NEMO13NEMO14NEMO15DORY4DORY5NEMO16NEMO17
Perc
ent G
ood
0
50
100
ADCP,TADCP,T,WQMTSamplingWave RiderRadar
Gliders

Carter et. al., 2012
HOW DO STRONG INTERNAL TIDES AFFECT STATE ESTIMATES AND
PREDICTIONS OF THE MESOSCALE CIRCULATION?
A Philippine Sea case study
Cole%e Kerry1,2 and Brian Powell2
1 Coastal and Regional Oceanography Lab, School of Mathema,cs and Sta,s,cs, UNSW, Sydney, Australia
2 Department of Oceanography, School of Ocean and Earth Sciences, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu, HI, United States

Challenges in Understanding and Predic,ng the Ocean Observations are sparse in time and space
Models place these observations in a dynamical setting and make predictions
Data assimilation: minimize difference between model and observations
Assumptions and limitations…. What processes are important? What processes are a significant component of the observations?
Which processes does the model resolve?

How might the internal ,des affect our es,mates of the sub,dal dynamics?
How do the non-‐deterministic internal tides affect the value of assimilated observations?
SSH time-series (m) Temperature at 333m time-series (°C)
Days in May Days in May
Do the tides influence the mesoscale dynamics?

How do strong internal ,des affect state es,mates and predic,ons of the mesoscale
circula,on in the Philippine Sea?
Study Area Model Description How do the internal tides vary? How do the internal tides affect our estimates of the subtidal dynamics? Twin Experiment Configuration Comparison of Low Frequency dynamics
Conclusions

Philippine Sea case study
RMS SSH variability (Qiu and Chen 2010)
SW corner of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre Enhanced mesoscale eddy energy
Kuroshio formation Strong internal tides PhilEx observation campaign 2010-‐2011
Ideal case study for investigating internal tides and mesoscale interactions

Philippine Sea case study
SW corner of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre Enhanced mesoscale eddy energy
Kuroshio formation Strong internal tides PhilEx observation campaign 2010-‐2011
Ideal case study for investigating internal tides and mesoscale interactions
Dep
th (k
m)
!8!7!6!5!4!3!2!10
120 125 130 135 140 145
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
120 125 130 135 140 145
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
Taiwan
Philippines
Philippine Sea
Mariana Arc
South China Sea
Luzon Strait

How do strong internal ,des affect state es,mates and predic,ons of the mesoscale
circula,on in the Philippine Sea?
Study Area Model Description How do the internal tides vary? How do the internal tides affect our estimates of the subtidal dynamics? Twin Experiment Configuration Comparison of Low Frequency dynamics
Conclusions

Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS) 4.5-‐8 km horz resolution, 25 s-‐levels Boundary forcing from global model
Mercator Atmospheric forcing from NCEP M2 tides from TPXO 1 year simulation, 2010
Model – M2 ,des and background circula,on SSH (m) and
Surface currents Baroclinic Energy Fluxes (kW/m)

How do strong internal ,des affect state es,mates and predic,ons of the mesoscale
circula,on in the Philippine Sea?
Study Area Model Description How do the internal tides vary? How do the internal tides affect our estimates of the subtidal dynamics? Twin Experiment Configuration Comparison of Low Frequency dynamics
Conclusions

Key Points – How do the internal ,des vary?
Remotely generated internal tides impact conversion at the opposing generation sites in the Philippine Sea, separated by ~2600 km. Kerry, C. G., B. S. Powell, and G. S. Carter, 2013: Effects of Remote Generation Sites on Model Estimates of M2
Internal Tides in the Philippine Sea. JPO.
Low frequency variation in internal tide generation when subtidal circulation is included is due to changes in stratification AND varying remote effects.
Horizontal propagation of baroclinic tides is affected by mesoscale eddies. Kerry, C. G., B. S. Powell, and G. S. Carter, 2014: The Impact of Subtidal Circulation on Internal Tide Generation
and Propagation in the Philippine Sea. JPO.
Subtidal circulation causes increased dissipation of baroclinic tidal energy in the far field, and introduces temporal variability in dissipation. Kerry, C. G., B. S. Powell, and G. S. Carter, 2014: The Impact of Subtidal Circulation on Internal Tide Induced
Mixing in the Philippine Sea. JPO, in press.
The highly variable, non-‐deterministic nature of the baroclinic tides has implications for sampling the ocean state.

How do strong internal ,des affect state es,mates and predic,ons of the mesoscale
circula,on in the Philippine Sea?
Study Area Model Description How do the internal tides vary? How do the internal tides affect our estimates of the subtidal dynamics? Twin Experiment Configuration Comparison of Low Frequency dynamics
Conclusions

Twin Experiments Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions“TRUE STATE”
Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2010

Twin Experiments Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions“TRUE STATE”
Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2010
TWIN 1(tides)
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009
Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
TWIN 2
(without tides)
Non-linear forward model for 2010- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009

Twin Experiments Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions“TRUE STATE”
Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2010
TWIN 1(tides)
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009
Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
Actual Obs.
TWIN 2
(without tides)
Non-linear forward model for 2010- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009

Twin Experiments
Actual Obs.
Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions“TRUE STATE”
Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2010

Twin Experiments Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions“TRUE STATE”
Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2010
TWIN 1(tides)
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009
Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
TWIN 2
(without tides)
Non-linear forward model for 2010- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009

Twin Experiments Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions“TRUE STATE”
Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2010
TWIN 1(tides)
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009
Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
TWIN 2
(without tides)
Non-linear forward model for 2010- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009

Twin Experiments Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions“TRUE STATE”
Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2010
TWIN 1(tides)
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009
Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
TWIN 2
(without tides)
Non-linear forward model for 2010- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009

Twin Experiments Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions“TRUE STATE”
Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2010
TWIN 1(tides)
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009
Non-linear forward model for 2010- M2 tides from TPXO- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
TWIN 2
(without tides)
Non-linear forward model for 2010- NCEP atmos. forcing- Mercator boudary conditions
INCORRECT Initial conditions - Jan. 1 2009

Observa,ons Argo
• AVISO SSH daily – (1/3◦x 1/3◦)
• OSTIA SST daily– (0.054 ◦by 0.054◦)
• Argo floats • PhilEx Gliders • PhilEx CTDs
• PhilEx Moorings (high freq. T and S, and ADCPs)
• JMA CTDs

How might the internal ,des affect our es,mates of the sub,dal dynamics?
How do the non-‐deterministic internal tides affect the value of assimilated observations?
SSH time-series (m) Temperature at 333m time-series (°C)
Days in May Days in May

How do strong internal ,des affect state es,mates and predic,ons of the mesoscale
circula,on in the Philippine Sea?
Study Area Model Description How do the internal tides vary? How do the internal tides affect our estimates of the subtidal dynamics? Twin Experiment Configuration Comparison of Low Frequency dynamics
Conclusions

Results -‐ How do the Low Frequency dynamics compare? SSH
RMS Analysis Error (m)
TWIN 2 – no tides TWIN 1 - tides
RMS Forecast Error (m)
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
0
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
0
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
0
RM
S A
naly
sis -
Tru
th (m
)
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
0 RM
S Fo
reca
st -
Trut
h (m
)
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
0
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
0
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
0
RMS
Ana
lysis
- Tr
uth
(m)
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
120 125 130 135
18
20
22
24
0 RMS
Fore
cast
- Tru
th (m
)
• Tidal mixing controls upper ocean temperature in the SCS and the Kuroshio regions • Mixing over shallow shelf and in SCS results in a cooler upper ocean
• SCS and Kuroshio water masses mix at the Luzon Strait
• Subsurface temperature and SSH are dynamically linked

Phil.
124°E
Low frequency es,mates and predic,ons in ,me – Philippine Sea basin
Phil.
124°E 129°E
129°E
Spatial RMS forecast and analysis SSH error (m)
Spatial RMS forecast and analysis T error over cross sections (°C)

Phil.
124°E
Phil.
124°E 129°E
129°E
Spatial RMS forecast and analysis SSH error (m)
Spatial RMS forecast and analysis T error over cross sections (°C)
Low frequency es,mates and predic,ons in ,me – Philippine Sea basin

Phil.
124°E
Phil.
124°E 129°E
129°E
Spatial RMS forecast and analysis SSH error (m)
Spatial RMS forecast and analysis T error over cross sections (°C)
Low frequency es,mates and predic,ons in ,me – Philippine Sea basin

Phil.
Spatial RMS forecast and analysis SSH error (m)
Spatial RMS forecast and analysis T error over cross sections (°C)
124°E
Phil.
124°E 129°E
129°E
Low frequency es,mates and predic,ons in ,me – Philippine Sea basin

• Mean Low Frequency dynamics not significantly affected by the internal tides in the model
• BUT the estimates and predictions of temporal and spatial evolution of the mesoscale field are
• Related to the prior observation errors
Why are the Philippine Sea basin es,mates worse without ,des?
• SSH estimates are worse when internal tide expression is not resolved
• Subsurface temperature is less constrained due to higher errors if internal tides are not resolved
• SSH is correlated to upper ocean temperature, so errors in SSH predictions lead to errors in temperature predictions, and vice versa
Kinetic Energy Profiles (m2/s2)
LF RMS error LF Time-mean

How do strong internal ,des affect state es,mates and predic,ons of the mesoscale
circula,on in the Philippine Sea?
Study Area Model Description How do the internal tides vary? How do the internal tides affect our estimates of the subtidal dynamics? Twin Experiment Configuration Comparison of Low Frequency dynamics
Conclusions

Conclusions Internal tides in the Philippine Sea are highly variable.
Implications for interpreting internal tide observations The internal tides are a significant source of noise in surface and
subsurface observations
Background circulation and remote effects are important in estimating internal tide dynamics.
Internal tides are important to reduce observation uncertainty in estimating subtidal dynamics.
In developing an assimilation system for reanalysis and forecasting mesoscale circulation in a region of strong internal tides, improved estimates are expected by resolving the tides in the dynamical model.