Accounting equation
-
Upload
afzalur-rahman -
Category
Education
-
view
184 -
download
0
Transcript of Accounting equation
Accounting Equationwww.afzalur.com
Accounting Equation
This topic is on the demand of the students as a separate chapter.
Accounting EquationChapter at a Glance• Basic Accounting Equation• Assets• Liabilities• Owner’s Equity• Investment• Drawing • Revenue • Expenses• Explanation of the transaction
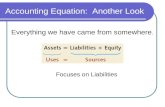
Accounting EquationThe Basic Accounting EquationAccording to the Dual Aspect Concept every transaction has two aspect. One is debited and other is credited. The above concept of the accounting forms a equation that is called Accounting equation. The basis of accounting equation is
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity
Accounting EquationAssets• Assets are resources owned by a business.• They are things of value used in carrying out such activities
as production and exchange.
To recognize the assets quickly we can say that Cash is an asset and all the things that could be convert into cash or have some future value and benefit is an assets.
Accounting EquationLiabilities• Liabilities are claims against assets.• They are existing debts and obligations.
Accounting EquationOwners Equity• Owner’s Equity is equal to total assets minus total liabilities.• Owner’s Equity represents the ownership claim on total assets.• Owner’s Equity are effective by:
1. Capital2. Drawings3. Revenues4. Expenses
Accounting EquationInvestment • Investments by owner are the assets put into the business
by the owner.• These investments in the business increase owner’s equity.
It also has the following meaning. Deployment of funds with the intention and expectation that it
will earn a return. In common parlance, it refers to shares
and debentures of companies or mutual funds or bonds issued by the financial institutions or by the Government.
Accounting EquationDrawings• Drawings are withdrawals of cash or other assets by the
owner for personal use.• Drawings decrease total owner’s equity.
Accounting EquationRevenues• Revenues are the gross increases in owner’s equity resulting
from business activities entered into for the purpose of earning income.
• Revenues may result from sale of merchandise, performance of services, rental of property, or lending of money.
• Revenues usually result in an increase in an asset.
Accounting EquationExpenses• Expenses are the decreases in owner’s equity that result
from operating the business.• Expenses are the cost of assets consumed or services used in
the process of earning revenue.• Examples of expenses include utility expense, rent expense,
and supplies expense.
Accounting EquationIncrease and Decrease in Owner’s Equity
In next slide we will analyze some transaction and will check the effect on capital, assets and Liability in form of equation i.e.Capital + Liabilities = Assets
INCREASES DECREASESInvestments by
Owner
Revenues
Withdrawals by Owner
Expenses
Owner’s Equity
Accounting EquationTransaction Analysis1. Mr. Ahmad started a business with cash of $5,000
2. He took a bank loan of $8,000
Assets = Owner’s Equity LiabilitiesCash↑ 5,000 Capital ↑ 5,000
Assets = Owner’s Equity LiabilitiesCash↑ 5,000 Capital ↑ 5,000Cash ↑ 8,000 -- Bank Loan ↑ 8,000
Total 13,000 5,000 8,000
Accounting EquationTransaction Analysis3. Purchased Motor vehicle of $2,000
You can see here that the Assets is equal to the Owner’s Equity plus Liabilities
Assets = Owner’s Equity LiabilitiesCash↑ 5,000 Capital ↑ 5,000Cash ↑ 8,000 -- Bank Loan ↑ 8,000
Total 13,000 5,000 8,000Motor Vehicle↑ 2,000Cash ↓ (2,000) -- --
Total 13,000 5,000 8,000
Accounting EquationTransaction Analysis4. Purchased trading goods of $1000.• Trading goods is special type of assets that we purchased with
and indentation to resaleAssets = Owner’s Equity LiabilitiesCash↑ 5,000 Capital ↑ 5,000Cash ↑ 8,000 -- Bank Loan ↑ 8,000
Total 13,000 5,000 8,000Motor Vehicle↑ 2,000Cash ↓ (2,000) -- --
Total 13,000 5,000 8,000Goods ↑ 1,000 -- --Cash ↓ (1,000)
Total 13,000 5,000 8,000
Accounting EquationTransaction Analysis5. Sold Goods of costing $500 in $800.
Assets = Owner’s Equity LiabilitiesCash↑ 5,000 Capital ↑ 5,000Cash ↑ 8,000 -- Bank Loan ↑ 8,000
Total 13,000 5,000 8,000Motor Vehicle↑ 2,000Cash ↓ (2,000) -- --
Total 13,000 5,000 8,000Goods ↑ 1,000 -- --Cash ↓ (1,000)
Total 13,000 5,000 8,000Goods ↓ (500) Profit ↑ 300Cash ↑ 800
Total 13,300 5,300 8,000
Accounting EquationTransaction Analysis6. Salary Paid $200 in cash• Salary is an expense and increase in expense will reduce the owner’s equityHere the equation is continue with the balancing figure
Assets = Owner’s Equity LiabilitiesTotal 13,300 5,300 8,000
Cash ↓ 200 Expense ↑ (200)Total 13,100 5,100 8,000
Accounting EquationTransaction Analysis6. Purchase Furniture of $100 from ABC Ltd. on credit.Here the liabilities is increasing and also Assets (Furniture)
Assets = Owner’s Equity LiabilitiesTotal 13,300 5,300 8,000
Cash ↓ 200 Expense ↑ (200)Total 13,100 5,100 8,000
Furniture ↑ 100 ABC Ltd. 100Total 13,200 5,100 8,100
We can show the summary of the above transaction in form of Balance sheet. We transfer the net result of( revenue and profit) Less (Expenses and loss) in owner’s equity. In next slide you can see the balance sheet.
Accounting EquationTransaction AnalysisWe know that Capital + Liabilities = AssetsCapital and Liabilities Amount Assets AmountOwner’s Equity (Capital) 5,100 Motor Vehicle 2, 000Bank Loan 8,000 Goods (Unsold Stock) 500Liabilities 100 Cash 10,700
13,200 13,200