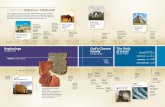
A Timeline Of Europe
-
Upload
montathomas -
Category
Education
-
view
11.323 -
download
0
description
Transcript of A Timeline Of Europe

A Timeline of Europe

I Early HistoryA 400-300 BC. Greece is the major world
civilization of the time. They form the City State which were linked by language and culture. They also introduced the idea of democracy.
B 27 BC-AD 180. Roman Empire reaches its height. Romans made important breakthroughs in government and law
C 43 AD. Romans invade Britain

II Romans and the Beginning of the Middle Ages
A 300-400. Romans pushed out of Britain. This ushers in the middle ages (500-1500).
B 400. Roman empire falls to Germanic forces.C 400s. The Eastern part of the Roman Empire
survives and becomes known as the Byzantine Empire and had its capital in Constantinople.
D 400s-500s. Early Slavic people start spreading throughout Eastern Europe

Middle Ages continuedE 500-1500. Angles, Saxons, and Jutes invade
Britain. Also, Scandinavian powers raid the coasts of Europe leading Norway, Sweden, and Denmark to develop
F 500-900. Germanic Franks rule with the most famous ruler being Charlemagne, who reigned from 768 to 814. He developed a system where land was distributed among lords, and peasants paid taxes to the lords for the right to live on the land. This became known as Feudalism.
G 711. Spain is invaded by a Muslim group called the Moors and control much of Spain for 700 years.

III End of the Middle Ages and the Renaissance
A 962-1806. The Holy Roman Empire dominated Western Europe and Emperors, Nobles, and Popes fought for power.
B 1066. Normans invade England and set up Feudalism.
C 1000s. Western European armies (including England) fight a series of wars to take back Palestine, the birth place of Christianity, from the Muslims. Called the crusades, they failed to capture the land but did extend trade routes to the Mediterranean.

Renaissance continued
D 1300s. The Renaissance begins in Italy. This is a great period of artistic and intellectual achievement.
E 1400s. Scandinavia is united; at the end of the century they divide and fight for power.
F 1453. Byzantine Empire in southeastern Europe Falls and the Ottoman Empire takes over.

IV Winds of ChangeA 1500s. The Reformation introduced
Protestantism and weakened the control of the Catholic church in northern and western Europe.
B 1500s. Spain and Portugal start to grow wealthy from developing trade routes around the world, including the “New World”.
C 1600. Wars were fought for control of land and religious power. France emerged as a major power.

Winds continuedD 1700s. Enlightenment, a movement that brought
value to reason and to question traditions. At this time many were pushing for a voice in Government. It was during this time that British people passed a bill of rights limiting the power of the monarch.
E 1700s-1800s. The beginning of the Industrial revolution starts to replace man power with mechanical power. Industrialization leads to capitalism, which eventually lead some dissatisfied with capitalism to develop Communism.
F 1700s. French Revolution brought an end to the monarchy and they would never have absolute power again.

V World Wars and the Shifting of Power
A 1800s. During the Mid 1800s Prussia rose to power and was successful at unifying Germany. Southern Europe undergoes many battles and brings increased Nationalism.
B 1900s. Sees WWI, WWII, the Holocaust and the Cold War between the United States and their areas of influence and the Soviet Union and their areas of influence. Spain remains neutral, but fights its own Civil war in the 1930s.

Wars continuedC 1900s. Slavs overthrow the Ottoman Empire
on the Balkan Peninsula. Slavs in the region have a hard time uniting and cooperating. Balkanization becomes a term used to any region of the world that splits up into smaller regions that don’t get along and fight with each other. This was the location of ethnic cleansing in the region.
D 1950s-2007. Development of the European Union

Timeline Assignment
• On a large piece of paper construct a linear timeline of the major events in European History.
• Use your outline as well as pages 296,297,301,302,308,314,315. to illustrate at least 10 events from your timeline. Create simple drawings to help you remember the events.
• Hint. Choose events that are also vocabulary words from Chapter 12.