A Requests Bundling DRAM Controller for Mixed-Criticality ...
Transcript of A Requests Bundling DRAM Controller for Mixed-Criticality ...

A Requests Bundling DRAM Controller for Mixed-Criticality System
by: Danlu Guo, Rodolfo Pellizzoni
April 23, 2017 RTAS 2017

Outline
§ Introduction
§ DRAM Background
§ Predictable DRAM Controller Evaluation
§ Requests Bundling DRAM Controller
§ Worst Case Latency Analysis
§ Evaluation
§ Conclusion
PAGE 2

Introduction
§ Multicore architecture - Shared DRAM main memory
- Inter-core memory interference
§ Real-Time system - Hard Real-Time (HRT) applications
- Soft Real-Time (SRT) applications
§ What do we want from DRAM - Tighter upper bound latency for HRT request
- Better lower bound bandwidth for SRT request
§ Solution: - Innovative predictable DRAM controllers
PAGE 3
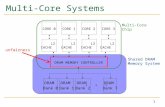
Multicore architecture
LL Cache
Core 0
CPU
Cache
Core N
CPU
Cache
DRAM controller
DRAM main memory

Outline
§ Introduction
§ DRAM Background
§ Predictable DRAM Controller Evaluation
§ Requests Bundling DRAM Controller
§ Worst Case Latency Analysis
§ Evaluation
§ Conclusion
PAGE 4

DR
AM Bank 0
DR
AM Bank N
DRAM Background
§ Organization - Channel: Independent DRAM controller
- Rank: Share Command/Data Bus
- Bank: Access in Parallel
- Row, Column, Row Buffer: data cells
PAGE 5
Row
Decoder
Row Buffer
Row
Column
DR
AM R
ank N
DR
AM R
ank 0
DRAM CHIP 7
DRAM CHIP 6
DRAM CHIP 0
DR
AM Channel
ADDRESS/ COMMAND BUS
DATA BUS
DR
AM Controller

DRAM Background
§ Operation - Activate (ACT): retrieve data
- Column-Access-Strobe (RD/WR): access data
- Precharge (PRE): restore data
- Timing Constraints (DDR Specifications)
§ RD [0,0,1]
PAGE 6
Row
Decoder
Row
Column D
RAM
Bank 0 x y z
x y z
y
A tRCD R tRL Data PtRTP

DRAM Background
§ Page Policy - Close-Page: Precharge (PRE) after access (CAS)
- Open-Page: Precharge (PRE) when required
PAGE 7
A tRCD R tRL Data PtRTP
tRC
A tRCD R tRL Data R tRL Data
RD[0,0,1], RD[0,0,0]
P tRP
Close (Miss) Open (Hit)
Close Close
A tRCD R tRL Data PtRTP

DRAM Background
§ Data Allocation § Shared Banks
§ Allows data sharing among cores
§ Contention on the same bank
§ Private Bank
§ Allows isolation between cores/banks
§ Limits data sharing
PAGE 8
Bank 0
0 1 2
3 4 5
6 7 8
Bank 1
9 10 11
12 13 14
15 16 17
Bank 0
0 1 2
3 4 5
6 7 8
Bank 1
9 10 11
12 13 14
15 16 17
Core 0
Core 1

Outline
§ Introduction
§ DRAM Background
§ Predictable DRAM Controller Evaluation
§ Requests Bundling DRAM Controller
§ Worst Case Latency Analysis
§ Evaluation
§ Conclusion
PAGE 9

Predictable DRAM Controllers Evaluation
§ Shared bank + Close-Page
§ Private Bank + Open-Page
PAGE 10
Bank0 Bank1 Bank2 Bank3
tRC
A WtRCD tWL Data
Bank0 Bank1 Bank2 Bank3
PP
PP
PRE
AA
AAtRP
ACT
W
tRCD
R tRTW
WR tRTW
tWTR
CAS (Open)
tWL Data
Core 0
Core 2
Core 1
Core 3
N – 1 reactivation on the same bank
N-1 PRE N-1 ACT N-1 CAS Switching
A RtRCD PtRC
A WtRCD PtRC
A RtRCD P

Predictable DRAM Controllers Evaluation
§ Private Bank + Open-Page
§ Private Bank and Open-Page + CAS reordering [L.Ecco & R.Ernst,RTSS’15 ]
PAGE 11
ABank0 Bank1
tRCD Bank2 Bank3
AA
A
PP
PP tRP
PRE ACT
WR tRTW
WR tRTW
tWTR
CAS (Open)
tWL Data
ABank0 Bank1
tRCD Bank2 Bank3
AA
A
PP
PP tRP
PRE ACT
WR
WR tRTW
tCCD
CAS (Open)
tWL Data
Ex: DDR3-1600H RD-RD: 4 RD-WR: 7
WR-RD: 18
32 cycles
15 cycles

Predictable DRAM Controllers Evaluation
§ Current Analytical Model
§ Pipeline System
PAGE 12
Bank0 Bank1 Bank2 Bank3
CC
CC
CAS
Data
PP
PP tRP
PRE
A
tRCD
AA
A
ACT
Bank0 Bank1 Bank2 Bank3
PP
PP tRP
PRE
A
tRCD
AA
A
ACT
CC
CC
CAS
Data
Not the actual command
arrival time
HRT Latency Objective

Predictable DRAM Controllers Evaluation
§ Mixed Criticality System
§ Co-existing of HRT and SRT applications on different cores
§ Fixed priority can guarantee the HRT latency but limit SRT bandwidth
PAGE 13
Bank0 Bank1 Bank2 Bank3
Request Request
Request Request
Request Request
Request Request
Bank4 SRT Request
Starvation
SRT Request
SRT Bandwidth Objective

Objective Summary
§ HRT Latency: - Apply Pipelining can cover the overlap interference.
- Apply Reordering can avoid the repetitive CAS switching.
§ SRT Bandwidth: - Apply Co-schedule of SRT and HRT requests can avoid the starvation.
PAGE 14
Requests Bundling DRAM Controller
Reordering CAS breaks the execution sequence

Outline
§ Introduction
§ DRAM Background
§ Predictable DRAM Controller Classification
§ Requests Bundling DRAM Controller
§ Worst Case Latency Analysis
§ Evaluation
§ Conclusion
PAGE 15

HRT Latency
§ Isolation - Private bank
§ Pipelining and Reordering
- Close-Page
=> Fixed command sequence
- Reordering on the request level
=> Avoid multiple switching
=> Fixed request sequence
SRT Bandwidth
§ Fast Access - Shared bank + Open-page
§ Co-schedule SRT and HRT requests - Fixed SRT execution slots before HRT
Requests Bundling (REQBundle) DRAM Controller
PAGE 16

Command Scheduler
PAGE 17
Starts
WR
RD
InRound
HRT Banks InRound Scheduler
OutRound Scheduler SRT Banks
Command Scheduler Schedule SRT Commands only
Schedule HRT & SRT Commands Bundle same type of requests Switch access type between round
Bank0 Bank1 Bank2 Bank3
Write SRT Bank
OutRound
Read RD
WR
Ends/Start
Switch
Write
Write
InRound
Ends
Switch

InRound Scheduler
PAGE 18
RD
RD
Round Starts Ends
RD
tSnapshot
§ Execution Time of an InRound
tissueACT- : time to issue the last HRT ACT
- : time to issue the last SRT CAS tSRTCAS
- : time to determine the number of HRT requests (N) tSnapshot
tswitchCAS SRT CAS
tCCD
R
R
tSRTCAS
tRCD R
A
A
AtissueACT
Bank3
Bank2
Bank1
Bank0 Data
A WSRT Bank
- Execution time R(N) = max( + (N-1) * , + ) tCCD tissueACT tRCDtswitchCAS
tinter–bankACT
A
tintra–bankACT
SRT ACT SRT ACT
NSRTACT
= 2
Not Care
SRT ACT SRT ACT
SRT CAS

Outline
§ Introduction
§ DRAM Background
§ Predictable DRAM Controller Evaluation
§ Requests Bundling DRAM Controller
§ Worst Case Latency Analysis
§ Evaluation
§ Conclusion
PAGE 19

RD
Request Arrival Time and Latency
PAGE 20
§ Case0: Arrives before snapshot of same type of round § = R(N0) + tRL + tBus
LReq
R0 Ends R0 Starts
Bank3
Bank2
Bank1
Bank0 SRT ACT
A R
tSnapshot
A R D
LReq
tRL tBus

Request Arrival Time and Latency
PAGE 21
§ Case1: Arrives before/after snapshot of different type of round § = R(No) + R(N1) + tRL + tBus
RD
LReq
R0 Ends R1 Starts R0 Starts
Bank3
Bank2
Bank1
Bank0 SRT ACT
A W
tSnapshot
SRT ACT
A R
R1 Ends
A R
LReq
D tRL tBus

Request Arrival Time and Latency
PAGE 22
§ Case2: Arrives after snapshot in the same type of round § = R(No) + R(N1) + R(N2) + tRL + tBus (Worst Case)
RD
LReq
R0 Ends R1 Starts R0 Starts
Bank3
Bank2
Bank1
Bank0 SRT ACT
A R
tSnapshot
SRT ACT
A W
R1 Ends R2 Starts SRT ACT
A R
R2 Ends
LReq
D tRL tBus

Outline
§ Introduction
§ DRAM Background
§ Predictable DRAM Controller Evaluation
§ Requests Bundling DRAM Controller
§ Worst Case Latency Analysis
§ Evaluation
§ Conclusion
PAGE 23

Evaluation
§ Implemented in a general DRAM controller simulation framework in C++ § [DRAMController Demo RTSS’16]
§ EEMBC benchmark memory traces generated from MACsim § CPU 1GHz
§ Private L1/2 Cache
§ Shared L3 Cache
§ Evaluate against Command Bundling (CMDBundle) DRAM Controller
§ [L.Ecco and R.Ernst,RTSS’15 ]
§ Burst Mode
§ Non-Burst Mode
PAGE 24

Benchmark Worst Case Execution Time (8 HRTs)
§ HRT0 runs benchmark trace and other 7 HRTs run memory intensive traces
§ Normalized on CMDBundle (non-burst)
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
a2,me cache basefp irrflt aifirf tblook
Normalized
Execu0o
nTime
REQBuddle CMDBundle(Burst)
PAGE 25

Worst Case HRT Request Latency (8 HRTs)
§ WR Request § RD Request
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
800D 1066E 1333G 1600H 1866K 2133L
WorstCaseReadLatency(ns)
CMDBundleH(NBurst) CMDBundleM(NBurst) REQBundle
CMDBundleH(Burst) CMDBundleM(Burst)
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
800D 1066E 1333G 1600H 1866K 2133LWorstCaseW
riteLatency(ns)
CMDBundleH(NBurst) CMDBundleM(NBurst) REQBundle
CMDBundleH(Burst) CMDBundleM(Burst)
PAGE 26

Worst Case SRT Requests Bandwidth (8 HRTs)
§ WR Bandwidth § RD Bandwidth
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
SRT0 SRT1 SRT2 SRT3 SRT4
SRTRe
adBan
dwidth(G
B/s)
1066E 1333G 1600H 1866K 2133L
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
SRT0 SRT1 SRT2 SRT3 SRT4
SRTWriteBa
ndwidth(B
G/s)
1066E 1333G 1600H 1866K 2133L
PAGE 27

Mixed-Criticality System (8 HRTs, 8 SRTs)
§ SRT Bandwidth § HRT Latency
§ Implement virtual HRT requestor mechanism for CMDBundle § Considered as a HRT cores in the system
§ All SRT requests share the virtual requestors
0
30
60
90
120
150
180
0 1 2 3 4
HRTR
eque
stLatency(Cycle
s)
REQBundle CMDBundle(Burst)
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 1 2 3 4
SRTB
andw
idth(
GB/s)
REQBundle CMDBundle
PAGE 28

Outline
§ Introduction
§ DRAM Background
§ Predictable DRAM Controller Evaluation
§ Requests Bundling DRAM Controller
§ Worst Case Latency Analysis
§ Evaluation
§ Conclusion
PAGE 29

Conclusion
§ Employing request bundling with pipelining can improve the worst case request latency.
§ Considering the command timing constraints gaps can provide a good trade-off between the SRT bandwidth and HRT latency.
§ Compared with a state-of-the-art real-time memory controller and show the balance point based on the row-hit ratio of a task. § Measurement row hit ratio is lower than 50%. A guaranteed row hit ratio requires static
analysis and is lower than measured ratio.
PRESENTATION TITLE PAGE 30

THANK YOU
PRESENTATION TITLE