A case of S. aureus infection
-
Upload
ena-farillas -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of A case of S. aureus infection
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
1/37
CASE NO. 5A CASE OF Staphylococcus aureus
INFECTIONEVANGELISTA | FABROS | FARILLAS
GASTARDO | ILAGAN
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
2/37
CASE PRESENTATION
An 18 month old female infant was rushed to theemergency room because of difficulty of breathing .1 week ago, she was noted to have multipleabscess formation on her scalp. 3 days prior to
consult she had fever and cough. Consult was madein a nearby health center where carbocisteine andamoxicillin were prescribed. However cough andfever persisted until day of consult when she was
noted to have difficulty of breathing manifested aschest indrawing with flaring of the alae nasi. Chestxray done in the emergency room revealedpneumatocoele formation.
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
3/37
Staphyloccocus aureus
1. What is the most likely etiologic agent
involved?
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
4/37
Characteristics
Gram-positve cocci occuring in clusters
Non-motile, non-sporeforming, facultative
anaerobe
Fermentation of glucose produces mainly lactic acid
Ferments Mannitol (distinguishes from S.
epidermidis)
Catalase positive
Coagulase positive
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
5/37
Characteristics
Golden yellow colony on agar
Normal flora of humans found on nasal passages,
skin and mucous membranes
Pathogen of humans
Causes a wide range of suppurative infections, as
well as food poisoning and toxic shock syndrome
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
6/37
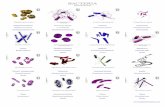
Morphology
Kayser, Medical Microbiology 2005 Thieme, p. 231
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
7/37
2. What biochemical tests can be requested to
assist you in differentiating this microorganism
from the rest of its relative species?
Biochemical tests that may be requested
include:
Catalase Test
Coagulase Test
DNAse Test
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
8/37
Catalase Test
This is performed to differentiate between
genus Staphylococcus and Streptococcus:
Place a drop of H2O2 on a clean glass slide.
Take a small portion of test organism using a
sterile wooden stick or plastic loop and mix with
the drop of H2O2.
Observe for immediate bubbling (gas production).
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
9/37
Catalase Test
Negative (no bubbles)
Positive (bubbles)
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
10/37
Coagulase Test
Coagulase
An extracellular protein which binds to
prothrombin in the host, forming
staphylothrombin
Clots blood plasma surrounding the cocci;
enabling bacteria to resist phagocytosis by the
hostsimmune system Good indicator of pathogenic potential ofS.
Aureus
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
11/37
Two forms of Coagulase
Bound Coagulase/Clumping Factor
Bount to the cell wall
Adsorbs fibrinogen from the plasma and alters it
so it precipitates on the staphylocci, causing them
to clump (cell agglutination)
Detected by the slide coagulase test
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
12/37
Two forms of Coagulase
Free Coagulase
Liberated by the cell wall
Reacts with a substance in plasma to form a fibrin
clot
Detected by tube coagulase test (together with
bound coagulase)
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
13/37
Two Types of Coagulase Test
Coagulase Slide Method
Emulsify a colony of Staph. sp. From the mediaona drop of saline solution on a glass slide
Mix a loopful of fresh plasma with the emulsifiedspecimen
Observe in the next 5 seconds for the appearanceof white clumps on the slide, indicating a positive
result
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
14/37
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
15/37
Two Types of Coagulase Test
Coagulase Tube Method
Place 0.5 ml diluted plasma into a sterile test tube
Inoculate a loopful of bacteria into the dilute plasma
Incubate at 35
o
C Observe for clotting at 1, 2 and 24 hour
*False Negatives can occur when clots were only
observedat the 24thhour because some strains thatproduce coagulase also produce fibrinolysin, which
dissolves clot.
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
16/37
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
17/37
DNAse Test
This is done to detect production of DNAse enzyme
Inoculate a single colony of test organism on DNAseagar plate.
Incubate the plate overnight at 37
o
C. Cover the surface of the agar plate with HCl
(Hydrochloric acid)
Look for clear zones around the colonies within 5
minutes after adding the acid. If clear zones seen around the colonies the test is
DNAse +ve
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
18/37
DNAse negative DNAse positive
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
19/37
3. Cite the characteristics of the clinically significant
species in this genus in terms of hemolysis and tests
used for presumptive diagnosis.
Test(s) S. aureus S. epidermidis S.
saprophyticus
Pigment Gold-white White-yellow White-yellow
Hemolysis + - -
Catalase + + +
Coagulase + - -
Novobiocin Susceptible Susceptible Resistant
Mannitol + - -
Mannose + + -
Trehalose + - +
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
20/37
3. Cite the characteristics of the clinically significant
species in this genus in terms of hemolysis and tests
used for presumptive diagnosis.
HEMOLYSISTEST FOR PRESUMPTIVE
DIAGNOSIS
S. aureus -hemolysis (+) Coagulase TestS. epidermidis hemolysis (-) Trehalose fermentation
S. saprophyticus hemolysis(-) Mannose fermentation
(-) Novobiocin
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
21/37
4. Name the culture media to be used for
definitive diagnosis and describe its colony
characteristics
Gram staining
PRELIMINARY IDENTIFICATION
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
22/37
Definitive Diagnosis
Inoculation in culture media
4. Name the culture media...
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
23/37
4. Name the culture media...
MANNITOL-SALT AGAR (MSA) pH of 7.4
Contains the following:
Casein digest
Animal tissue digest Beef extract
D-mannitol
NaCl
Phenol Red - indicator
Agar
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
24/37
4. Name the culture media...
MANNITOL-SALT AGAR (MSA) Selectively favors growth of S. aureus because of
the 7.5% NaCl
S. aureus can ferment mannitol while other
Staphylococcal organisms can not.
Color change from red to yellow indicates
fermentation of mannitol.
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
25/37
4. Name the culture media...
MANNITOL-SALT AGAR (MSA)
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
26/37
4. Name the culture media...
Blood Agar and Chocolate Agar Enriched bacterial growth medium.
Includes:
Base with protein source
Soybean protein digest NaCl
5% sheep blood
Casein
dH2O Agar
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
27/37
4. Name the culture media...
Blood Agar and Chocolate Agar Enzymes like hemolysin diffuse outward and
cause complete or partial destruction of RBCs in
the medium and complete Hgb denaturation
within cell products
Chocolate agar has similar contents except it
contains lysed RBCs instead of whole RBCs
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
28/37
4. Name the culture media...
Blood Agar and Chocolate Agar Most staphylococci grow on agar media
containing peptone
Growth within 24 hours at 35 to 37 degrees
Celsius
S. aureus colonies appear YELLOW and exhibit -
HEMOLYSIS on sheep blood agar, but these may
also occur with other Staphylococcal species.
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
29/37
4. Name the culture media...
Blood Agar and Chocolate Agar
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
30/37
Other DiseasesBacteremia
Empyema
Endocarditis
Meningitis
Osteomyelitis
Pneumonia
Toxic Shock Syndrome
5. Name other diseases that are associated with this
organism; Include toxin-related diseases.
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
31/37
Functions of Virulence Factors Evade phagocytosis by macrophages
Mediate adherence to host tissues Promote tissue destructionProduction of
toxins and hydrolytic enzymes
6. Name virulence factors associated with
this organism.
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
32/37
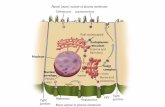
Structural Constituents in the Bacteria
BACTERIAL
CAPSULE
Inhibits chemotaxis and phagocytosis;
Prevents proliferation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes
PEPTIDOGLYCAN
Elicits the production of endogenous pyrogen IL-1 and
opsonic antibodies by monocytes
Also a chemoattractant to leukocytes promoting
abscess formation
TEICHOIC ACIDS Peptidoglycan component that bind to fibronectin to
allow adherence to host tissues
PROTEIN A Binds to IgG and effectively prevents antibody-
mediated clearance of the bacteria
VIRULENCE FACTORS OF S. aureus
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
33/37
Toxins
CYTOTOXINS
-hemolysinheterogeneous protein that acts on a broad
spectrum of eukaryotic cell membranes
-toxindegrades sphingomyelin and can affect RBCs
-toxindisrupts biological membranes and may be involve
in diarrheal diseases
-hemolysincan interact with Panton-Valentine Leukocidin
to lyse WBCs
EXFOLIATIVE
TOXINS (ETA and ETB)
Epidermolytic toxins that contain serine proteases to splitintercellular bridges of stratum granulosum yielding to
desquamation on staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
ENTEROTOXINS
(from A to R)
Superantigens that stimulate T cell proliferation and cytokine
release
Stimulate release of inflammatory mediators Increase intestinal peristalsis and fluid loss leading to nausea
and vomiting
TOXIC SHOCK
SYNDROME TOXIN -1
Prototypical superantigen that stimulates proliferation of T
cells and release of cytokines, leading to leakage and
endothelial cell destruction
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
34/37
Hydrolytic Enzymes
COAGULASE Enzymatically activate and initiate fibrin
polymerization
HYALURONIDASE Spreading factorhydrolyzes hyaluronic acids inconnective tissue
FIBRINOLYSIN Dissolves fibrin clots
LIPASES Hydrolyze membrane lipids
NUCLEASES Hydrolyze DNA
VIRULENCE FACTORS OF S. aureus
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
35/37
7. Create a schematic diagram for the
laboratory identification of this organism.
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
36/37
7. Create a schematic diagram for the
laboratory identification of this organism.
-
8/11/2019 A case of S. aureus infection
37/37
END. THANK YOU!