The Cell Cycle and Mitosis Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Cytokinesis.
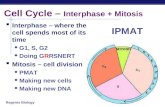
8.2 The Cell Cycle The sequence of growth and division of a cell Interphase Mitosis IPMAT.
-
Upload
norma-gray -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of 8.2 The Cell Cycle The sequence of growth and division of a cell Interphase Mitosis IPMAT.

8.2 The Cell CycleThe sequence of growth and division of a cell
Interphase
Mitosis
IPMAT

Cell Size Limitations
Materials must be able to pass through the cytoplasm quickly
DNA material must be enough in the nucleus to control cell activities
Volume increases faster than surface area as cell’s size increase

Chromosomes Short, stringy, dark-staining
structures Contains DNA Exist as chromatin (strands of
DNA) Coils, shortens, thickens before
cell division

A. Interphase
G-1- Cell growth occurs S - Chromosomes replicate G-2- More cell growth occurs G-o phase – cells in this phase do
not reproduce, most cells of the human body are in this phase
Animal cell in prophase

Review of terms
Sister chromatids Two halves of the doubled
chromosomes

B. Mitosis Division phase Results in two new cells Chromosome sets are identical to
those of the parent cell

Phases of Mitosis
ProphaseMetaphase Anaphase
TelophaseCytokinesis

Prophase First, longest phase Sister chromatids held together by
centromere Nucleus, nucleolus disappears Centrioles move to opposite ends
of cells Spindle forms

Metaphase Short phase Double chromosomes attach to
spindle fibers at centromere Chromosomes line up at the
equator

Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate Centromeres split apart

Telophase
Reverse of prophase occurs Chromosomes uncoil Spindle breaks down Nucleolus reappears New nuclear membrane forms
around chromosomes Plasma membrane separate the
two nuclei

CytokinesisDivision of the cytoplasm
Plants – cell plate forms across cell’s equator
Animals – plasma membrane pinches along the equator

8.3 Control of Cell CycleDNA- Genetic Blueprint for Cells
Gene- segment of DNA that controls production of a single protein
Cancer- Uncontrolled cell division

Cancer Mistake in cell cycle Uncontrolled cell division Cancerous cells forms tumors
(masses of tissue) Tumors deprive normal cells with
nutrients

Factors that affect cancer Environmental
Cigarette smoke UV radiation Air and water pollution
Genetic Programmed in the genes