6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis
-
Upload
stephen-taylor -
Category
Education
-
view
90.397 -
download
3
description
Transcript of 6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis

Nerves Hormones amp Homeostasis
Stephen Taylor i-Biologynet
Assessment Statements Obj
651 State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves and is composed of cells called neurons that carry rapid electrical impulses 1
652 Draw and label a diagram of the structure of a motor neuron 1
653 State that nerve impulses are conducted from receptors to the CNS by sensory neurons within the CNS by relay neurons and from the CNS to effectors by motor neurons 1
654 Define resting potential and action potential (depolarisation and repolarisation) 1
655 Explain how a nerve impulse passes along a non-myelinated neuron 3
656 Explain the principles of synaptic transmission 3
657 State that the endocrine system consists of glands that release hormones that are transported in the blood 1
658State that homeostasis involves maintaining the internal environment between limits including blood pH carbon dioxide concentration blood glucose concentration body temperature and water balance
1
659 Explain that homeostasis involves monitoring levels of variables and correcting changes in levels by negative feedback mechanisms 3
6510 Explain the control of body temperature including the transfer of heat in the blood and the roles of the hypothalamus sweat glands skin arterioles and shivering 3
6511 Explain the control of blood glucose concentration including the roles of insulin glucagon and α and β cells 3
6512 Distinguish between type I and type II diabetes 2
Assessment statements from Online IB Biology Subject GuideCommand terms httpi-biologynetibdpbiocommand-terms
Diagram from httpcommonswikimediaorgwikiFileAnatomy_and_physiology_unlabeled_neuronjpg
The Motor Neuron
nerve impulse
httpbcswhfreemancomthelifewirecontentchp444402sswf
From McGraw Hill httpgoogltI2MD
httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewsactionphtml
httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewschannelhtml
httpoutreachmcbharvardeduanimationssynapticswf
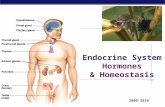
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 Pineal gland2 Pituitary gland3 Thyroid gland4 Thymus5 Adrenal gland6 Pancreas7 Ovary (female)8 Testes (male)
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
This is a Creative Commons presentation It may be linked and embedded but not sold or re-hosted
Please consider a donation to charity via Biology4GoodClick here for more information about Biology4Good charity donations
IBiologyStephen
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Slide 33
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
-

Assessment Statements Obj
651 State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves and is composed of cells called neurons that carry rapid electrical impulses 1
652 Draw and label a diagram of the structure of a motor neuron 1
653 State that nerve impulses are conducted from receptors to the CNS by sensory neurons within the CNS by relay neurons and from the CNS to effectors by motor neurons 1
654 Define resting potential and action potential (depolarisation and repolarisation) 1
655 Explain how a nerve impulse passes along a non-myelinated neuron 3
656 Explain the principles of synaptic transmission 3
657 State that the endocrine system consists of glands that release hormones that are transported in the blood 1
658State that homeostasis involves maintaining the internal environment between limits including blood pH carbon dioxide concentration blood glucose concentration body temperature and water balance
1
659 Explain that homeostasis involves monitoring levels of variables and correcting changes in levels by negative feedback mechanisms 3
6510 Explain the control of body temperature including the transfer of heat in the blood and the roles of the hypothalamus sweat glands skin arterioles and shivering 3
6511 Explain the control of blood glucose concentration including the roles of insulin glucagon and α and β cells 3
6512 Distinguish between type I and type II diabetes 2
Assessment statements from Online IB Biology Subject GuideCommand terms httpi-biologynetibdpbiocommand-terms
Diagram from httpcommonswikimediaorgwikiFileAnatomy_and_physiology_unlabeled_neuronjpg
The Motor Neuron
nerve impulse
httpbcswhfreemancomthelifewirecontentchp444402sswf
From McGraw Hill httpgoogltI2MD
httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewsactionphtml
httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewschannelhtml
httpoutreachmcbharvardeduanimationssynapticswf
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 Pineal gland2 Pituitary gland3 Thyroid gland4 Thymus5 Adrenal gland6 Pancreas7 Ovary (female)8 Testes (male)
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
This is a Creative Commons presentation It may be linked and embedded but not sold or re-hosted
Please consider a donation to charity via Biology4GoodClick here for more information about Biology4Good charity donations
IBiologyStephen
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Slide 33
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
-

Diagram from httpcommonswikimediaorgwikiFileAnatomy_and_physiology_unlabeled_neuronjpg
The Motor Neuron
nerve impulse
httpbcswhfreemancomthelifewirecontentchp444402sswf
From McGraw Hill httpgoogltI2MD
httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewsactionphtml
httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewschannelhtml
httpoutreachmcbharvardeduanimationssynapticswf
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 Pineal gland2 Pituitary gland3 Thyroid gland4 Thymus5 Adrenal gland6 Pancreas7 Ovary (female)8 Testes (male)
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
This is a Creative Commons presentation It may be linked and embedded but not sold or re-hosted
Please consider a donation to charity via Biology4GoodClick here for more information about Biology4Good charity donations
IBiologyStephen
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Slide 33
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
-

httpbcswhfreemancomthelifewirecontentchp444402sswf
From McGraw Hill httpgoogltI2MD
httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewsactionphtml
httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewschannelhtml
httpoutreachmcbharvardeduanimationssynapticswf
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 Pineal gland2 Pituitary gland3 Thyroid gland4 Thymus5 Adrenal gland6 Pancreas7 Ovary (female)8 Testes (male)
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
This is a Creative Commons presentation It may be linked and embedded but not sold or re-hosted
Please consider a donation to charity via Biology4GoodClick here for more information about Biology4Good charity donations
IBiologyStephen
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Slide 33
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
-

From McGraw Hill httpgoogltI2MD
httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewsactionphtml
httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewschannelhtml
httpoutreachmcbharvardeduanimationssynapticswf
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 Pineal gland2 Pituitary gland3 Thyroid gland4 Thymus5 Adrenal gland6 Pancreas7 Ovary (female)8 Testes (male)
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
This is a Creative Commons presentation It may be linked and embedded but not sold or re-hosted
Please consider a donation to charity via Biology4GoodClick here for more information about Biology4Good charity donations
IBiologyStephen
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Slide 33
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
-

httpwwwblackwellpublishingcommatthewschannelhtml
httpoutreachmcbharvardeduanimationssynapticswf
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 Pineal gland2 Pituitary gland3 Thyroid gland4 Thymus5 Adrenal gland6 Pancreas7 Ovary (female)8 Testes (male)
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
This is a Creative Commons presentation It may be linked and embedded but not sold or re-hosted
Please consider a donation to charity via Biology4GoodClick here for more information about Biology4Good charity donations
IBiologyStephen
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Slide 33
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
-

httpoutreachmcbharvardeduanimationssynapticswf
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 Pineal gland2 Pituitary gland3 Thyroid gland4 Thymus5 Adrenal gland6 Pancreas7 Ovary (female)8 Testes (male)
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
This is a Creative Commons presentation It may be linked and embedded but not sold or re-hosted
Please consider a donation to charity via Biology4GoodClick here for more information about Biology4Good charity donations
IBiologyStephen
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Slide 33
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
-

The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 Pineal gland2 Pituitary gland3 Thyroid gland4 Thymus5 Adrenal gland6 Pancreas7 Ovary (female)8 Testes (male)
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
This is a Creative Commons presentation It may be linked and embedded but not sold or re-hosted
Please consider a donation to charity via Biology4GoodClick here for more information about Biology4Good charity donations
IBiologyStephen
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Slide 33
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
-

The Endocrine SystemA stimulus is received and processed Hormones are secreted directly into the blood They are carried to the target tissues (the place of intended action) The action of the hormone changes the condition of the tissue This change in monitored through feedback Most hormonal change results in negative feedback
Key endocrine glands 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Endocrine glands from httpenwikipediaorgwikiEndocrine_gland
This is a Creative Commons presentation It may be linked and embedded but not sold or re-hosted
Please consider a donation to charity via Biology4GoodClick here for more information about Biology4Good charity donations
IBiologyStephen
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Slide 33
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
-

This is a Creative Commons presentation It may be linked and embedded but not sold or re-hosted
Please consider a donation to charity via Biology4GoodClick here for more information about Biology4Good charity donations
IBiologyStephen
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Slide 33
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
-