5.2 Mitosis
description
Transcript of 5.2 Mitosis

5.2 Mitosis

Some Terms You Need to Understand
• Chromosome– long strand of DNA• Chromosomes condense at the beginning of
Mitosis• DNA will wrap around histones, which condenses
it.

Chromosome Structure
DNA doublehelix
DNA andhistones
Chromatin SupercoiledDNA

A Few More Terms
• Chromatin—When DNA wraps around histones, what is formed is called a chromatin.
• Chromatid– 1 half of a duplicated chromosome.
• Centromere• telomere
Condensed, duplicated chromosome

The Beautiful Process Called The Cell Cycle
• Interphase prepares the cell to divide– Time for duplication of organelles and DNA
replication– 2 full sets of DNA that are large enough to divide– G1, Synthesis, G2– G1—after cell division, matures and grows, makes
cytoplasm and organelles, carries out normal functions
– S—DNA replication– G2—makes all structures needed to survive


Cell Division in Prokaryotes
• Prokaryotes have no nucleus• Divide asexually by binary fission• Chromosome (circular) copies itself and
becomes 2x the original size• Cell wall forms between chromosomes and
parent cell splits in two• Results in 2 identical daughter cells


Cell Division in Eukaryotes
• MITOSIS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!

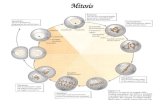
Mitosis
• PMAT• Prophase—chromatin
condenses to chromosome.– Nuclear envelop breaks
down, nucleolus disappears, centromeres and centrioles start to migrate to opposite sides
– Spindle fibers grow from centrioles and radiate to center of cell.

PMAT
• Metaphase– spindel fibers attach to protein structure on centromere– Align chromosome along the equator of cell

PMAT• Anaphase—sister chromatids separate – Spindle fibers begin to shorten– This pulls sister chromatids away from each other– They move to opposite sides of the cell

PMAT
• Telophase—complete set of identical chromosomes are at each pole of the cell– Nuclear membrane
starts to form– Chromosomes start to
uncoil– Spindle fibers fall apart

The Final Part• CYTOKINESIS—divides
cytoplasm into 2 cells and goes through the cycle again.

Mitosis at a Glance

Find the Stage