2 molecular formula writing
-
Upload
nmacintoshwqsbqcca -
Category
Documents
-
view
592 -
download
4
Transcript of 2 molecular formula writing

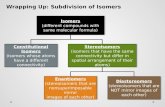
MOLECULAR FORMULAS
ACIDSACIDS
BASES
BASES
SALTS
SALTS

Objectives2.3 To differentiate among acids,
bases, and salts based on their formulas.
2.4 To justify the need to produce various acids, bases, and salts based on their uses/properties.
Molecular Formulas

Allows one to determine the nature of the compound
Deals with letters/symbols from the periodic table to describe substances instead of words
EXAMPLE:
Acids, bases and salts all have their own rules to follow when constructing their molecular formulas
Molecular formulas
Words
Molecular Formulas

**sometimes hydrogen is found at the end……ex. CH3COOH- H at the end of formula are called “organic acids”
Usually begins with the letter “H” (hydrogen)
Usually combines with a nonmetal or a group of atoms (ex. SO4, ClO4)
ACIDS
Exception
The Rules…..
HCl
HS
HF
HNO3
H2SO4

CH3
CH4
C & H only –
are NOT acids!!!
C8H18
C3H8

CH3
CH4
C3H8
ACIDS EXCEPTIONS(misleading solutions)
HNO3
H3PO4
HCl
Examples
NOTE: any “H” combined with carbon by itself is usually an exception and not considered an acid
(called hydrocarbons or“false acids”)

TESTERS: Where do you think these solutions belong? CLICK ENTER FOR THE CORRECT ANSWER
ACIDS “FALSE ACIDS”
1. HNO3
6. H2SO4
2. C4H8
3. HBr
4. CH3
5. C3H8

Usually ends with an OH Usually combines with a metal or a
NH4 group
BASESThe Rules…..
NaOH
KOH
Mg(OH)2
LiOH
NH3

CH3OH
C2H4(OH)2
Alcohols –
are NOT bases!!!
C2H5OH
**When OH is found at the end of the formula but attached to a carbon and
hydrogen it is considered to be a “false base”
- these are called alcohols

C2H5OH
CH3OH
CH3COOH
BASES EXCEPTIONS(misleading solutions)
NaOH
LiOH
Mg(OH)2
NOTE: any “OH” combined with a carbon and a hydrogen together is usually a “false base”.
-called alcohols
Examples

***salts are formed during the neutralization of an acid with a base***
SALTSThe Rules…..
NaClKI
K3PO4
LiBr
Salt formulas neither start with H nor end with OH
Generally begin with a metal and end with a nonmetal or a group of atoms

PCl3
2 non-metals
are NOT salts!!!
CCl4
CF4CO2

PCl3
CCl4
SALTS EXCEPTIONS(misleading solutions)
MgCl2NH4Cl
KI
NOTE: these exceptions just have to be memorized
Examples

TESTERS: Where do you think these solutions belong?
ACIDS BASES SALTS
1. H3PO4
6. KOH
2. C8H18
3. Ca(OH)2
4. HI
5. MgCl2

Which of the following substances is a base? a. LiCl
b. CH3OH
c. KOH
d. HNO3
Be careful – CH3OH is an alcohol

Which of the following substances is a salt? a. HCl
b. Mg(OH)2
c. CF4
d. CaF2Be careful – CF4 is made from 2
non-metals, so it is NOT a salt

Which of the following substances is are acids?
1. HCl
2. CH3COOH
3. KOH
4. H2CO3
5. C2H6
6. Na2SO4
7. NH3
8. HF
Be careful! This is
vinegar or acetic acid!

You are given three substances & asked to classify their nature in the table below.
Which table correctly identifies the nature of each substance?
Nature Substance
? MgCl2? HBr
? NaOH
Nature Substance
Acid MgCl2Salt HBr
Base NaOH
Nature Substance
Salt MgCl2Base HBr
Acid NaOH
Nature Substance
Salt MgCl2Acid HBr
Base NaOH

ACIDS:-common in foods (enhance flavors and preserve food)-medications
BASES:-used in fertilizers, pulp and paper, plastics and food industry-processing of chemical products-common in household cleaning products-extremely important in soaps and detergents as it dissolves grease
SALTS:-used in dyes-changes physical properties by lowering freezing or melting point (ex. salt on our roads to melt ice)
Roles of Acids, Bases & Salts

Acids usually begin with H Bases usually end with OH Salts begin with a metal & end with either a
non-metal or group Exceptions:
CH3COOH is an acid (vinegar) A formula with only C & H are not acids, bases or
salts (hydrocarbons) A formula with only C & H, ending with OH are not
bases (alcohols) NH3 is a base (ammonia) A formula with 2 non-metals are not salts (ex.
PCl3)

Worksheet #2 Study guide Module 3, page 4-5 Text Book
-page 323 #1, #2, #6-page 331 #3 (under exercises)
-page 346 #1, #2, #3
Activities

References
Science Quest, Grenier,Daigle & Rheaume, 1998
Physical Science Student Study Guide 416-436
Animation Factory Google Images