170207 digestive system - epu.ucc.ie
Transcript of 170207 digestive system - epu.ucc.ie

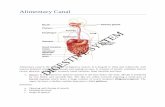
The digestive system

Layout of the digestive system
1

Layout of the digestive system
•The digestive system is essentially a tube whose ends can be opened or closed•Its contents are outside the body although enclosed by it
2

Processes in the digestive system
•Motility: moving food along the gut•Secretion: of the “tools” for digesting food (enzymes, bile etc)•Absorption: the aim of digestive function
3

Parts of the digestive system
10 s
1-3 hours
7-9 hours
25-30 h
30-120 h
When food arrives at each point:
4

Parts of the digestive system
Mouth
Oesophagus
Stomach
Small intestine5

Parts of the digestive system
Pancreas
Liver
Small intestine
6

Parts of the digestive system
Small intestine
Large intestine
RectumAnus
7

Mouth and teeth
Palatine tonsils: protect against infection entering from mouth and nose
Tongue and cheeks: hold food in place to be chewed
8

Deciduous (“milk”) teeth
10 upper teeth
10 lower teeth
9

Permanent teeth
16 upper teeth
16 lower teeth
Four quadrants
10

Salivary glands
11

Saliva contains:
•Mucin (lubrication)•Lysozyme and immunoglobulins (antibacterial)•Salivary amylase: Breaks down starch into maltose and isomaltose (both glucose + glucose)
Glucose
Starch
Maltose
Salivary amylase
12

Swallowing: controlled by swallowing centre in brainstem
13

Events in swallowing
Reflex triggered by contact of food with the back of the
throat
14

...followed by a wave of contraction down the oesophagus (peristalsis)
15

Stomach
•Acid and enzyme secretion•Agitation and mechanical breakdown•Very minor role in absorption
16

Gastric secretion•Acid: hydrochloric acid•Enzyme: pepsinogen (gets converted into pepsin)•Mucus: lubrication and protection of stomach wall•Secreted from cells in the gastric pits
17

Gastric motility•Gastric filling: reflex relaxation•Mixing waves (about 3 per minute): mix food with gastric secretions to produce chyme•Gastric emptying: squeezing liquid chyme through pyloric sphincter
18

Small intestine anatomy
Three parts in this order (starting from the stomach end):•Duodenum: about 30 cm (12 inches) long•Jejunum: about 2.5 m long•Ileum: about 3.5 m long•Structure and function are similar all the way along
19

Small intestine anatomy
20

Small intestine anatomy
Absorption through:•capillaries•lacteals (lymph vessels)
21

Small intestine functions
•Motility: segmental contractions mix contents, peristaltic contractions propel them
•Secretion: several enzymes secreted from intestinalmucosa and also from the pancreas
•Absorption: most absorption takes place in the duodenum and jejunum, some in the ileum
•Associated organs: liver and pancreas
22

Small intestine motility
•Peristalsis: relaxation/contraction pushes food along
23

Small intestine motility
•Segmental contraction: contraction at different points divides and mixes food
24

Small intestine secretion
•Mucus: protects the wall of the intestine•Enzymes: bound to the microvilli- disaccheridases convert maltose/sucrose to simple sugars (glucose, fructose)- peptidases break down small amino acid chains- nucleases break down nucleic acids
•Added to the intestinal secretion are secretions from the liver and the pancreas
25

Absorption in the small intestine
e.g. sugars
26

What is absorbed where?
Food Water27

The liver
28

The liver
29

Liver functions
•Bile production:- bile helps to neutralise stomach acid- bile is a “detergent”: important role in fat digestion
•Storage of glycogen
•Interconversion of nutrients eg amino acids to glucose
•Detoxification eg alcohol dehydrogenase
•Synthesis of blood proteins
30

Inside the liver
31

Inside the liver
32

The gallbladder
•Bile is stored in the gallbladder: enters small intestine after meals
•Gallstones can form in the gallbladder (from excess cholesterol)
33

The pancreas
34

The pancreas
Endocrine (blue) Exocrine (pink)(Islet of Langerhans)
35

Pancreatic functions
Endocrine function (secretion into the blood):•secretion of insulin•secretion of glucagonSee Term 2
Exocrine function (secretion into the gut):•secretion of bicarbonate (HCO3
–) to neutralise stomach acid•secretion of enzymes:- trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase to break down proteins- amylase to break down sugars- lipases to break down fats- nucleases to break down nucleic acids
36

Large intestine
•Absorption of water: contents become “faeces”•Secretion of mucus•Motility: “mass movements” 3-4 times a day (usually after meals)
37

Large intestine reflexes
•Fullness of stomach and duodenum stimulate mass movements•Faeces are pushed into the rectum•Rectal fullness stimulates defecation reflex•Internal anal sphincter relaxes•When the time is right...- voluntary relaxation of external anal sphincter- inspiration, forceful contraction of abdominal muscles, faeces emerge
38

Water absorption and secretion
•Food intake: 1200 ml•Secretions: 7000 ml•Absorbed: 8100 ml•Excreted: 100 ml
39

Reading
Digestive system chapter inSeeley series textbooks