1. Molecular physics Ielibrary.vssdcollege.ac.in/web/data/books-com-sc/msc-final/Physics... ·...
Transcript of 1. Molecular physics Ielibrary.vssdcollege.ac.in/web/data/books-com-sc/msc-final/Physics... ·...

1. Molecular physics I 1
1. Molecular physics I
≫1 about the course
2 introduction
3 quantum mechanics
RDT / FK7012 /

1.1 about the course 2
Course ObjectivesThis course equips you with the tools to build yourself a “molec-ular toolkit,” and provides you with opportunities to use thesetools to investigate and answer questions such as these.
The course has three goals.
• To equip you with the right toolsYou will explore, examine and discuss the physical basis for molecularproperties, together with those approximations necessary to theoreti-cally describe both the molecule and its properties. Furthermore, youwill investigate the interaction of molecules with their environment,and basic chemical reaction kinetics and dynamics.
• To allow you to use the toolsYou will apply the tools and skills you have learnt in . . .
– The laboratory. The student will measure, interpret and explaincommon types of molecular spectra.
– The computer. The student will use and apply basic electronstructure theories to analyse molecules and molecular bonds.
• DemonstrationYou will demonstrate the skills you have acquired by solving basic prob-lems in molecular physics, explaining the fundamental concepts behindmolecular physics, extending and applying these concepts to other areasof science, and theorising as to their influence and importance.
RDT / FK7012 /

1.1 about the course 3
Course overview
The course is suitable for anyone either pursuing a PhD programme contain-ing a molecular physics component or a science student with an interest inbasic molecular physics. The course consists of three parts:
• Lectures There are 18 scheduled lectures of 2 hours each. Thecourse has been divided into 6 subject areas:
– Introduction and chemical concepts
– Intramolecular bonding
– Molecular structure and spectroscopy
– Intermolecular interactions and bonding
– Quantum chemistry
– Elements of molecular dynamics and chemical reactionkinetics
The detailed lecture plan given later lists the topics covered in these areas,together with the relevant chapters from the course textbook. It is recom-mended that these chapters be read before the lecture to allow discussionand interaction. Attendance at lectures is not compulsory, since the lecturenotes will be available online. However, time during lectures is given overto discussion of the home and laboratory exercises, together with generaldiscussions on molecular physics.
Course Textbook:Title ”Chemical Physics of Free Molecules.”Authors: Norman H. March, Joseph F. Mucci.* Hardcover: 393 pages, ISBN: 0306442701* Publisher: Plenum Publishing Corporation (June 1, 1993)
Course Web pages:http://www.physto.se/studentexpedition/kursfakta/kursfakta.php?kurs=FK7012
http://www.physto.se/~rdt
RDT / FK7012 /

1.1 about the course 4
• Laboratory exercises Several experiments are available for thestudents who will use lasers to obtain spectra from simple molecules.Using the tools and techniques obtained from the lectures, the stu-dents will analyse these spectra to obtain the molecule’s fundamentalproperties and to answer questions about these properties.
• Examination and assessment Home exercises (ho)These are distributed at the end of each subject area, and must bereturned within 1 week. Individual solutions are required, which mustbe clearly structured and written such that any course participant couldunderstand and assess them. The exercises are corrected by coursefellows and returned by the next week. The results and solutions will beopenly discussed, and final solutions must be returned to the teacherstwo days before the oral exam.
• Laboratory exercises As with the home exercises, these mustbe returned within a week. Individual solutions are required, and theexercises are corrected by course fellows and returned to the studentby the next lecture. The results will be discussed, and final solutionsmust be returned to the teachers within two weeks.
• Oral exam - 1 hour. This is an individual exam encom-passing the whole course material. The aim of the assessment is toprovide the student with a relaxed atmosphere to explain the conceptsand ideas discussed in the course and to apply their appreciation ofmolecular physics through free discussion rather than simple yes/noanswers. Opportunities will be given to expand on the topics coveredin the course. To “start the ball rolling,” three set questions will bediscussed with the students one week before the exam, with the knowl-edge that one of them will be asked. This allows the student to preparein advance these topics in detail and provides an opportunity for themto demonstrate the grasp of molecular physics. The exam provides thebasis for grading, which is currently done under the guidelines of theBologna process.
RDT / FK7012 /

1.1 about the course 5
Teaching goals of the course After you have completed the course, youshould be able to:
• explain how and why molecules form.
• describe the connection between molecular properties and differentspectroscopic methods and motivate the choice of method to inves-tigate a specific property.
• Discuss and describe the strengths and weaknesses of the most commontheoretical molecular models.
• Apply a simple model to extract the geometry of small polyatomicmolecule.
• Explain the effect of intermolecular interactions and how this effectsmolecular structure and properties such as boiling point and viscosity.
• Use a simple kinetic model to describe the meaning of a transition stateand activation energy in molecular reactions.
Each of these goals will be tested in the discussion and you will receive agrade on the new Bologna scale, A-F.
Exam grading
Grade Percent Assessment DescriptionA 95-100 Excellent The student demonstrates excellent understand-
ing of the concepts in the course and is almostfaultless in describing the most important princi-ples in the six teaching goals. The student cananalyse problems within the field to an excellentdegree. The student has mastered both the ideasand theoretical aspects of the course to a goodlevel. The student demonstrates an excellent de-gree of independent thought, independent judge-ment and problem solving.
RDT / FK7012 /

1.1 about the course 6
Exam grading
Grade Percent Assessment DescriptionB 80-94 Very good The student demonstrates both a very good un-
derstanding of the concepts in the course and indescribing the most important principles in the sixteaching goals. The student can analyse problemswithin the field to an high degree. The studenthas mastered both the ideas and theoretical as-pects of the course to a good level. The studentdemonstrates a very good degree of independentthought, judgement and problem solving.
C 68-79 Good The student demonstrates a good understandingof the majority of the concepts in the course andis can describe most of the important principlesin the six teaching goals. The student can anal-yse problems within the field to a competent level.The student understands both the ideas and the-oretical aspects of the course to a good level. Thestudent demonstrates a good degree of indepen-dent thought, judgement and problem solving.
D 56-67 Satisfactory The student demonstrates a satisfactory under-standing of the majority of the concepts in thecourse and is can describe parts of the most impor-tant principles in the six teaching goals. The stu-dent can analyse problems within the field. Thestudent understands some of the ideas and theo-retical aspects of the course. The student demon-strates some degree of independent thought andindependent judgement and problem solving.
E 50-55 Sufficient The student demonstrates a sufficient understand-ing, but not more, in some, or parts, of the mostimportant principles in the six teaching goals, atleast to an acceptable level. The student can anal-yse some of the problems within the field. Thestudent understands some of the ideas and the-oretical aspects of the course. The student candemonstrate, at least to some level, a degree of in-dependent thought, judgement and problem solv-ing.
RDT / FK7012 /

1.1 about the course 7
Exam grading
Grade Percent Assessment DescriptionFx 45-49 Insufficient The student has not demonstrated a sufficient
understanding of molecular physics, and cannotdemonstrate an understanding of the most impor-tant principles in the six teaching goals, at leastto an acceptable level to pass. The student cananalyse some of the problems within the field, butnot to an acceptable level. The student under-stands none of the ideas and theoretical aspectsof the course. The student does not demonstrate,at least to a passing level, a degree of independentthought, judgement and problem solving.
F 0-44 Wholly in-sufficient
The student has not demonstrated any sufficientunderstanding of molecular physics, and cannotdemonstrate an understanding of the most impor-tant principles in the six teaching goals. The stu-dent cannot analyse any of the problems withinthe field and understands none of the ideas andtheoretical aspects of the course. The studentdemonstrate no degree of independent thought,judgement and problem solving.
All exercises must be completed two days before the exam occasion. A courseassessment form will be made available to the students which can be filledin anonymously and submitted before the exam.
RDT / FK7012 /

1.1 about the course 8
Lecture plan – Autumn 2012
# / NN SUBJECT LITT.
1 / RTTue 09/0413:15-15:00
Molecular Physics I
– about the course– introduction– quantum mechanics
---
2 / RTFri 09/0710:15-12:00
Molecular physics survival kit
– atoms– chemical concepts and methods
1.1-1.7,1.8.1-2,A1.1-2,A5.6,ho
3 / ALTue 09/1113:15-15:00
Intramolecular bonding I
– solving the Schrodinger equation– the Born-Oppenheimer approximation– the variational principle – H+
2 and H2
2.1-2.3,A2.1-3
4 / ALThu 09/1310:15-12:00
Intramolecular bonding II
– cont. H+
2 and H2
– the LCAO approximation
2.3-2.5
5 / ALFri 09/1413:15-15:00
Intramolecular bonding III
– symmetry classification– heteronuclear diatomic molecules
2.6-2.8,ho
6 / RTTue 09/1813:15-15:00
Molecular structure and spectroscopy I
– molecular spectroscopy – introduction– light-matter interaction
1.8.4-5,A5.5
RDT / FK7012 /

1.1 about the course 9
Lecture plan – Autumn 2012
# / NN SUBJECT LITT.
7 / RTFri 09/2110:15-12:00
Molecular structure and spectroscopy II
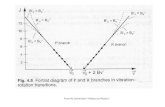
– rotation– vibration
5.1-5,A5.1-3
8 / RTTue 09/2513:15-15:00
Molecular structure and spectroscopy III
– rotation-vibration– electronic spectroscopy– photoelectron spectrocopy
5.6-9,1.8.3,A5.4,A5.6,A6.2
9 / RTThu 09/2710:15-12:00
Molecular structure and spectroscopy IV
– nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy– electron spin resonance spectroscopy
5.10-11,ho
10 / RTFri 09/2810:15-12:00
Intermolecular interactions and bonding I
– intermolecular forces3.1-4
11 / RTTue 10/0213:15-15:00
Intermolecular interactions and bonding
II
– the hydrogen bond– relation to experimental studies
3.5-6,ho
12 / RTFri 10/05
Possible spectroscopy lab
13 / ALTue 10/0913:15-15:00
Quantum chemistry I
– the Hartree-Fock method4.5,A4.6,ho
RDT / FK7012 /

1.1 about the course 10
Lecture plan – Autumn 2012
# / NN SUBJECT LITT.
14 / ALThu 10/1110:15-12:00
Quantum chemistry II
– density functional theory4.1-7
15 / ALFri 10/1210:15-12:00
Quantum chemistry III
– symmetries of polyatomic molecules– hybrid orbitals
6.1-5
16 / ALTue 10/1813:15-15:00
Quantum chemistry IV
– Huckel molecular orbital method6.6-12
17 / ALFri 10/19
Possible computational lab
18 / RTTue 10/2313:15-15:00
Elements of molecular dynamics and
chemical reaction kinetics
– reaction rates and rate laws– absolute rate theory– chemical dynamics
7.1-2,7.6,7.8,A7.2
19 /Fri 10/2610:15-12:00
Cancelled
20 /Tue 10/3013:15-15:00
Cancelled
RDT / FK7012 /

1. Molecular physics I 11
Lecture plan – Autumn 2012
# / NN SUBJECT LITT.
21 / BothThu 11/0113:15-15:00
Molecular physics research at AlbaNova
– molecular quantum wavepacket dynamics– ultrafast molecular spectroscopy– electron-mediated chemical dynamics
Discussion and exam prep.
– laboratories– oral exam times
RDT / FK7012 /

1. Molecular physics I 12
1. Molecular physics I
1 about the course
≫2 introduction
3 quantum mechanics
RDT / FK7012 /

1.2 introduction 13
What’s particular about molecules?
the system
• N nuclei +∑N
i=1Zi electrons
• non-relativistic (except spin & heavy nuclei)
classically
N atoms ⇒ 3N nuclear degrees of freedom:
3 translation
3 rotation3N − 6 (5) vibration (linear)
RDT / FK7012 /

1.2 introduction 14
What’s particular about molecules? (cont’d)
quantum mechanically
All degrees of freedom (incl. electronic) quantised anddescribed by wavefunctions
electronic
wavefuntion
⊳ measured
⊳ calculated
spectroscopy
alternative for the electronic part may: electron density
(wf squared)
RDT / FK7012 /

1.2 introduction 15
What’s particular about molecules? (cont’d)
energy scales
RDT / FK7012 /

1.2 introduction 16
What’s particular about molecules? (cont’d)
interaction
van-der-Waals forces cause condensation
hydrogen bond – electrostatic, partly covalent
molecular dynamics and chemical reaction rates
Nuclear motion ⇒
• non-adiabatic effects within molecules
• energetic, kinematic & dynamic restrictions in chemicalreactions
RDT / FK7012 /

1. Molecular physics I 17
1. Molecular physics I
1 about the course
2 introduction
≫3 quantum mechanics
RDT / FK7012 /

1.3 quantum mechanics 18
time dependent Schrodinger equation
ih∂Ψ(x, t)
∂t=
[
−h2
2m
∂2
∂x2+ V (x, t)
]
Ψ(x, t)
statistical interpretation
The wavefuncion Ψ(x, t) squared gives the probability
density of finding the system in a given volume
∫ b
a
|Ψ(x, t)|2 dx = P (x ∈ [a, b], t)
which means the wavefunction must be normalised
∫ ∞
−∞
|Ψ(x, t)|2 dx = 1
RDT / FK7012 /

1.3 quantum mechanics 19
operators and observables
operators
obtained from classical mechanics by the substitutions
x→ x ; p→h
i
∂
∂x
The commutator of two operators
[A, B] = AB − BA
observables
have real expectation values and are represented by Hermi-
tian operators (Q = Q†)
〈Q〉 =
∫ ∞
−∞
Ψ∗(x, t)QΨ(x, t)dx
RDT / FK7012 /

1.3 quantum mechanics 20
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
standard deviation
For any observable A
σ2
A = 〈(A− 〈A〉)2〉
generalised uncertainty relation
σ2
Aσ2
B ≥
(
1
2i〈[A, B]〉
)2
in particular, σxσp ≥ h/2
time-energy uncertainty relation
With ∆E = σH and ∆t = σQ/|d〈Q〉/dt|, for time-independent
Q
∆E∆t ≥ h/2
RDT / FK7012 /

1.3 quantum mechanics 21
Fermi exclusion principle
two kinds of particles
bosons have integer spin
fermions have half-integer spin
exclusion principle
Two identical fermions cannot occupy thesame state
RDT / FK7012 /

1.3 quantum mechanics 22
time independent Schrodinger equation
With the ansatz Ψ(x, t) = ψ(x)ϕ(t) and time independent V ,the TDSE separates into
dϕ
dt= −
iE
hϕ ⇒ ϕ(t) = e−iEt/h
and the time independent Schrodinger equation
[
−h2
2m
d2
dx2+ V (x)
]
ψ(x) = Eψ(x)
stationary states
The infinite multitude of eigenfunctions ψn(x) corre-spond to stationary Ψn(x, t) = ψn(x)e
−iEnt/h and the eigen-
values En = 〈H〉n
orthogonality
∫ ∞
−∞
ψ∗n(x)ψm(x)dx = δnm
RDT / FK7012 /

1.3 quantum mechanics 23
time independent Schrodinger equation (cont’d)
completeness
Any function f(x) may be expanded in the set {ψn(x)}
f(x) =
∞∑
n=0
cnψn(x)
cn =
∫ ∞
−∞
ψ∗n(x)f(x)dx
The general wavefunction can be obtained as a superposition of
stationary states
Ψ(x, t) =∞
∑
n=0
cnΨn(x, t) =∞
∑
n=0
cnψn(x)e−iEnt/h
RDT / FK7012 /

1.3 quantum mechanics 24
time independent Schrodinger equation (cont’d)
types of solutions
RDT / FK7012 /