1 Infer How do genetic disorders such as CF support the theory of evolution 2 Review Explain two sex...
-
Upload
gordon-park -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of 1 Infer How do genetic disorders such as CF support the theory of evolution 2 Review Explain two sex...
1 Infer How do genetic disorders such as CF support the theory of evolution
2 Review Explain two sex chromosome disorders3 Description Write a paragraph explaining the
process of nondisjunction
Changes in DNA sequence can change proteins by altering the amino acid sequences, which may affect the phenotype.
African and European ancestry are more likely to have wet earwax (dominant form)
Asian or Native American ancestry most often have the dry form (recessive)
Single DNA base change from guanine (G) to adenine (A) in the gene for a membrane-transport protein causes this change.
Disorders Caused by Individual Genes
Lots of genetic disorders are caused by changes in individual genes.
Sickle Cell Disease
Caused by a defective allele for beta-globin (protein in hemoglobin)
Makes hemoglobin less soluble Causes hemoglobin molecules to stick together
with low blood oxygen level Molecules clump into long fibers.
Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle-shaped cells are more rigid than normal red blood cells
Get stuck in the capillaries Blood stops moving through the capillaries,
damaging cells, tissues, and organs.
Cystic Fibrosis
Results from deleting three bases in the gene for a protein CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator).
CFTR normally allows chloride ions (Cl−) to pass across cell membranes
Deletion causes protein to fold improperly Misfolded protein is then destroyed.
Cell membranes unable to transport Cl−
Tissues malfunction Children have serious digestive problems and
produce thick, heavy lung mucus.
One normal copy of the CF allele are unaffected by CF
Two copies of the defective allele are needed to produce the disorder.
Huntington’s Disease
Caused by a dominant allele for a protein found in brain cells
Allele for this disease contains a long string of CAGs (glutamine) repeats over 40 times more repeats the more severe
Mental deterioration and uncontrollable movements usually do not appear until middle age.
Genetic Advantages
In the United States CF allele is found 1 person in 12 of African ancestry 1 person in 25 of European ancestry
Why that common if it can be fatal if you have 2 copies.
Most African Americans today are descended from west central Africa, where malaria is common
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infection caused by a parasite that lives inside red blood cells.
Nondisjunction
Homologous chromosomes fail to separate
Results in gametes with an abnormal number of chromosomes.
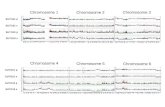
Nondisjunction of the X Chromosomes
Turner Syndrome 45, X Karyotype Usually short, underdeveloped, and sterile
Klinefelter Syndrome 47, XXY karyotype.
Geography of Malaria
Malaria is apotentially fatal disease transmitted by mosquitoes. Its cause is a parasite that lives inside red blood cells. The upper map shows the parts of the world where malaria is common. The lower map shows regions where people have the sickle cell allele.
The map is on the following slide
1. Analyze Data What is the relationship between where malaria and the sickle cell allele are found
2. Infer In 1805, a European expedition tried to find the source of the Niger River in Africa. During the expedition most of them died of malaria. Why do you think their native African guides survived
3. Form a Hypothesis Propose an explanation why the sickle cell allele is not found in populations of southern Africa.