1 General Anatomy and Planes
-
Upload
mini-ruzicka -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of 1 General Anatomy and Planes
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
1/44
General anatomy
An overview
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
2/44
Learning Objective
At the end of the lecture the students should be
able to
1. Define anatomy2. Understand the importance of anatomic
history
3. Identify the subdivisions of anatomy4. Explain the anatomial planes and sections
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
3/44
Definition
Anatomy is the branch of biology which dealswith the structure of animals and plants
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
4/44
Anatome (Greek word) - cutting up
Anatomy forms the foundation of medicine
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
5/44
Anatomy today make use of knowledge from
many fields of science to explore and
understand how the structure of an
organisms cells, tissues and organs relates to
their function
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
6/44
History
The study of anatomy begins at least as early
as 1600 BC
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
7/44
History
Greek period (AD)
Hippocrates- Father of medicine
Herophilus- Father of anatomy---first to dissect
human body
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
8/44
Hippocrates (Greek physician) 460-337 BC- is
the earliest medical scientist
His work demonstrates a basic understandingof muscular skeletal structure and function of
certain organs
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
9/44
Aristotle (4th century) produced a more
empirically founded system based on animal
dissection
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
10/44
Roman period (BC)
Galen- Prince of physicians
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
11/44
14th century
Mundinus (Italian)- the restorer of anatomy
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
12/44
15th century
Leonardo da Vinci (Italy) originator of cross-
sectional anatomy
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
13/44
17th century
William Hunter (London) anatomist and
obstetrician
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
14/44
1st cadaveric dissection
Occurred In the 4th century BC when
Herophilus and Erasistratus performeddissection of cadavers in Alexenderia
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
15/44
The first major anatomist was a great ancient
medical practitioner, Greek physician Cladius
Galen ( AD 131-200) dissected and observed
accurately all kinds of animals
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
16/44
Modern Anatomy
Was founded by Andreas Vesalius (1514-1564)
He dissected the human bodies and pointed
out many Galenis observations
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
17/44
Contribution of Muslim physicians &
scientists
After the fall ofRoman empire, the study of
anatomy became stagnant in Christian Europebut flourished in the medieval Islamic world
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
18/44
The Persian Physician Avicenna (980-1037)
transformed the Galenic teaching on Anatomy
His book remains the most influential andauthoritative book
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
19/44
Ibn-al-Nafis (1213-1288) was an Arabian
Physician He was one of the earliest proponents of
human dissection and postmortem autopsy
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
20/44
Ibn-e-Zuhr (Avenzoar) 1091-1161 was the
first Arab Physician known to have carried out
the dissection
Similarly other physicians contribute a lot o
the science of anatomy
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
21/44
Division of Anatomy
The subject of Anatomy can be divided into
two components
1. Macroscopic or gross anatomy-structures canbe seen with the naked eyes
2. Microscopic or histology/ cytology- structurescan be seen with the help of a microscope
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
22/44
Subdivisions of anatomy
Cadaveric anatomy
Living anatomy
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
23/44
Subdivision:cont
Developmental anatomy (embryology)
Microscopic anatomy (Histology)
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
24/44
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
25/44
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
26/44
Explaination
Regional anatomy- deals with the different
regions of the body like the
limbs/abdomen/head and neck ect
Systemic anatomy- deals with different
systems of the body. These organs work in a
coordinated manner to perform a particular
function e.g CVS, Respiratory system, GIT
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
27/44
Developmental anatomy (embryology) deals
with the formation of different organs and
their gradual transformation into a complete
structure
Not restricted to embryo
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
28/44
Histology- study of tissues and their structure
at microscopic level
Clinical anatomy- related to clinical sciencese.g difficulty in knee bending after RTA
Surgical anatomy- anatomical structure
related to surgeons i.e know how of the basic
anatomy encountered during surgery
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
29/44
Radiological anatomy- real body scan in livingsubjects like MRI, CT, X-ray
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
30/44
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
31/44
Comparative anatomy
Physical anthropology (different races)
Applied anatomy (clinical) Experimental anatomy
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
32/44
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
33/44
Department of anatomy
Strategies
LECTURE PBL
QUIZ
ASSIGNMENT
SKILLSTUTORIAL
CBD
MUSEUM/
MODELS
DISSECTION
MICROSCOPICinteractive
didactic
scenario
based
General anatomy
An overview
General anatomy
An overview
PBL
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
34/44
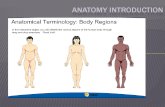
POSITIONAL TERMS
The positional terms usually go in pairs
For example superior and inferior go together
Superior means above and inferior means below
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
35/44
So you could write a statement stating that the
head is superior to the chest or to be more
specificthe cephalon is superior to the
thorax
AND
The reverse would also be true:
The thorax is inferior to the cephalon
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
36/44
Here are some other terms:
Anterior means towards the front
Posterior means towards the back
Ex: the sternum is anterior to the heartOR the heart is posterior to the sternum
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
37/44
Medial means toward the midline of the body.
Lateral means away from the midlineEx: the ears are lateral to the nose
AND
The nose is medial to the ears
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
38/44
Proximal means towards the trunk of the body
Distal means away from the trunkProximal and distal are usually used when
describing structures in the extremities
Ex: the elbow is proximal to the wristThe wrist is distal to the elbow
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
39/44
Superficial means toward the surface
Deep means under the surface
Ex: the skin is superficial to the stomach
The stomach is deep to the skin
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
40/44
Ipsilateral means on the same side
Contralateral means on the opposite side
Ex: the right shoulder and elbow are ipsilateral
The right shoulder and left elbow are contralateral
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
41/44
ANATOMICAL PLANES
Next we will look at how anatomical planes
divide the body.
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
42/44
Body Planes
Sagittal
Divides body into right and left portions.
Transverse
Divides body into superior and inferior portions.
Coronal
Divides body into anterior and posterior portions.
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
43/44
References
KLM
Snell
Grays
Sadler TW. Medical embryology. 10th Ed.Lippincott. Philadelphia;2007.
Persaud M. The developing human. 7th Ed.
Saunders.Philadelphia;2003.
www.electricscotland.com
-
8/3/2019 1 General Anatomy and Planes
44/44