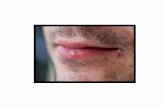
1 30/11/98 Herpes Viruses Cytomegalovirus. 2 30/11/98 Presentation Outline Structure ...
-
Upload
gwendoline-clarke -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
2
Transcript of 1 30/11/98 Herpes Viruses Cytomegalovirus. 2 30/11/98 Presentation Outline Structure ...
22 30/11/9830/11/98
Presentation OutlinePresentation Outline
StructureStructureClassificationClassificationMultiplicationMultiplicationClinical manifestationsClinical manifestationsEpidemiologyEpidemiologyDiagnosisDiagnosisControlControl
33 30/11/9830/11/98
Latent InfectionsLatent Infections
ALLALL herpes viruses can establish latent herpes viruses can establish latent infections. The viral genome may become infections. The viral genome may become incorporated into the host DNA or remain incorporated into the host DNA or remain extrachromosomalextrachromosomal
Latent viruses can be reactivated by stress, Latent viruses can be reactivated by stress, menstruation or uv lightmenstruation or uv light
Reactivation may be asymptomatic or lead Reactivation may be asymptomatic or lead to mild or severe disease.to mild or severe disease.
44 30/11/9830/11/98
Herpes DiagnosisHerpes Diagnosis
Isolation of virus by tissue cultureIsolation of virus by tissue culture herpevirinae cause cytopathic effectsherpevirinae cause cytopathic effectsintranuclear fluorescence of scrapings using intranuclear fluorescence of scrapings using
fluorescent antibodiesfluorescent antibodiesPCR being developedPCR being developed
CMV retiniitis is diagnosed clinicallyCMV retiniitis is diagnosed clinically
66 30/11/9830/11/98
CytomegalovirusCytomegalovirus
Cytopathic effect on the host cell. The cell swells and a large inclusion body forms in the Cytopathic effect on the host cell. The cell swells and a large inclusion body forms in the nucleus.nucleus.
Transmission: Transmission: not highly infectious, virus found in saliva, urine and blood. not highly infectious, virus found in saliva, urine and blood. infants and children acquire CMV from other children.infants and children acquire CMV from other children.congenital. In utero, at birth during perinatal period.congenital. In utero, at birth during perinatal period.see clinical note in the textbook.see clinical note in the textbook.Clinical forms of Cytomegalovirus infectionClinical forms of Cytomegalovirus infectionCongenital:Congenital:the following possibilities relate to the congenital type.the following possibilities relate to the congenital type.severe deformities and death.severe deformities and death.survive with serious defects - physical and mental.survive with serious defects - physical and mental.survive with out deformities.survive with out deformities.newborns: - Enlarged liver and spleen, jaundice, capillary bleeding, microcephaly, ocular newborns: - Enlarged liver and spleen, jaundice, capillary bleeding, microcephaly, ocular
inflammation.inflammation.
77 30/11/9830/11/98
Disseminated cytomegalovirusDisseminated cytomegalovirus
Symptoms:Symptoms:fever, severe diarrhea, hepatitis, arthritis, pneumonia, high mortality.fever, severe diarrhea, hepatitis, arthritis, pneumonia, high mortality.activation of inapparent infection.activation of inapparent infection.also due to:also due to:
immunosuppressive therapy.immunosuppressive therapy. cancer.cancer. AIDS.AIDS.
Virus in blood or organ:Virus in blood or organ:post transfusion.post transfusion.post organ transplant.post organ transplant.Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis:Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis:teenage, young adult similar to other mono.teenage, young adult similar to other mono.
88 30/11/9830/11/98
Epidemiology of CMVEpidemiology of CMV
whereever human populations tested - high percentage (40-100%) were positive for whereever human populations tested - high percentage (40-100%) were positive for the antibodies.the antibodies.
newborns 7.5% positive in the USA & UK.newborns 7.5% positive in the USA & UK.woman of child bearing age were 20-100% positive in many countries that were woman of child bearing age were 20-100% positive in many countries that were
studied (pregnant - virus in the urine).studied (pregnant - virus in the urine).IV drug users were 100% positive for the antibodies.IV drug users were 100% positive for the antibodies.homosexual males were 30% positive for the antibodies - high percentage shed virus.homosexual males were 30% positive for the antibodies - high percentage shed virus.Transmission:Transmission:saliva, respiratory mucus, milk, urine, semen, cervical secretions, feces and saliva, respiratory mucus, milk, urine, semen, cervical secretions, feces and
lymphocytes.lymphocytes.Diagnosis:Diagnosis:the differential diagnosis in neonates must include toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpes the differential diagnosis in neonates must include toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpes
simplex, bacterial sepsis.simplex, bacterial sepsis.in adults it must be differentiated from Epstein-Barra and hepatitis A & B.in adults it must be differentiated from Epstein-Barra and hepatitis A & B.
99 30/11/9830/11/98
Cytomegalovirus - con’tCytomegalovirus - con’t
Laboratory diagnosis:Laboratory diagnosis:virus can be grown from all organs.virus can be grown from all organs.many serological tests.many serological tests.Treatment:Treatment:gancyclovir, foscarnet, hyperimmune CMV immunoglobulin, have some effect.gancyclovir, foscarnet, hyperimmune CMV immunoglobulin, have some effect.interferon does not prevent infection or promote recovery.interferon does not prevent infection or promote recovery.Prevention:Prevention:no animal can be found that can be infected with CMV.no animal can be found that can be infected with CMV.Two deterents:Two deterents:vaccine stimulated antibodies may not be protective. Patients already vaccine stimulated antibodies may not be protective. Patients already
seropositve can be reinfected.seropositve can be reinfected.a vaccine could be oncogenic.a vaccine could be oncogenic.
1010 30/11/9830/11/98
EBV and burkitt’s lymphoma were shown to be the same virus when a lab technician acquired mononucleosis while working with the Burkitt’s lymphoma
virus.
EBV and burkitt’s lymphoma were shown to be the same virus when a lab technician acquired mononucleosis while working with the Burkitt’s lymphoma
virus.
1212 30/11/9830/11/98
Intranuclear inclusionsIntranuclear inclusions
The cell swells The cell swells and a large and a large inclusion body inclusion body forms in the forms in the nucleus.nucleus.
1313 30/11/9830/11/98
CytomegalovirusCytomegalovirus
Nuclear & cytoplasmic inclusionsNuclear & cytoplasmic inclusions
1414 30/11/9830/11/98
Transmission: CMV Transmission: CMV
not highly infectious, virus found in saliva, not highly infectious, virus found in saliva, urine and blood. urine and blood.
infants and children acquire CMV from infants and children acquire CMV from other children.other children.
congenital. In utero, at birth during congenital. In utero, at birth during perinatal period.perinatal period.
1515 30/11/9830/11/98
Congenital: CMVCongenital: CMV
the following possibilities relate to the congenital the following possibilities relate to the congenital type.type.
severe deformities and death.severe deformities and death.survive with serious defects - physical and mental.survive with serious defects - physical and mental.survive with out deformities.survive with out deformities.newborns: - Enlarged liver and spleen, jaundice, newborns: - Enlarged liver and spleen, jaundice,
capillary bleeding, microcephaly, ocular capillary bleeding, microcephaly, ocular inflammation.inflammation.
1616 30/11/9830/11/98
Disseminated cytomegalovirusDisseminated
cytomegalovirus
fever, severe diarrhea, hepatitis, arthritis, fever, severe diarrhea, hepatitis, arthritis, pneumonia, high mortality.pneumonia, high mortality.
activation of inapparent infection.activation of inapparent infection.also due to:also due to:
immunosuppressive therapy.immunosuppressive therapy. cancer.cancer. AIDSAIDS..
1717 30/11/9830/11/98
Virus in blood or organ:Virus in blood or organ:
post transfusion.post transfusion.post organ transplant.post organ transplant.
1818 30/11/9830/11/98
Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis:Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis:
teenage, young adult similar to other mono.teenage, young adult similar to other mono.
1919 30/11/9830/11/98
Epidemiology of CMVEpidemiology of CMV high percentage (40-100%) were positive for the high percentage (40-100%) were positive for the
antibodies.antibodies.newborns 7.5% positive in the USA & UK.newborns 7.5% positive in the USA & UK.woman of child bearing age were 20-100% positive woman of child bearing age were 20-100% positive
in many countries that were studied (pregnant - in many countries that were studied (pregnant - virus in the urine).virus in the urine).
IV drug users were 100% positive for the IV drug users were 100% positive for the antibodies.antibodies.
homosexual males were 30% positive for the homosexual males were 30% positive for the antibodies - high percentage shed virus.antibodies - high percentage shed virus.
2020 30/11/9830/11/98
Transmission:Transmission:
saliva, respiratory mucus, milk, urine, saliva, respiratory mucus, milk, urine, semen, cervical secretions, feces and semen, cervical secretions, feces and lymphocytes.lymphocytes.
2121 30/11/9830/11/98
Differential Diagnosis:Differential Diagnosis:
the differential diagnosis in neonates must the differential diagnosis in neonates must include toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpes include toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpes simplex, bacterial sepsis.simplex, bacterial sepsis.
in adults it must be differentiated from in adults it must be differentiated from Epstein-Barra and hepatitis A & B.Epstein-Barra and hepatitis A & B.
2222 30/11/9830/11/98
Laboratory diagnosis: CMVLaboratory diagnosis: CMV
virus can be grown from all organs.virus can be grown from all organs.many serological tests.many serological tests.
2323 30/11/9830/11/98
Treatment: CMVTreatment: CMV
gancyclovir, foscarnet, hyperimmune CMV gancyclovir, foscarnet, hyperimmune CMV immunoglobulin, have some effect.immunoglobulin, have some effect.
interferon does not prevent infection or interferon does not prevent infection or promote recovery.promote recovery.
2424 30/11/9830/11/98
Prevention:CMVPrevention:CMV
no animal can be found that can be infected no animal can be found that can be infected with CMV.with CMV.
Two deterents:Two deterents:vaccine stimulated antibodies may not be vaccine stimulated antibodies may not be
protective. Patients already seropositve can protective. Patients already seropositve can be reinfected.be reinfected.
a vaccine could be oncogenic.a vaccine could be oncogenic.