09063407 d individual_paper
-
Upload
lsgi4321 -
Category
Technology
-
view
311 -
download
0
description
Transcript of 09063407 d individual_paper

LSGI 4321 Geoinformation for Urban and Regional Studies
Student Name Leung Wing Yan Jacqueline
Student ID 09063407D
Topic Discuss the strength and limitations of GIT applications in
helping decision-making and public engagement in the
planning of new graveyards and columbaria.
With the increasing population and aging population in Hong Kong, the
demand for columbarium facilities increases rapidly over the past few
years. According to the statistics from the Food and Health Bureau
(FHB, 2010), the number and percentage of cremations have raised
substantially over the past 30 years from about 7300 (35%) in 1975 to
36 500 (89%) in 2009. In Hong Kong, there are only six government
crematoria. There are other columbarium facilities operated by private
institutions. However, the supply is still not enough to cope with the
huge demand. As a result, it is essential to plan for new graveyards and
columbaria.
In planning for new graveyards and columbaria, there are two
processes involved. They are public engagement and decision making.
1. Public Engagement
Public Engagement is the involvement of specialists listening to,
developing their understanding of, and interacting with, non-
specialists (HEFCE, 2006). There are nine principles which need to
consider carefully in the process of public engagement. They are
careful planning and preparation, inclusion and demographic
diversity, collaboration and shaded purpose, openness and learning,
transparency and trust, impact and action, and sustained
engagement and participatory culture.

In the process of public engagement, two kinds of technology can be
involved. They are Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Virtual Reality
(VR). A brief introduction of each technology will be given below.
After that, the application of the technologies in public engagement
will be discussed.
A) Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is a useful design and
visualization tool. It is the use of technology for design
demonstration. CAD helps to provide some conceptual ideas in
either 2-Dimensional or 3-Dimensional. As a result, it has the
ability to provide others with a better, more realistic view of the
urban environment (Batten, 2002).
CAD helps to construct precise 3-D models for the proposed
design and planning on columbarium facilities in the site. With
the 3-D models, it provides the public a 3-D view of the
columbarium facilities. It reflects the real word in a certain extent.
Also, CAD helps the planners to create valid Outline Zoning
Plans (OZPs). The OZPs shows the proposed land-uses and
major road systems of individual planning scheme areas and the
objectives of various land use zonings on the plan (Town
Planning Board, 2008).
However, there is lack of data connectivity in CAD models
(Autodesk). The model constructed is in the form of independent
lines in different files. When one of files is deleted from a model,
the GIS data will not be updated automatically. Instead, there will
be problems when the exporting the file.
B) Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual Reality is electronic simulation of environments experienced via bead-mounted eye goggles and wired clothing enabling the end user to interact in realistic three-dimensional

situations (Coates, 1992). VR can be applied to many areas including design, simulation studies, games, and education to add realism (Makanae, 2003). VR model achieves understanding of planned building object. It is a mean of communication in the urban development process and the features of building interact with the properties of the environment (Kaj Sunesson, Carl Martin Allwood, Dan Paulin,Ilona Held, 2008). VR can be divided into two major parts - the simulation of real environments and the development of an imagined environment.
In the process of public engagement, it is essential for the general public to know more about the planning of the columbarium facilities. The VR model can demonstrate how the columbarium facilities are organized in potential sites with simulation of real environment. Also, it can show the design of the columbarium facilities. As a result, the public can view the plan on the columbarium facilities virtually and obtain more information about it. This helps the public to evaluate the plan in a more efficient way.
2. Decision Making
Decision making is the mental processes which is a selection of an
option by severing or eliminating all the others (Perdicoúlis, 2010).
According to Arkansas Program, there are eight moral stages
involved in the decision making. The first step is establishing
community. This is to create and nurture the relationships, norms
and procedures. The second step is perception. This is to recognize
the existing moral problem. The third step is interpretation. This is
the identification and evaluation on competing explanations for the
moral problem. The forth step is judgment. This is the sifting through
various possible actions or responses and determining which is more
morally justifiable. The fifth step is motivation. It is to examine the
competing commitments which may distract from a more moral
course of action and then prioritizing and committing to moral values

over other. The sixth step is courage and character. It is following
through with action that supports the morally justified decision.
Integrity is supported by the ability to overcome distractions and
obstacles, developing implementing skills, and ego strength. The
seventh step is reflection in action. The eighth step is reflection on
action.
In the process of decision making, it focuses on the site selection for
the columbarium facilities. Since GIS offers the spatial data, it is
useful for deciding the potential location of the columbarium facilities.
A) Geo-information System (GIS)
GIS relates tangible elements of the real world such as roads,
trees, memorials and buildings, to information such as records,
documents, photographs, history and statistics (Damian
Bradley,LEES + Associates, 2010). It also displays graphics with
linked database and driving force behind database. GIS helps to
perform the site selection in the planning of new columbarium
facilities. There are several factors when deciding the sites for the
columbarium facilities.
i) Availability of Land
For graveyards, it needs a large piece of land for
development and further expansion. Using the satellites
images can help to define the land which is available for
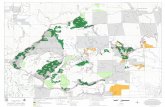
development. GIS helps to show the area of the
undeveloped area over Hong Kong. Through digitization, it
can show all the undeveloped area in Hong Kong. This
helps the planners to make decision with the accurate and
up-to-date information for further process on the
determination of the potential sites.
ii) Landscape: Gentle and Flat

With the gentle slope, people can easily access the sites.
Also, it is easier for future development and expansion.
When facing natural disasters, with flat land, it can
minimize the damage to the graveyards. For example,
when landslide is occurred, gentle slope can help to slow
down the movement and mud. The landslide will not ruin
the graves. With ArcScene of ArcGIS, it can show the
landscape over Hong Kong in a 3-D view. This can help to
evaluate the potential sites.
iii) Good Transportation
The potential site needs to cope with huge demand on
some public holidays, for example, Ching Ming Festival.
During some public holidays, people will go to columbarium
facilities for graveside rituals. As a result, good
transportation is essential. Proximity Analysis is needed to
for evaluation of site accessibility. Buffering can be set to
calculate the number of stations within the proposed site.
Furthermore, the shortest distance algorithm can be
applied to locate the nearest transport station from the
sites.
iv) Far Away from the Residential Area
From the survey carried out by the government about the
new columbarium facilities, most of the interviewees do not
want the columbarium facilities to be located near their
homes. They are worried about the new columbarium
facilities will lower their existing properties’ values (FHB,
2010). As a result, the potential site should have least local
disturbance and noise and air pollution. Proximity Analysis
is needed to evaluate the affected area. It is essential to set
several distances of buffers to track how many residents
will be affected from the potential sites.

v) Good Environment for Building Columbarium Facilities
With good vegetation, air quality can be improved since
there will be much smoke produced from the sites. Also,
there should be greening spaces. In this case, remote
sensing can help to determine the air quality of the sites by
using MODIS to evaluate the aerosol optical thickness
(AOT) (Ngai, 2011). AOT is a measure of radiation
extinction due to the interaction of radiation with aerosol
particles in the atmosphere (NASA, 2010). Low AOT value
implies that it is a good environment for building
columbarium facilities. Also, overlay and buffering can help
to calculate the size of the greening space in the potential
sites. The polygon shapefiles of green areas can overlay
with the satellite image onto the basemap. Buffering can be
set to indicate the size of greening space. With more
greening space, the environment will be better.
3. Limitation on GIT
Firstly, there are different opinions from the public in the public
engagement. It is difficult to present the idea from a particular
interviewee on planning of columbarium facilities. It will be time
consuming and costly if everyone’s idea is presented with the use of
GIT.
Secondly, the psychological view from the general public cannot be
considered by using GIT. According to the view from the public, there
is local disturbance among the communities in the building of
columbarium facilities. To comfort them, there are alternative
solutions in planning the graveyards’ locations and the design of
columbarium facilities. For the location of the graveyards, the
government can consider outlying islands. Although the accessibility
may not be as good as other developed areas in Hong Kong, such

locations can minimize the local disturbance. The transport network
to the outlying island can be designed in the later planning stage.
The columbarium facilities can be in form of Cemetery Park. This can
provide more supplies to cope with the increasing demand from the
public.
Alternatively, the columbarium facilities can be located in some
buildings with trees surrounded. When columbarium facilities are
located in buildings, it is difficult for people to recognize them from
the outlook of the buildings. Also, if there are trees surrounding the
buildings, it will become more difficult for people to know what kind of
buildings they are. This can reduce the annoyance on the
columbarium facilities for the public.
In conclusion, CAD, VR and GIS help in the process of planning new
columbarium facilities. In the stage of public engagement, both CAD
and VR help to produce accurate and reliable information on the design
of new columbarium facilities. In the stage of decision making, GIS
helps to define the potential sites for new columbarium facilities with 5
criteria - availability of land, gentle and flat aspects of landscapes, good
transportation, distances from the residential area and suitable
environment. However, there are limitations on GIT. Firstly, an opinion
from a particular resident cannot be reflected with the use of GIT.
Secondly, GIT ignores the psychological views of the public. For the
solution of the limitations, the new columbarium facilities can be located
on the outlying islands or using trees as a barrier to hide the
columbarium facilities.

Reference
1. Sunesson, K., Allwood, C. M. & Paulin, D. (2008) Virtual Reality As a
New Tool in the City Planning Process, .
2. (2008). Retrieved November 5, 2011 from Town Planning Board,
Web site: http://www.info.gov.hk/tpb/en/list_of_plans/intro.html
3. Bradley, D. (2010). Cemetery Mapping: What can GIS do for you?
4. Autodesk (2009). CAD and GIS: Critical Tools, Critical Links.
Retrieved November 5, 2011 from
h ttp://images.autodesk.com/adsk/files/3582317_CriticalTools0.pdf
5. NASA (2010). Giovanni Online User Manual. Retrieved November 2,
2011 from http://disc.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/additional/users-
manual/G3_manual_Chapter_19_AOT_comparison#whatis_AO T
6. (2010). Public Consultation on Review of Columbarium Policy.
Retrieved November 2, 2011 from Food and Health Bureau, Web
site:
http://www.fhb.gov.hk/download/press_and_publications/consultation
/100706_f_columbarium/e_columbarium_consultation.pdf
7. Metin, R., & (2001). GPS-Single Point Positioning Without Selective
Avaliability,10 .
8. Batten & Lawrence, G. (2002). National Capital Urban Planning
Project: Development of a Three-Dimensional GIS Model ,5.
9. Coates (1992). Program from Invisible site - a virtual sbo, a
multimedia performance work
10. Makanae & Koji (2003). Development of the VR-CAD System for
Landscape and Town Planning
11.Ngai, C. C. & (2010). GIS to determine the potential locations of
columbarium., 75 .