chhsmscience.weebly.comchhsmscience.weebly.com/.../2210538/body_systems_notes.docx · Web...
Transcript of chhsmscience.weebly.comchhsmscience.weebly.com/.../2210538/body_systems_notes.docx · Web...

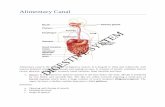
BODY SYSTEMS NOTES Digestive System
o Main Purpose: Break down food to absorb nutrients for energy.o Two types of digestion
physical or mechanical (through actual breaking apart and tearing of food) chemical (enzymes breaking down the food)
o Mouth site of physical digestion from teeth and tongue) chemical digestion from saliva mastication=chewing
o Esophagus tube that connects mouth to stomach peristalsis - the movement of muscles in the digestive tract that constantly pushes
food from mouth to anus reverse peristalsis = vomiting or throwing up
o Stomach Chemically breaks down proteins with pepsin and HCl (hydrochloric acid) Physically breaks down food through churning
o Small Intestine Absorption of nutrients
o Large intestine/Colon Absorption of water
o Rectum and Anus Collects and release fecal waste
o Some of the organs that aren’t in the actual digestive tube, but are helpful: Gall Bladder
secretes bile (used to break down fats in the small intestine) Liver
secretes bile converts extra sugar to glycogen for storage detoxifies poisons (alcohols, toxins, pesticides, etc.)

Circulatory Systemo main job: transport body fluids throughout bodyo 3 types of blood vessels
arteries- carry blood away from the heart capillaries- tiny blood vessels where blood diffuses into the body tissues to deliver
nutrients and oxygen veins- carry blood toward the heart
o Components of Blood Red Blood Cells- Carry oxygen White Blood Cells- Fight off infections Platelets- Clotting and wound healing
o Process (use picture to the right)o red = oxygen rich bloodo blue = oxygen depleted blood
1. Heart pumps oxygen rich blood to body tissues2. Capillaries help exchange oxygen and CO2 in body
tissues3. Veins transport oxygen depleted blood back to heart4. Heart pumps oxygen depleted blood to lungs5. In lungs, the oxygen depleted blood is dropped off in
capillaries (and we exhale)6. When we inhale, the oxygen rich blood is picked up
in capillaries and transported to the heart7. Repeat steps 1-6 for each breath/heart beat
CO2 being picked up in body tissues is a byproduct of cellular respiration. O2 is a necessary reactant for cellular respiration. Cellular respiration makes ATP, which our bodies use for energy.

Respiratory Systemo main job: gas exchangeo We inhale (breathe in) oxygen (O2) to deliver to our body cells for cellular respirationo We exhale (breathe out) carbon dioxide (CO2) which is a byproduct from cellular
respirationo Process:
1. Breathe in through either the nasal cavity or the mouth2. Air passes through trachea3. Air splits into two bronchi to enter each lung4. Bronchi split into even smaller bronchioles5. Air eventually makes it to tiny air filled sacs called alveoli
Capillaries that will pick up oxygen to be delivered to the heart surround alveoli. The heart will pump the oxygen rich blood to the body Deoxygenated blood will be delivered back to the alveoli through the circulatory
system6. Deoxygenated blood delivers CO2 to the alveoli7. CO2 travels back up the bronchioles, bronchi, trachea, and out through either the mouth
or the nasal passages o The diaphragm is a muscle under the lungs that controls breathing
As it contracts or relaxes it makes more or less room for the lungs which causes air to either rush into the body or be pushed out
Excretory System Main job: Rid body of wastes made through metabolic processes Excretion is the process of ridding the body of toxic chemicals, excess water, salts, and carbon
dioxide while maintaining osmotic pressure and pH balance Main organs
o Lungs: excrete carbon dioxide and water vaporo Skin: excretes water, salts, and small amounts of nitrogen wastes in sweat o Kidneys: excrete nitrogen wastes, salts, water, and other substances in urine
Each kidney has 1 million tiny tubes called nephrons Each tube has a ball surrounded by capillaries to help remove waste from the
blood Urine is produced in kidneys
o Urine is composed of urea, salts, and waters left over after useful molecules have been reabsorbed into the blood
Ureters are tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder The bladder is a hollow sac that holds urine When the bladder becomes full, the nervous system signals the brain, and
you feel the urge to urinate Urine passes from the bladder through a urethra to exit the body
o Female urethra is separate from the reproduction systemo Male urethra passes both urine and semen from the reproduction
system

Endocrine System Main job: produce and secrete hormones in
the body Hormones can do the following things by
sending chemical messages to cellso regulate growth, development,
behavior, and reproductiono coordinate the production, use, and
storage of energyo maintain homeostasis (temperature
regulation, metabolism, excretion, and water and salt balance)
o respond to stimuli from outside the body
Glands are responsible for producing and secreting hormones (all glands and tissues that are in the endocrine system are show to the right)
How hormones work:o Each hormone is secreted by a cell
into the blood streamo It has a special shapeo The cell it wants to signal have receptors with special shapeso When the hormone attaches to the cell, it tells the cell what to change about its activities
(shown below)
The endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis through feedback mechanismso The body detects how much of a hormone is in the bloodo When there is not enough, it helps the body produce moreo When there is too much, it tells the body to stop producing
Blood Glucose levels are controlled by a feedback mechanismo A lot of glucose in the blood causes the production of insulin
Insulin is a hormone that causes muscles to take up glucose and convert it to glycogen for storage in the liver
o When there is not enough glucose in the blood, glucagon is produced Glucagon is a hormone that causes the liver to release glucose into the blood
o People with diabetes cannot covert glucose into glycogen because they can’t produce insulin

Skeletal System main job: protect internal organs, support your body, and enable movement bones
o hard outer covering of compact boneo inner spongy bone coreo bone marrow: fills the spongy area of the bone
produces both red and white blood cells and platelets joints: where two bones meet
o cushioned by pads of cartilage to help with the pressureo types of joints
immovable: little to no movement between bones joints of the skull
slightly movable joints: allow limited movement vertebrae of the skeleton
freely movable joints: allows movement ball-and-socket: all types of movement: hips and shoulders pivot joint: allows for rotation: top of spine (turning of head) hinge joint: bending and straightening (elbows, knuckles) gliding joint: sliding motion (wrists and ankles) saddle joint: rotation, bending, straightening (base of thumbs)
ligaments: strong bands of connective tissue that hold joints together disorders of the skeletal system
o osteoporosis: “porous bones” causes brittle and easily fractured bones
o arthritis: swelling of joints
Muscular System main job: move the body by pulling on bones muscles are connected to bones by connective tissue called
tendons Muscle Structure
o protein filaments that are stretchy actin myosin
o sarcomeres are the units of muscles linked end to end Muscle Contraction
1. sarcomere is relaxed; actin and myosin are partially overlapped
2. nerves stimulate the muscle to contracta. causes the sliding of actin and myosin so
they overlap even more3. sarcomere is completely contracted; actin and
myosin are completely overlappeda. the sarcomere is shorter in length, which
makes the muscle shorten and causes the bones to pull in a direction
the movement of actin and myosin requires ATPo ATP is made during cellular respiration,
which requires oxygeno increased muscle movement causes a higher heart rate and breathing rate so that more
oxygen can be delivered to the muscle cells to maintain homeostasis

Immune System Nonspecific defenses
o skin and mucus membranes protect against pathogens entering the body pathogen: any disease causing agent
o inflammatory response (inflammation/swelling) skin is punctured pathogens enter body white blood cells exit capillaries to attack and destroy pathogens
the extra cells in the area causes swelling and rednesso fever
body increases temperature because many bacteria cannot withstand high temperatures
Specific defeneseso antigen: substance that triggers an immune response
present on the surface of an infected body cello proteins on the outside of helpter T cells called receptors bind to antigens
targeting them for destructiono pg 928 in book explains the process of how our bodies attack infected body cells
HIV infects Helper T cellso because it attacks the immune system, it is very hard for the body to fight off
other infections like the common cold, flu, etc.
Nervous System Main job: transmit information
o neuron: nerve cells send electrical signals called
nerve impulses dendrites-extend from cell
body (like antennae) receive information
from other cells cell body- collects
information from dendrites axon- carries the signal from
the cell body to other neurons transmitting through the axon terminal
bundles of axons are called nerves covered in myelin sheath which helps the nerve impulses move faster
o when a neuron meets another cell, they do not touch there is a gap called the synapse when the signal reaches the gap, neurotransmitters (special molecules) are
signaled to exit and enter the surrounding cells to cause a response to a stimulus Central Nervous System
o Brain and Spinal Cord brain is the main processing center contains 100 billion neurons spinal cord: dense cable of nerves running down the vertebral column (backbone)

controls reflexes: sudden involuntary contraction of muscles in response to a stimulus
Peripheral Nervous Systemo connects brain and spinal cord to rest of body with many nerves
sensory division : directs sensory information to central nervous system (CNS) sight, smell, feeling
motor divison : carries out responses to sensory information how the body reacts to a sensory stimulus
Look at table on 961 to see how drugs affect the nervous system
Integumentary System skin is largest organ in body
o protects body from injuryo first line of defense against diseaseo regulates body temperatureo prevents body from drying out due to evaporation
2 layerso Epidermis
outermost layer of skin constantly being regenerated because it is constantly falling off due to damage
o dermis layer just beneath epidermis contains hair follicles, nerve cells, blood vessels temperature regulation
when hot: blood vessels dilate and push blood to surface so heat will leave body
when cold: blood vessels constrict and keep blood deep within skin to prevent heat from leaving body
Hairo helps protect and insulate the bodyo made of mostly dead keratin-filled cells
Nailso keratin filled cells on fingertips and toes to help protect
Reproductive System Male System
o sperm cells are produced by meiosis in the testeso sperm mature and are stored in the epididymis (a coiled tube above the testes)o a mature sperm cell has a head, a midpiece, and a powerful tail for swimmingo sperm move through the epididymis and the vas deferens (long tube that meets up with the
urethra) and exit the body through the urethra Female System
o Egg cells are produced through meiosis in the ovarieso An egg cell matures in a 28-day cycleo The menstrual cycle prepares the uterus for pregnancy
these cycles are regulated by hormoneso If no fertilization occurs, the prepares uterus sheds its lining (menstruation)
Development

o After a sperm fertilizes an egg, cleavage (cell division) begins and then it implants in the uterine wall
o It takes 9 months for the child to completely developo First three months (trimester) have the most crucial stageso baby is fed through a placenta (a series of tissues that diffuse nutrients to baby)
Sexual Transmitted Infectionso many caused by bacteria and viruseso syphilis: bacterial; can destroy bones, nervous system, and skin if untreatedo gonorrhea and chlamydia: common bacterials STIs; can scar fallopian tubes and cause
infertilityo genital herpes is viral; causes blistering