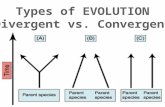
Speciation and Macroevolution Speciation Divergent Evolution Convergent Evolution.
· Web viewDifferentiate among and give examples of convergent evolution and divergent evolution...
-
Upload
vuongkhuong -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of · Web viewDifferentiate among and give examples of convergent evolution and divergent evolution...

AP Bio Bio 11 Review PacketINTRODUCTION:It is recommended to do this packet alongside the rest of AP; try to do a couple phyla each week focussing on structure/function and how each phylum is more advanced than the previous. Focus on unique variations found in each phyla and be able to explain why each phyla has them.
TO DO LIST:
_____ Overviews
_____ Vocab
_____ Classification Chart
PHYLUM CHECK LIST: Evolution Viruses and bacteria Plants :
o Bryophytao Pteridophytao Gymnospermso Angiosperms
Animalia : Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda Mollusca Annelida Arthropoda Echinodermata Chordata :
o Hemichordatao Urochordatao Cephalochordatao Vertebrata
Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes Amphibia Reptila Aves Mammalia

Evolution Reminders Name:
1. What does it mean to say that an animal is the “most fit”?
2. What are the 3 possible types of selection?
3. Define “species”
4. Define “gene pool”
5. Define “population”
6. Compare and contrast gradualism and punctuated equilibrium
7. Who are these people and what did they do: Jean Baptiste LaMarck, Charles Darwin, Eldridge and Gould, Alfred Russell Wallace?
8. Describe the 5 ways to change a gene pool
9. Define “speciation”
10. Compare and contrast micro and macro evolution
11. Why are these examples used in evolution: Peppered Moth, Galapagos Finches, Giraffes’ necks?
12. Describe the “Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics” (AKA_______________________)
13. What does DNA have to do with evolution?

ANALOGOUS VS. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES
1. DEFINITION OF ANALOGOUS STRUCTURES: _________________
2. WHICH OF THESE STRUCTURES ANALOGOUS AND WHICH ARE HOMOLOGOUS?
3. COLOUR THE HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES THE SAME COLOUR TO PROVE THEY ARE HOMOLOGOUS.

Evolution Study GuideVocabulary:
o Complementary base pairing Convergent evolution
o Directional selection o Divergent evolution o Disruptive selection
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Double helix
o Evolution
o Fitness o Gene flow o Gene pool o Genetic drift o Gradualism o Macro-evolution o Micro-evolution o Mutationo Natural selection
o Nitrogenous bases o Non-random mating o Punctuated
equilibrium o Species o Speciation o Stabilizing selection o Sugar-phosphate
backbone
Can You…?:1. Describe the basic structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) using the following information:– double helix– sugar-phosphate backbone– nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, G)– complementary base pairing (A=T, CΞG)
2. Explain the role of DNA in evolution
3. Explain the theories of evolution prior to Darwin (i.e. Lamarck and Erasmus) and after Darwin (i.e. Russell-Wallace, Eldridge and Gould)
4. Describe how the five agents of micro-evolution (mutation, genetic drift, gene flow, non-random mating, and natural selection) effect the gene pool
5. Explain how understanding a gene pool can help us to understand evolution
6. Explain the 3 types of selection and how they show that evolution is occurring
7. Describe how selective pressures can alter a gene pool
8. Differentiate among and give examples of convergent evolution and divergent evolution
9. Explain how convergent evolution and divergent evolution are related to speciation
10. Compare the gradual change model with the punctuated equilibrium model of evolution
11. Explain how the four types of evidence support the theory of evolution

Microbiology Study Guide
Vocabulary:Viruses: Antibody Lytic cycleAntigen Nucleic acid coreDNA Protein capsidHost cell RNALysogenic cycle Viral specificityPatient zero WHOWhite blood cellCDC Incubation time
Bacteria: Aerobic respirationAntibioticClassificationConjugation
DisinfectantEcological roleFermentationMotility
MutationPhotosynthesisProkaryoteResistance
Can You…?Viruses:identify the criteria for classifying organisms as living (i.e. 8 characteristics of life) describe the basic structure of a virus, including the antigens, the protein capsid, and the nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA) identify the role of the host cell in viral reproductioncompare the lytic and lysogenic cyclesdefine and give examples of viral specificity – explain using antigens and the idea only getting sick with a specific virus once describe the body’s basic lines of defense against a viral attack, including
- reverse phagocytosis- interferon- white blood cells and their antibodies
Bacteria: draw a prokaryotic cell and label all the structures describe:
– classification of bacteria– form and arrangement

– movement– ecological role (pros and cons)– nutrition (Energy, Carbon source and O2)– reproduction (binary fission, transformation, conjugation and transduction)– a few human diseases caused by bacteria
describe sterile technique:– i.e. agar plates, bacteria collection techniques, staining etc
explain how bacteria become resistant to antibioticsKingdom Plantae Study Guide
Vocabulary:AdaptationAlternation of generationsAngiospermAntheridium/antheridiaArchegonium/archegoniaBryophytaCarpelChlorophytaColonialCotelydonsCuticleDicotsEnclosed seedsFern FertilizationFiddleheadFlowers
FrondFruitGametophyteGymnospermHeterokontophytaHyphaeLeavesMonocotsMossMulticellularPetalPhloemPollenPollinationProthallusPteridophytaRhiziods
RhodophytaRootsSeedsSepalShootsSporangium/sporangiaSporesSporophyteSorus/soriStamenStemsStigmaStomataStyleUnicellularVascular tissueXylem
Can You…?1. State the phylum of brown, red and green algae and give an example of each?
2. Use examples of unicellular, colonial, and multicellular green algae to illustrate their increasing complexity?
3. Describe bryophyte and pteridophyte characteristics?
4. Describe alternation of generations in bryophytes and pteridophytes?
5. Describe features of bryophytes and pteridophytes that have enabled them to adapt to life on land?
6. Describe gymnosperm and angiosperm characteristics?
7. Explain how gymnosperms are adapted for survival on land using: alternation of generations, roots, stems, leaves, seeds, pollen, vascular
tissue
8. Differentiate between monocots and dicots?

9. Describe how angiosperms are adapted for survival on land using: alternation of generations, flowers, pollen, enclosed seeds, fruit, roots,
stems, leaves, vascular tissue
10. Compare and contrast the characteristics of bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms?
Biology 11 Animalia Intro Name:
Animalia Characterisitcs:
Classification Criteria:
1. Symmetry: Radial
Bilateral
2. Germ Layers: None
Diploblastic
Triploblastic
3. Body Plan: Acoelomate:
Pseudocoelomate
Coelomate
4. Segmentation: None

Simple
Specialized
5. Evolution: Lower Invertebrates
Higher Invertebrates: Protostomes
Deuterostomes
Vertebrates

Kingdom Animalia Overview Name: ____________Phylum:
1. Porifera
2. CnideriaClass:
Hydrazoa
Anthozoa
Scyphazoa
3. PlatyhelminthesClass:
Turbelleria
Trematoda
Cestoidea4. Nematoda
Free living
Parasitic
5. AnnelidaClass:
Oligochaeta
Polychaeta
Hirudinea6. Arthropoda
Class:Chilopoda
Diplopoda
Insecta
Arachnida

Crustacea
7. MolluscaClass:
Polyplacophora
Gastropoda
Bivalvia
Cephalopoda
8. EchinodermataClass:
Asteroidea
Echinodea
Holothuroidea
Crinoidea
9. ChordataSub-Phylum:
VertebrataClass:
Agnatha
Chondrichthyes
Osteichthyes
Amphibia
ReptiliaOrder:
SquamataRhynchoephaliaCheloniaCrocodilia
Aves
MammaliaOrder:
MonotremesMarsupialsPlacentals

COELOM GERM LAYER DIPLOBLASTIC ACOELOMATE
CNIDARIA RADIAL SYMMETRY PSEUDOCOELOM TRIPLOBLASTIC
PORIFERA INVERTEBRATE CHORDATEBILATERAL SYMMETRY
NEMATODA VERTEBRATE ECTODERM CEPHALIZATION
PLATYHELMINTHES
ENDODERM ANNELIDA MESODERM
MOLLUSCA ECHINODERMATA AVES ARTHROPODA
CHONDRICHTHYES OSTEICHTHYES MAMMALIA AMPHIBIA

REPTILIA MULTICELLULAR HETEROTROPHIC EUKARYOTIC
Biology 11 Higher Invert Overview
PHYLUM:
Annelida
Class:
Oligochaeta
Polychaeta
Hirudinea
Mollusca
Class:
Polyplacophora
Gastropoda
Bivalvia

Cephalopoda
Arthropoda
Class:
Chilopoda
Diplopoda
Insecta
Arachnida
Crustacea
Echinodermata
Class:
Asteroidea
Echinodea

Holothuroidea
Crinoidea

Include: example animals, body plans, specialized organs, key terms, systems (circulatory, respiratory, excretory, digestive, reproductive, nervous)Annelida: Mollusca:
Arthropoda: Echinodermata:

Name of Phylum: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8Example Animal:Body Wall Layers: 2 3Body Symmetry: None/Radial BilateralBody Segmented: Yes / NoBody Cavity: None Pseudocoelom True CoelomDigestive System:a) Many water canals and one exitb) Gastrovascular cavity one openingc) Food tubes mouth and anusCirculatory System: Closed OpenTentacles: Yes / NoAntennae: None 1 Pair 2 PairJointed Walking Legs:Yes / NoSkeleton: None Internal External (or in mantle)
Biology 11 Comparison of Representative Invertebrates Name: _______


Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: ChordataLower Chordates
Subphylum Characteristics Example Animal
Diagrams
Hemichordata
Notocord:
Nerve Cord:
Gills:
Tail:
Urochordata
Notocord:
Nerve Cord:
Gills:
Tail:
Cephalochordata
Notocord:
Nerve Cord:
Gills:
Tail:

Higher Chordates: Subphylum Vertebrata
Class Characteristics Example Animals Diagrams/Dissections
Agnatha
Chondrichthyes
Osteichthyes
Amphibia
Reptilia ORDERS:

Aves
Mammalia
ORDERS:

Biology 11 Chordata Overview:Name:
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum : Hemichordata
Urochordata
Cephalochordata
Vertebrata
Class : Agnatha
Chondrichthyes
Osteichthyes 1. Teleosts2. Lung fish/ Lobe-finned fish
Amphibia
Reptilia Order: Rynchoephalia
Chelonia
Crocodilia
Squamata
Aves (birds)
Mammals (us)Order: Monotreme
Marsupials
Placentals

Kingdom Animalia Review!!!
Animal name Phyla DefiningCharacteristics
Quick Sketch Layers/cavity/Special feature


THE ULITMATE REVIEW FOR AP BIOLOGY:PARADE THROUGH THE KINGDOMS
Bacteria and VirusesPART 1. Directions: All answers are to be completed on your own and neatly written.
1. How common are prokaryotes on earth?
2. Describe the size and shape of bacteria.
3. How do bacterial cell walls differ from plant cell walls?
4. How does the cell wall aid in classifying the bacteria?
5. List the methods bacteria use to move and adhere or attach.
6. How do bacteria typically reproduce?
7. Explain how conjugation can modify bacteria genetically.

8. Identify and briefly define the four nutritional categories of bacteria.
9. How has comparative biochemistry led to classifying prokaryotes into two domains?
10. What is the ecological significance of prokaryotes?
PART 2. Directions: Outline the key characteristicsthat distinguish the three domains. Include examples of organisms in each domain.
DOMAIN CHARACTERISTICS EXAMPLE
Bacteria

Archae
Eukarya
ProtistansPART 1. Directions: All answers are to be completed on your own and neatly written.
11. Why are Protistans said to be the most diverse of all eukaryotes?
12. What process is thought to be involved in the genesis of eukaryotes from
prokaryotes? (Ch. 21.4)

13. Define serial endosymbiosis?
14. Why are Protistans difficult to classify?
Animals: The Invertebrates22. Outline the major characteristics used to define an animal.
23. List an hypothesis for the origin of animals.
24. Describe the two forms of symmetry found in animals.
25. What is the significance of cephalization as an evolutionary trend?
26. Define the following terms and describe their significance in classifying animals.
a. Acoelomates ____________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________

b. Pseudocoelomates _______________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
c. Coelomates ____________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
d. Protostomes ____________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
e. Deuterostomes __________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
f. spiral, determinate cleavage _______________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
g. radial, indeterminate cleavage ______________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
27. List a number of the major differences between the Protostomes and Deuterostomes.
28. Label the stages of early embryonic development of animals.

PART 2. Directions: Using the figure below, outline the key characteristics of each branch of the Kingdom Animalia identified on the diagram. Use definitions from Question 25 to supply the details in your chart. Include examples of organisms in each division.


DIVISION CHARACTERISITICS EXAMPLE
Porifera
(Sponges)
Cnidaria
Ctenophora
(Comb Jellies)
Platyhelminthes
(Flatworms)
Nemertea
(Ribbon Worms)
Nematoda
(Round Worms)
Rotifera
(Rotifers)

PART 3.
29. How does the structure of a sponge relate to its method of nutrition?
30. Explain the body plan and tissue types common to the Cnidarians?
31. What are the two body forms within the Cnidarians and how do they differ?
DIVISION CHARACTERISTICS EXAMPLE
Mollusca
Annelida
Arthropoda
Echinodermata
Chordata

32. Describe the stages in the Cnidarian life cycle.
33. What are some evolutionary advancements we see in the Platyhelminthes?
34. Describe the body systems of flatworms?
35. What is unique in the structure and function of the Nematodes?
36. List ways in which Nematodes impact humans.
37. List common examples that could be classified as Coelomate Protostomes.
38. What are the three major body regions of a Mollusk?
39. Describe an evolutionary adaptation seen in gastropods bivalves and cephalopds.

40. What is the evolutionary significance of the coelom as seen in the Annelids?
41. What is the importance of segmentation?
42. Why are the Arthropoda regarded as the most successful of all animal phyla?
43. Identify a characteristic that was most significant to Arthropod success.
44. List phyla that could be classified as Coelomate Deuterostomes.
45. What traits are particularly unique to the Echinoderms?
Animals: The VertebratesPART 1. Directions: All answers are to be completed on your own and neatly written.
46. What are the four characteristics of the Chordates?
47. List and describe an example of an invertebrate chordate.

48. What characterizes the subphylum Vertebrata?
49. In the evolution of vertebrates, identify the significance of fish developing paired
fins?
PART 2. Directions: Using the information in the text, outline thekey characteristics that distinguish the major branches of the subphylum Vertebrataidentified on the diagram. Include examples of organisms in each class.

PART 3. Directions: All answers are to be completed on your own and neatly written.
CLASS CHARACTERISTICS EXAMPLE
Agnatha(Jawless fish)
Placodermi(Extinct)
Chondrichthyes
Osteichthyes
Amphibia
Reptilia
Aves
Mammalia

50. Describe the five key trends that sets primates apart from other mammals.
51. Describe the evolution of the first hominoids (when, where, why).
52. What two lineages branched from a common hominoid ancestor?
Part 4. Directions: Using the information in the text, complete the table below.Species Lived when and where Characteristics Lifestyle
Homo habilis
Homo erectus
Homo neanderthalensis
Homo sapiens