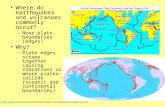
Most earthquakes occur at Plate Boundaries The deepest earthquakes occur at subduction boundaries.
20
Earthquakes!
-
Upload
lilian-fields -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Most earthquakes occur at Plate Boundaries The deepest earthquakes occur at subduction boundaries.
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Most earthquakes occur at Plate Boundaries The deepest earthquakes occur at subduction boundaries
- Slide 3
- The focus of an earthquake is the source, or where it originates. The epicenter is the point on the Earths surface directly above the focus.
- Slide 4
- Seismographs are used to record the various types of seismic waves that are generated during an eathquake. (see picture above right in packet to see how one looks/works)
- Slide 5
- P- Waves (elastic) push and pull the ground Travel through solids, Liquids & gases S-Waves (shear) move the ground up and down. Only travel through solids
- Slide 6
- L-waves (Rayleigh/Love waves)- rolling surface waves; arrive last Only travel through solids
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Seismographs record results on seismograms The difference in arrival times of p and s waves= lag time Using lag time we can find the distance to the epicenter
- Slide 9
- The further away the seismograph station, the greater the lag time.
- Slide 10
- Which city is located farthest from the epicenter? (use picture at left in packet) What is the difference between arrival times of the first P and S waves in the seismogram above (in the packet)?
- Slide 11
- Used to record the distance (measured in km) from the recording center to the epicenter of an earthquake
- Slide 12
- The difference in arrival times of p and s waves= lag time
- Slide 13
- When the first P-wave arrives 4 minutes before the first S-wave, the earthquake occurred _________ km from the recording station.
- Slide 14
- Using seismograms from 3 record stations and a travel-time graph, we can establish the location of the earthquake _______________________.
- Slide 15
- How far from the epicenter is each of these three cities?
- Slide 16
- Why do seismologists need to plot data from three recording centers?
- Slide 17
- We need 3 seismograph stations to find the epicenter of an earthquake. With one, it could be anywhere on the circle. With two, it could be either two areas they touch. With three, its where they all meet!
- Slide 18
- This is where the crust is under stress and potential energy is stored.
- Slide 19
- Measure of how much energy is released. Richter scale is used to plot, from 1 10, how strong an earthquake is. Each increase in 1 equals 10 times more energy released.
- Slide 20