Answer the following in complete thought sentences. You can use your notes from the other day. ...
-
Upload
sabrina-shields -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Answer the following in complete thought sentences. You can use your notes from the other day. ...

BELL WORK Answer the following in complete thought
sentences. You can use your notes from the other day.
What happens to the side lengths, perimeter and area of shape that is enlarged by a scale factor of 2?
Use at least two complete sentences. Get out a piece of paper to take notes. Open your books to Stretching and
Shrinking, page 40.

BELL WORK
Open your books to Stretching and Shrinking, Page 40
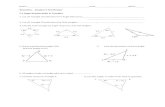
3
4
7.5
x
1. Determine the length of line JK.
2. What scale factor was used to go from Triangle ABC to Triangle JKL?
A B
C
JK
L
JK = 10
Scale Factor = 2.5

UNIT 3.2 REP-TILE TRIANGLES
Tessellate means to fit together exactly.

SOME TESSELLATIONS

THREE DIFFERENT TRIANGLES Sketch and make several copies of
each of the following shapes: a right triangle
an isosceles triangle
a scalene triangle

THREE DIFFERENT TRIANGLESA. Which of these triangles fit together to
make a larger triangle that is similar to the original? Make a sketch to show how the copies fit together.
All three triangles are rep-tiles. They can all be fit together to make a larger triangle that is similar to the original.

THREE DIFFERENT TRIANGLESB. Look at your sketches from
Question A. 1. What is the scale factor
from each original triangle to each larger triangle?2. How is the perimeter of the new triangle related to the perimeter of the original?3. How is the area of the new triangle related to the area of the original?

EXTEND THE REP-TILES

DIVIDING TRIANGLES

DIVIDING TRIANGLES To divide a triangle into four or small similar
triangles: Find the midpoints of each of its sides. Draw a straight line connecting each of the
midpoints to form the smaller triangles.
Important VocabularyMidpoint – A point that divides a line segment into two segments of equal length.

UNIT 3.3 SCALE FACTORS AND SIMILAR SHAPES

BELL WORK
Open your books to Stretching and Shrinking, Page 42.
Get your sheet of graph paper from last Thursday from your class’ exit slip box.
Have out paper and pencil and be ready to work.

UNIT 3.3 SCALE FACTORS AND SIMILAR SHAPES
For parts (1)-(3), draw a rectangle similar to rectangle A that fits the given description. Find the base and height of each new rectangle.
1. The scale factor from rectangle A to the new rectangle is 2.5.
2. The area of the new rectangle is ¼ the area of rectangle A.
3. The perimeter of the new rectangle is three times the perimeter of rectangle A.
The new rectangle is 10 by 20.
The new rectangle is 2 by 4.The scale factor is ½.
Sketch this rectangle on your paper.

UNIT 3.3 SCALE FACTORS AND SIMILAR SHAPES
For parts (1)-(2), draw a triangle similar to triangle B that fits the given description. Find the base and height of each new triangle.
1. The area of the new triangle is nine times the area of triangle B.
2. The scale factor from triangle B to the new triangle is ½.
What is the scale factor?
3New base: 21New height: 12
Sketch this triangle on your sheet.

UNIT 3.3 SCALE FACTORS AND SIMILAR SHAPES
4 cm

UNIT 3.3 SCALE FACTORS AND SIMILAR SHAPES
1.25
DF = 3.75 EF = 6.25 Angle F = 94 degrees Angle E = 30 degrees

EXIT SLIP
The rectangle on the left was reduced by a scale factor of ¼. What are the dimensions of the new rectangle on the right?
16
4 x
y